Schema-Based Testing  ¶
¶
Wallarm's Schema-Based Testing is a dynamic application security testing (DAST) solution that enables "shift-left" security. It uses an API's schema (such as an OpenAPI specification or a Postman collection) as a blueprint to automatically generate and execute targeted security tests. By integrating into CI/CD pipelines, Schema-Based Testing allows development teams to proactively identify a wide range of vulnerabilities—including OWASP API Top 10 risks, business logic flaws, and input validation issues—early in the development process, making them easier and cheaper to fix.
Schema-Based Testing capabilities:
-
Deep, dynamic analysis of API endpoints.
-
Detection of vulnerabilities in the application or API itself, as well as security misconfigurations in the underlying infrastructure or environment.
-
Visualization of found issues in the Wallarm Console's Security Issues section.
-
Lightweight execution via Docker container, enabling embedding into your CI/CD pipeline alongside functional tests, smoke test, and other security testing.
How it works¶
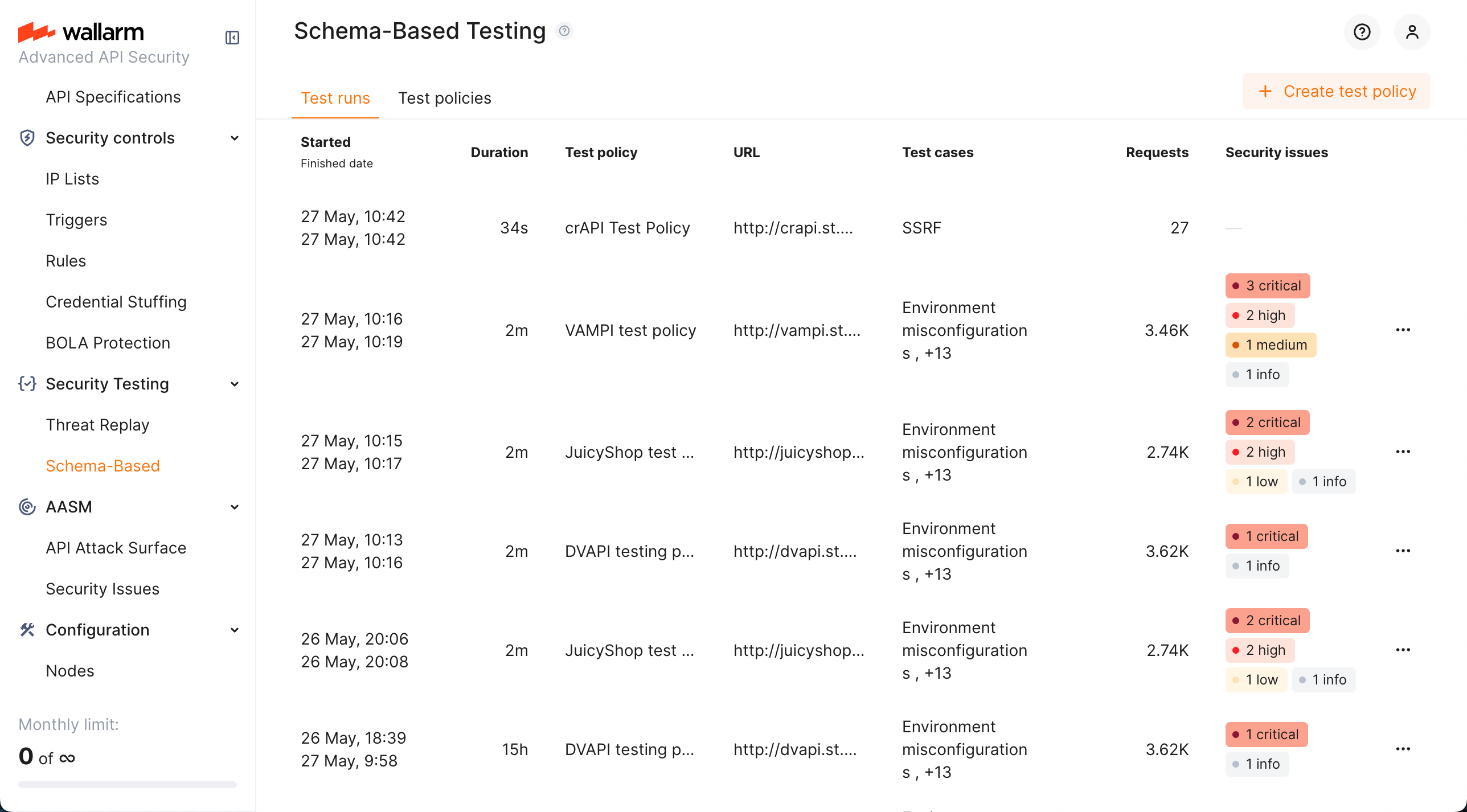
Use Schema-Based Testing by fulfilling the following steps:
-
Create test policy: specify the target application, provide its OpenAPI specification or Postman collection, base URL, and select the tests to run.
-
Copy Docker command: find your test policy on the Test policies tab, click it, and copy the provided Docker command.
-
Run and monitor: start the agent with the command. Track progress and view results on the Test runs tab.
Test basis¶
Schema-Based Testing can base its tests on:
-
OpenAPI specification (OAS) - precise and machine-readable blueprint of your API allows to build efficient and reliable test suite for your application. OAS-based testing is focused on input validation, injection, and misconfiguration detection.
-
RAML specification - if your API is documented using RAML (RESTful API Modeling Language), you can upload it directly. RAML files are automatically converted to OpenAPI specifications, enabling the same comprehensive security testing. See details.
