Event Search and Filters¶
Wallarm provides convenient methods for searching detected events (attacks and incidents). In the Attacks and Incidents sections of Wallarm Console, the following search methods available:
-
Filters to select filtering criteria
-
Search field to input search queries with attributes and modifiers similar to human language
The values set in the filters are automatically duplicated in the search field, and vice versa.
Any search query or a filter combination can be saved by clicking Save a query.
Filters¶
Available filters are presented in Wallarm Console in multiple forms:
-
Filters panel that is expanded and collapsed using the Filter button
-
Quick filters for excluding or showing only events with the specific parameter values
When values of different filters are selected, the results will meet all those conditions. When different values for the same filter are specified, the results will meet any of those conditions.
Search field¶
The search field accepts queries with attributes and modifiers similar to human language which makes submitting queries intuitive. For example:
-
attacks xss: to search for all XSS-attacks -
attacks today: to search for all attacks that happened today -
xss 12/14/2020: to search for all suspicions, attacks, and incidents of cross‑site scripting on 14 December 2020 -
p:xss 12/14/2020: to search for all suspicions, attacks, and incidents of all types within the xss HTTP request parameter (i.e.http://localhost/?xss=attack-here) as of 14 December 2020 -
attacks 9-12/2020: to search for all attacks from September to December 2020 -
rce /catalog/import.php: to search for all RCE attacks and incidents on/catalog/import.phppath since yesterday
When values of different parameters are specified, the results will meet all those conditions. When different values for the same parameter are specified, the results will meet any of those conditions.
Setting the attribute value to NOT
To negate the attribute value, please use ! before the attribute or modifier name. For example: attacks !ip:111.111.111.111 to show all attacks originated from any IP address excluding 111.111.111.111.
Below you will find the list of attributes and modifiers available for use in search queries.
Search by object type¶
Specify in the search string:
-
attack,attacks: to search only for the attacks that are not aimed at known vulnerabilities. -
incident,incidents: to search only for incidents (attacks exploiting a known vulnerability).
Search by attack type¶
Specify in the search string:
-
sqli: to search for SQL injection attacks. -
xss: to search for Cross Site Scripting attacks. -
rce: to search for OS Commanding attacks. -
brute: to search for brute-force attacks and blocked requests from IPs denylisted because of the attacks of this type. -
ptrav: to search for path traversal attacks. -
crlf: to search for CRLF injection attacks. -
redir: to search for open redirect attacks. -
nosqli: to search for NoSQL injection attacks. -
data_bomb: to search for logic bomb attacks. -
ssti: to search for Server‑Side Template Injections. -
invalid_xml: to search for usage of unsafe XML header. -
overlimit_res: to search for attacks aimed at overlimiting of computational resources. -
xxe: to search for XML External Entity attacks. -
vpatch: to search for virtual patches. -
dirbust: to search for forced browsing attacks and blocked requests from IPs denylisted because of the attacks of this type. -
ldapi: to search for LDAP injection attacks. -
scanner: to search for port scanner attacks. -
infoleak: to search for attacks of information disclosure. -
mail_injection: to search for Email Injections. -
ssi: to search for SSI Injections. -
overlimit_res: to search for attacks of the resource overlimiting type. -
experimental: to search for experimental attacks detected based on custom regular expression. -
bola: to search for attacks exploiting the BOLA (IDOR) vulnerability and blocked requests from IPs denylisted because of the attacks of this type. -
mass_assignment: to search for Mass Assignment attack attempts. -
api_abuse: to search for suspicious bot activity. -
account_takeover(api_abusebefore 4.10.6): to search for account takeover attempts. -
scraping(api_abusebefore 4.10.6): to search for scraping attempts. -
security_crawlers(api_abusebefore 4.10.6): to search for scanning attempts performed by security crawlers. -
ssrf: to search for Server‑side Request Forgery (SSRF) and attacks. -
blocked_source: to search for attacks from manually denylisted IPs. -
multiple_payloads: to search for attacks detected by the Number of malicious payloads trigger and blocked requests from IPs denylisted because of the attacks of this type. -
credential_stuffing: to search for attempts to use stolen authentication credentials (credential stuffing). -
