Attack Analysis¶
This article describes how you can analyze attacks detected by the Wallarm node and take actions regarding them.
Attack analysis¶
All the attacks detected by the Wallarm platform are displayed in the Attacks section of the Wallarm Console. You can filter the list by attack date, type and other criteria, expand any attack and its included requests for detailed analysis.
If a detected attack turns out to be a false positive, you can immediately mark it as one to prevent alike false positives in future. Also, on the basis of the detected attacks, you can create rules and perform other Wallarm configurations to mitigate further alike threats.
In Wallarm:
-
Attack is a group of hits
-
Hit is a malicious request plus metadata added by node
-
Malicious payload is a part of request with attack sign
Read details here.
Each attack details contain all necessary information for analysis, such as attack's hits and malicious payload summary. To simplify analysis, only unique hits are stored in the attack details. Repeated malicious requests are dropped from uploading to the Wallarm Cloud and not displayed. This process is called hit sampling.
Hit sampling does not affect the quality of attack detection and Wallarm node continues protect your applications and APIs even with hit sampling enabled.
Full context of threat actor activities¶
Once the malicious request is detected by Wallarm and displayed in the Attacks or Incidents section as the part of some attack, you have an ability to know the full context of this request: to which user session it belongs and what the full sequence of requests in this session is. This allows investigating all activity of the threat actor to understand attack vectors and what resources can be compromised.
To perform this analysis, in Wallarm Console → Attacks or Incidents, access the attack, and then specific request details. In request details, click Explore in API Sessions. Wallarm will open the API Session section filtered: the session, the initial request belongs to is displayed, only the initial request is displayed within this session.
Remove the filter by request ID to see all other requests in the session: now you have the full picture of what was going on within the session the malicious request belongs to.
False positives¶
False positive occurs when attack signs are detected in the legitimate request.
To prevent the filtering node from recognizing such requests as attacks in future, you can mark all or specific requests of the attack as false positives. This automatically creates a rule to skip similar attack sign detection in similar requests, though it does not appear in the Wallarm Console.
You can undo a false positive mark only within a few seconds after the mark was applied. If you decided to undo it later, this can be done only by sending a request to Wallarm technical support.
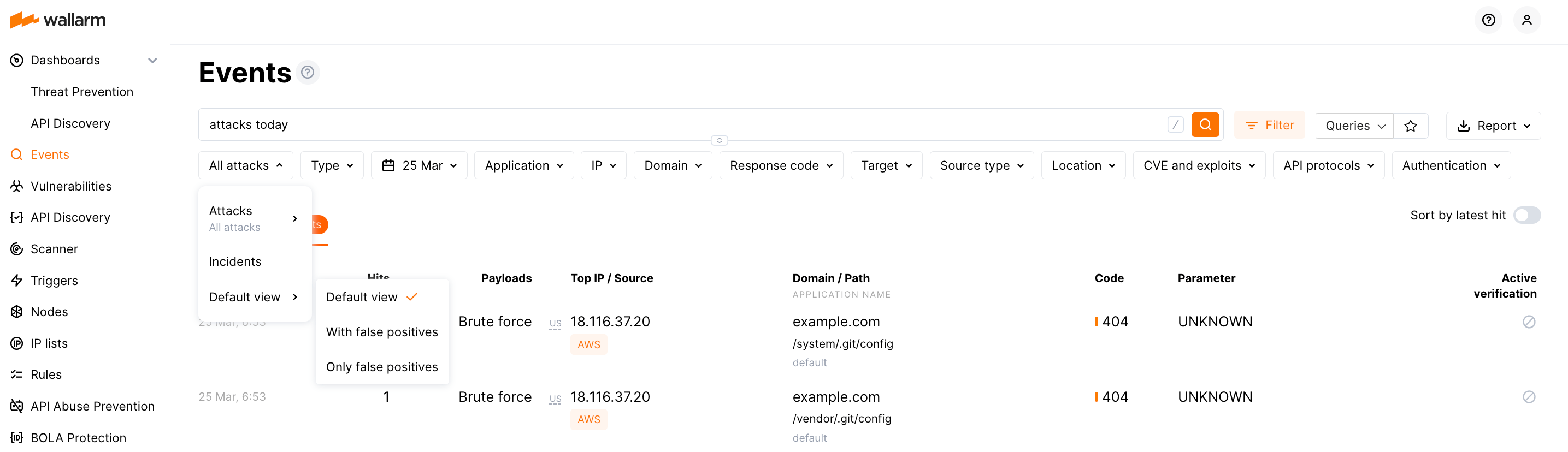
The default view of the attack list presents only actual attacks (without false positives) - to change that, under All attacks switch from Default view to With false positives or Only false positives.