-
Postman collection - if you use the Postman API design platform, the functional tests from its collections may be used to build security tests alongside. See details. Postman collection-based testing is focused on complex business logic and access control vulnerabilities.
Temporary limitation
Creating new policies based on Postman collections is temporarily not available. Existing policies that were previously created using Postman collections continue to work as expected.
Schema-Based Testing (Postman) vs API Security Testing via Postman¶
Wallarm also offers API Security Testing via Postman—a lighter option that runs inside Postman Agent Mode with no Docker or CI/CD. Both options can use your Postman collections; choose based on how you work and how deep you need to go:
| Schema-Based Testing (Postman collection) | API Security Testing via Postman | |
|---|---|---|
| Use when | You want automated, comprehensive DAST in CI/CD; you already have functional tests in Postman and want them to drive security tests. | You want a quick, conversational check inside Postman—ask in natural language and get results in the Agent chat in a few minutes. |
| How it runs | Dynamic testing: sends real requests, uses your collection's functional tests as a blueprint to generate and run security tests. | Passive, design-level analysis; no attack payloads, no traffic replay. |
| Depth | OWASP API Top 10, business logic, access control, input validation (injections, RCE, etc.), environment misconfigurations. | Auth gaps, data leaks, over-permissive endpoints, schema issues, basic BOLA/BOPLA—summarized for developers. |
| Where | Docker-based; runs in your pipeline or locally; results in Wallarm Console (Test runs, Security Issues). | Inside Postman (Agent Mode); results in chat and in Wallarm Cloud. |
In short: use Schema-Based Testing with a Postman collection when you need full DAST and pipeline integration; use API Security Testing via Postman for fast, in-Postman checks with minimal setup.
Test types¶
For OpenAPI specification-based tests, Schema-Based Testing uses several types of tests to detect security issues:
-
Authentication bypass checks for risks of bypassing the authentication mechanisms or exploiting their weaknesses.
-
Environment misconfiguration tests check for vulnerabilities and misconfigurations in the environment or infrastructure the application and APIs run on (not the API logic). Examples:
- Exposed source code, backups, configuration files.
- Accessible
.git,.env, or system files. - Insecure web server settings (e.g., directory listing, weak TLS).
-
GraphQL vulnerability detection checks for 10 GraphQL most popular misconfigurations (API2, API4).
-
Input parameter tests check each input point (parameters, headers, etc.) defined in the OpenAPI specification for application-level vulnerabilities. Covered vulnerabilities:
- Command injection
- CRLF injection
- LFI / RFI
- NoSQL injection
- Open redirect
- Path traversal
- Remote code execution (RCE)
- SQL injection
- SSRF
- SSTI
- XSS
- XXE
- Infoleak
Run types¶
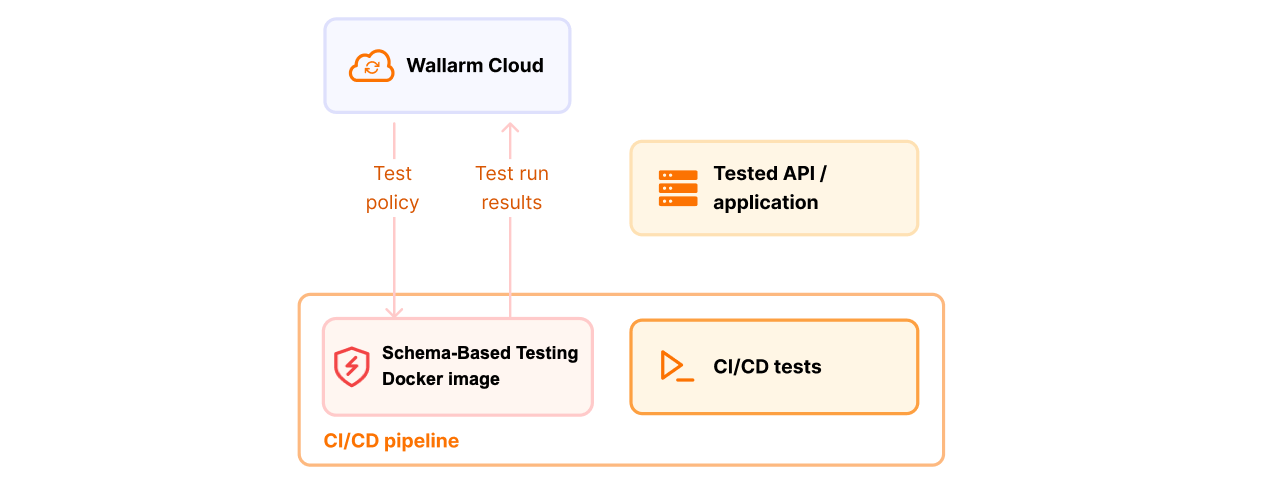
Any test run via Schema-Based Testing:
-
Is actually a Docker run
-
Is based on some schema (OAS or Postman)
-
Requires token from Wallarm
-
Is displayed in Test runs, results are displayed in Security Issues (see details)
In the same time, you are free to choose whether to use Wallarm's UI:
-
With UI: you create test policy in Wallarm, it contains token, your schema and all testing parameters and provides you a Docker run command linked to it.
-
Without UI: having token, you form Docker run command yourself defining all parameters locally. Note that you can still use Wallarm's wizard to help you with that.
-
Combination: you create test policy in Wallarm, it contains token, your schema and all testing parameters and provides you a Docker run command linked to it, but in this linked command you override any parameters, like use local file instead of the one attached to the policy. What is not overridden, is taken from the policy.
See details on each variant here.
Enabling and setup¶
To start using Schema-Based Testing, enable and configure it as described in Schema-Based Testing Setup.