ebpf: to search for attacks detected by the Wallarm eBPF-based solution. -
graphql_attacks: to search for all violations of the organization's GraphQL policy. Also, specific violations can be searched by:gql_doc_size: violation of maximum allowed total query sizegql_value_size: violation of maximum allowed value sizegql_depth: violation of maximum allowed query depthgql_aliases: violation of maximum allowed number of aliasesgql_docs_per_batch: violation of maximum allowed number of batched queriesgql_introspection: forbidden introspection querygql_debug: forbidden debug mode query
-
api_specification: to search for all specification-based violations. Also, specific violations can be searched by:undefined_endpoint: attempt to request the endpoint not presented in your specificationundefined_parameter: requests marked as attacks because they include parameters not presented for this endpoint in your specificationmissing_parameter: requests marked as attacks because they does not include the parameter or its value that are marked as required in your specificationinvalid_parameter_value: requests marked as attacks because some of their parameter's value in not in correspondence with its type/format defined by your specificationmissing_auth: requests marked as attacks because they do not contain the required information about the authentication methodinvalid_request: requests marked as attacks because they contain an invalid JSON- auxiliary search tag -
processing_overlimit: API Specification Enforcement has limits applied to comparing requests against specifications - when exceeding these limits, it stops processing the request and creates the event informing about that - see also:
spec:'<SPECIFICATION-ID>'here
An attack name can be specified in both uppercase and lowercase letters: SQLI, sqli, and SQLi are equally correct.
Search attacks associated with the OWASP top threats¶
You can find attacks associated with the OWASP top threats by using the OWASP threat tags. The format to search for these attacks is owasp_api1_2023.
These tags correspond to the original numbering of threats as defined by OWASP. Wallarm associates attacks with the OWASP API Top threats of the 2023 version.
Search by known attacks (CVE and well‑known exploits)¶
-
known: to search for requests that precisely attack since they exploit CVE vulnerabilities or other well‑known vulnerability types.To filter attacks by certain CVE or another well‑known vulnerability type, you can pass the appropriate tag in addition to the tag
knownor separate from it. For example:known:CVE-2004-2402 CVE-2018-6008orCVE-2004-2402 CVE-2018-6008to search for attacks exploiting the CVE-2004-2402 and CVE-2018-6008 vulnerabilities. -
!known: potential false positives. These requests may contain little‑known exploits or the context turning the exploits into legitimate parameter values.
To filter attacks by CVE and well‑known exploits, quick filters by event types and CVE and exploits can be used.
Search hits by API protocols¶
To filter hits by API protocols, use the proto: or protocol: tag.
This tag allows the following values:
-
proto:graphql -
proto:grpc -
proto:websocket -
proto:rest -
proto:soap -
proto:xml-rpc -
proto:web-form -
proto:webdav -
proto:json-rpc
Search hits by authentication protocols¶
To filter hits by authentication protocols attackers have used, use the auth: tag.
This tag allows the following values:
-
auth:none -
auth:api-key -
auth:aws -
auth:basic -
auth:bearer -
auth:cookie -
auth:digest -
auth:hawk -
auth:jwt -
auth:ntlm -
auth:oauth1 -
auth:oauth2 -
auth:scram
Search by the attack target¶
Specify in the search string:
-
client: to search for clients' data attacks. -
database: to search for database attacks. -
server: to search for app server attacks.
Search by risk level¶
Specify the risk level in the search string:
-
low: low risk level. -
medium: medium risk level. -
high: high risk level.
Search by event time¶
Specify time period in the search string. If the period is not specified, the search is conducted within the events that occurred during the last 24 hours.
There are the following methods to specify the period:
-
By date:
11/10/2020-11/14/2020 -
By date and time (seconds are disregarded):
11/10/2020 11:11,11:30-12:22,11/10/2020 11:12-01/14/2020 12:14 -
With relation to a certain moment of time:
>11/10/20 -
Using string aliases:
yesterdayequal to yesterday's datetodayequal to today's date-
last <unit>equal to the period from the entire past unit start to current date and timeweek,month,yearor the number of these units can be used as<unit>. For example:last week,last 3 monthorlast 3 months. -
this <unit>equal to current unitweek,month,yearcan be used as<unit>. For example:this weekwill return events detected on Monday, Tuesday and Wednesday this week if today is Wednesday.
Date and time format depends on the settings specified in your profile:
-
MM/DD/YYYY if MDY is selected
-
DD/MM/YYYY if DMY is selected
-
13:00if 24‑hour is ticked -
1pmif 24‑hour is unticked
The month can be specified as both number and name: 01, 1, January, Jan for January. The year can be specified in both full form (2020) and shortened form (20). If the year is not specified in the date, then the current year is used.
Search by IP address¶
To search by IP address, use the ip: prefix, after which you can specify
-
A specific IP address, for example
192.168.0.1—in this case, all attacks and incidents will be found for which the source address of the attack corresponds to this IP address. -
An expression describing a range of IP addresses.
-
A total number of IP addresses related to an attack or incident.
Search by IP address range¶
To set a required range of IP addresses, you can use
-
An explicit IP address range:
192.168.0.0-192.168.63.25510.0.0.0-10.255.255.255
-
A part of an IP address:
192.168.—equivalent to192.168.0.0-192.168.255.255. Redundant format with the*modifier is allowed—192.168.*192.168.0.—equivalent to192.168.0.0-192.168.0.255
-
An IP address or part of it with a range of values inside the last octet in the expression:
192.168.1.0-255—equivalent to192.168.1.0-192.168.1.255192.168.0-255—equivalent to192.168.0.0-192.168.255.255
Important
When using a range of values within an octet, a dot is not set at the end.
-
Subnet prefixes (CIDR notation):
192.168.1.0/24—equivalent to192.168.1.0-192.168.1.255192.168.0.0/17—equivalent to192.168.0.1-192.168.127.255
Note
You can combine the above methods for defining IP address ranges. To do this, list all the necessary ranges with the ip: prefix separately.
Example: ip:192.168.0.0/24 ip:10.10. ip:10.0.10.0-128
Search by number of IP addresses¶
It is possible to search by the total number of IP addresses that are related to an attack or an incident (only for attacks and incidents):
-
ip:1000+ last month—search for attacks and incidents over the past month for which the number of unique IP addresses is more than 1000 (equivalent toattacks incidents ip:1000+ last month). -
xss ip:100+—search for all cross‑site scripting attacks and incidents. The search result will be empty if the number of attacking IP addresses (with the XSS attack type) is less than 100. -
xss p:id ip:100+—search for all XSS attacks and incidents related to the id parameter (?id=aaa). This will return results only if the number of different IP addresses exceeds 100.
Search by the data center the IP address belongs to¶
To search by the data center, to which the IP address originated the attacks belongs, use the source: prefix.
This attribute value can be:
-
torfor the Tor network -
proxyfor the public or web proxy server -
vpnfor VPN -
awsfor Amazon -
azurefor Microsoft Azure -
gcefor Google Cloud Platform -
ibmfor IBM Cloud -
alibabafor Alibaba Cloud -
huaweifor Huawei Cloud -
rackspacefor Rackspace Cloud -
plusserverfor PlusServer -
hetznerfor Hetzner -
oraclefor Oracle Cloud -
ovhfor OVHcloud -
tencentfor Tencent -
linodefor Linode -
doceanfor Digital Ocean
Search by the country or region in which the IP address is registered¶
To search by the country or the region, in which the IP address originated the attacks is registered, use the country: prefix.
The country/region name should be passed to the attribute in the format corresponding to the standard ISO 3166-1 in uppercase or lowercase letters. For example: country:CN or country:cn for attacks originated from China.
Search for events originating from well-known malicious IPs¶
Wallarm scans public resources for IP addresses that are widely recognized as being associated with malicious activities. We then validate this information to ensure its accuracy, making it easier for you to take necessary actions, such as denylisting these IPs.
To search for events originating from these malicious IP addresses, use the source:malicious tag. This stands for Malicious IPs and is named accordingly in the denylist, in the section for blocking by source type.
We pull the data for this object from a combination of the following resources:
Search by server response status¶
To search by server response status, specify statuscode: prefix.
Response status can be specified as:
-
a number from 100 to 999.
-
«N–M» range, where N and M are figures from 100 to 999.
-
«N+» and «N-» ranges, where N is a number from 100 to 999.
Search by server response size¶
To search by the server response size, use the s: or size: prefix.
You can search for any integer value. Figures above 999 can be specified without a prefix. The «N–M», «N+» and «N-» ranges can be specified, where figures above 999 can also be specified without a prefix.
Search by HTTP request method¶
To search by HTTP request method, specify the method: prefix.
To search for GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, OPTIONS: if upper-case is used, then the search string can be specified without a prefix. For all other values, a prefix should be specified.
Search by a number of hits within attack/incident¶
To search attacks and incidents by a number of hits, specify the N: prefix.
For example, you can search for attacks that have more than 100 hits: attacks N:>100. Or search for attacks with less than 10 hits with attacks N:<10.
Search by domain¶
To search by domain, use the d: or domain: prefix.
Any string, that may be a domain of the second or a higher level can be specified without a prefix. Any string can be specified with a prefix.
You may use masks within a domain. The symbol * replaces any number of characters; the symbol ? replaces any single character.
Search by path¶
To search by path, either:
-
Use the
u:orurl:prefix and specify the path in quotes starting with/, e.g.:url:"/api/users", or -
Start the input with
/without any prefix, e.g.:/api/users
Search by application¶
To search by the application to which the attack was sent, use the application: or app: prefix (the former pool: prefix is still supported but not recommended).
The attribute value is the application name set on the Applications tab in the Settings section. For example: application:'Example application'.
Search by parameter or parser¶
To search by parameter or parser, use the p:, param:, or parameter: prefix, or the = suffix. If using the suffix, a string that does not start with / is considered to be a parameter (wherein the ending = character is not included in the value).
Possible attribute values:
-
Name of the aimed parameter.
For example, if you need to find attacks aimed at the
xssparameter but not at XSS-attacks (for instance, SQL-injection attack havingxssin the GET-parameter), then specifyattacks sqli p:xssin the search string. -
Name of the parser used by Wallarm node to read the parameter value. The name must be in uppercase.
For example,
attacks p:*BASE64to find attacks aimed at any parameter parsed by the base64 parser. -
Sequence of parameters and parsers.
For example:
attacks p:"POST_JSON_DOC_HASH_from"to find attacks sent in thefromparameter in the JSON body of a request.
You may use masks within a value. The symbol * replaces any number of characters, the symbol ? replaces any single character.
Search for anomalies in events¶
To search for anomalies in events, use the a: or anomaly: prefix.
To refine an anomaly search, use the following parameters:
-
size -
statuscode -
time -
stamps -
impression -
vector
Example:
attacks sqli a:size will search for all SQL-injection attacks, that have response size anomalies in their requests.
Search by request identifier¶
To search for attacks and incidents by request identifier, specify the request_id prefix.
The request_id parameter has the following value form: a79199bcea606040cc79f913325401fb. In order to make it easier to read, this parameter has been replaced by the placeholder abbreviation <requestId> in the examples below.
Examples:
-
attacks incidents request_id:<requestId>: to search for an attack or an incident with therequest_idequal to<requestId>. -
attacks incidents !request_id:<requestId>: to search for attacks and incidents with therequest_idnot equal to<requestId>. -
attacks incidents request_id: to search for attacks and incidents with anyrequest_id. -
attacks incidents !request_id: to search for attacks and incidents without anyrequest_id.
Search for sampled hits¶
To search for the sampled hits, add sampled to the search string.
Search by node UUID¶
To search for attacks detected by specific node, specify the node_uuid prefix, followed by the node UUID.
Examples:
-
attacks incidents today node_uuid:<NODE UUID>: to search for all attacks and incidents for today found by the node with this<NODE UUID>. -
attacks today !node_uuid:<NODE UUID>: to search for all attacks for today found by any node except the node with this<NODE UUID>.
Search only for new attacks
Only attacks detected after May 31, 2023 will be displayed when searching by node UUID.
You can find the node UUID in the Nodes section, node details. Click UUID to copy it or click View events from this node for the day (switches to the Attacks section).
Search by specification¶
To get the list of events related to specific specification policy violations, in the search field specify spec:'<SPECIFICATION-ID>'. To get <SPECIFICATION-ID>, in API Specifications, open your specification for editing - specid will be displayed in your browser address field.
Blocked and monitored events may be presented depending on the configured policy violation actions. In the event details, the violation type and link to the causing specification are displayed.
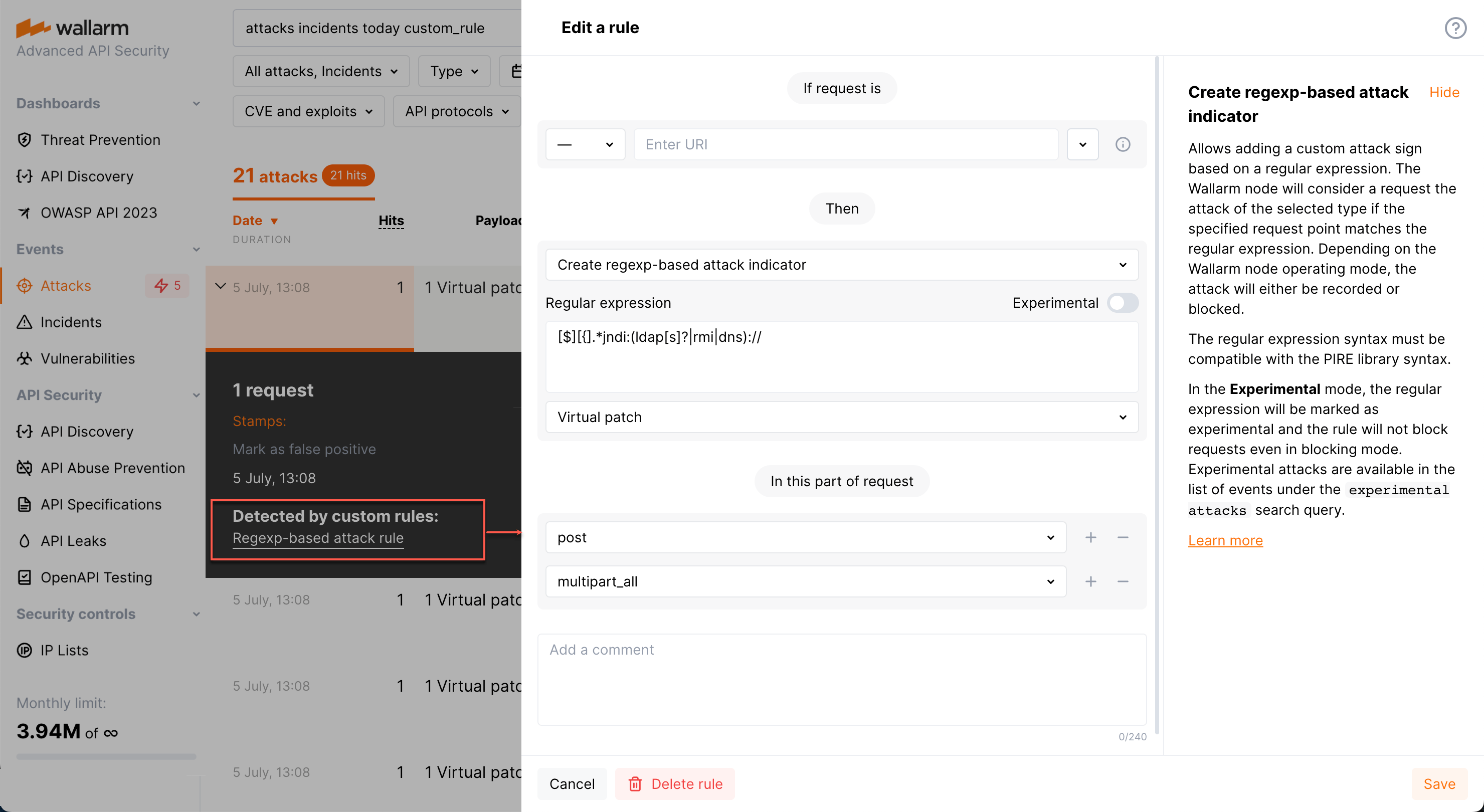
Search by regexp-based customer rule¶
To get the list of attacks detected by regexp-based customer rules, in the search field specify custom_rule.
For any of such attacks, in its details, the links to the corresponding rules are presented (there can be more than one). Click the link to access the rule details and edit them if necessary.
You can use !custom_rule to get the list of attacks not related to any regexp-based customer rules.