Responding to attacks¶
Is is important to understand if your applications and APIs are properly protected from the attacks to have the possibility to adjust the protection measures if necessary. You can use information from the Attacks section to get this understanding and respond correspondingly.
When dealing with this task, you will need to identify what type of attack took place, this will give you an understanding of what Wallarm's mechanisms provided protection and then adjust these mechanisms if necessary:
-
Identify - in the Payload field context menu, select Show only, then pay attention to the Type filter and search field content.
-
Check what was done for protection - note the Status column:
Blocked- all hits of the attack were blocked by the filtering node.Partially blocked- some hits of the attack were blocked and others were only registered.Monitoring- all hits of the attack were registered but not blocked.Bot detected- this is bot, check action within the attack.
-
Optionally (recommended), investigate the full context of the attack's malicious requests: to which user session they belong and what the full sequence of requests in this session is.
This allows seeing all activity and logic of the threat actor and understanding attack vectors and what resources can be compromised.
-
If you think it was not an actual attack, mark it false positive.
-
Understand - become aware of the Wallarm mechanism that detected and reacted to attack.
-
Adjust - tune the Wallarm's behavior ("how" depends on mechanism).
| Identify | Understand | Adjust |
|---|---|---|
sqli, xss, rce, ptrav, crlf, nosqli, ssi etc. | Standard tools for attack detection (libproton, libdetection and rules) | Expand an attack and explore CVEs summary for the attack and CVEs for separate requests. Pay your attention to the node mode (final_wallarm_mode tag), visit Rules (US or EU), analyze them by application name from the attack. If necessary, adjust the rules or filtration mode for applications or their specific hosts or endpoints. |
custom_rule | Custom attack detector | Expand an attack and follow the Detected by custom rules link(s) - if necessary, modify the rule(s) including partial disabling it for particular branches. |
vpatch | Virtual patch | Visit the Rules section (US or EU), search for "Create virtual patch" rules, if necessary, adjust the rule related to your attack. Have in mind that virtual patches work regardless of the filtration mode. |
brute,dirbust,bola,multiple_payloads | Trigger and IP lists: requests from denylisted IPs | Expand an attack and after analyzing the requests, click the displayed trigger name (if presented) and modify its parameters. Also note trigger tags, then go to Triggers (US or EU) and find trigger by name, if necessary - adjust it. If action is Blocked, this is done via denylist - go to IP Lists (US or EU) and search by IP: if necessary, adjust time period for IP staying in denylist. |
blocked_source | IP lists: requests from denylisted IPs | Expand an attack and analyze requests from denylisted IP; after that, click the displayed trigger name and - if necessary - modify trigger settings. For manually denylisted IPs (blocked_source), go to IP Lists (US or EU) and search by IP: if necessary, adjust time period for IP staying in denylist. |
| Specific module or function: | ||
api_abuse, account_takeover, security_crawlers, scraping (details) - note the Bot detected status for all | API Abuse Prevention and IP lists: requests from denylisted IPs | Expand an attack and analyze the heatmaps proving the confidence that it is a bot, note the date of the attack and source IP. If action is Blocked, this is done via denylist - go to IP lists, filter by date and IP, click Reason column to see IP address details, explore these details, click Triggered profile, explore it and change if necessary. Also, you can:
|
bola | BOLA autoprotection by API Discovery | Expand an attack, if one does not contain link to trigger (which is the sign of manual protection from BOLA) then it is autoprotection provided by the API Discovery (US or EU) module. If necessary, navigate to the BOLA Protection (US or EU) section to either disable this protection or adjust template with its settings. |
undefined_endpoint, undefined_parameter, invalid_parameter_value, missing_parameter, missing_auth, invalid_request (api_specification to search for all of them, details) | API Specification Enforcement | Expand an attack and follow the link to the violated specification. At the specification dialog, use the API specification enforcement tab to adjust settings, consider uploading the latest version of specification via the Specification upload tab. |
gql_doc_size, gql_value_size, gql_depth, gql_aliases, gql_docs_per_batch, gql_introspection, gql_debug (graphql_attacks to search for all of them, details) | GraphQL API Protection | Expand an attack and follow the GraphQL security policies link - if necessary, modify existing Detect GraphQL attacks rule(s) or create additional ones for particular branches. |
Dashboards¶
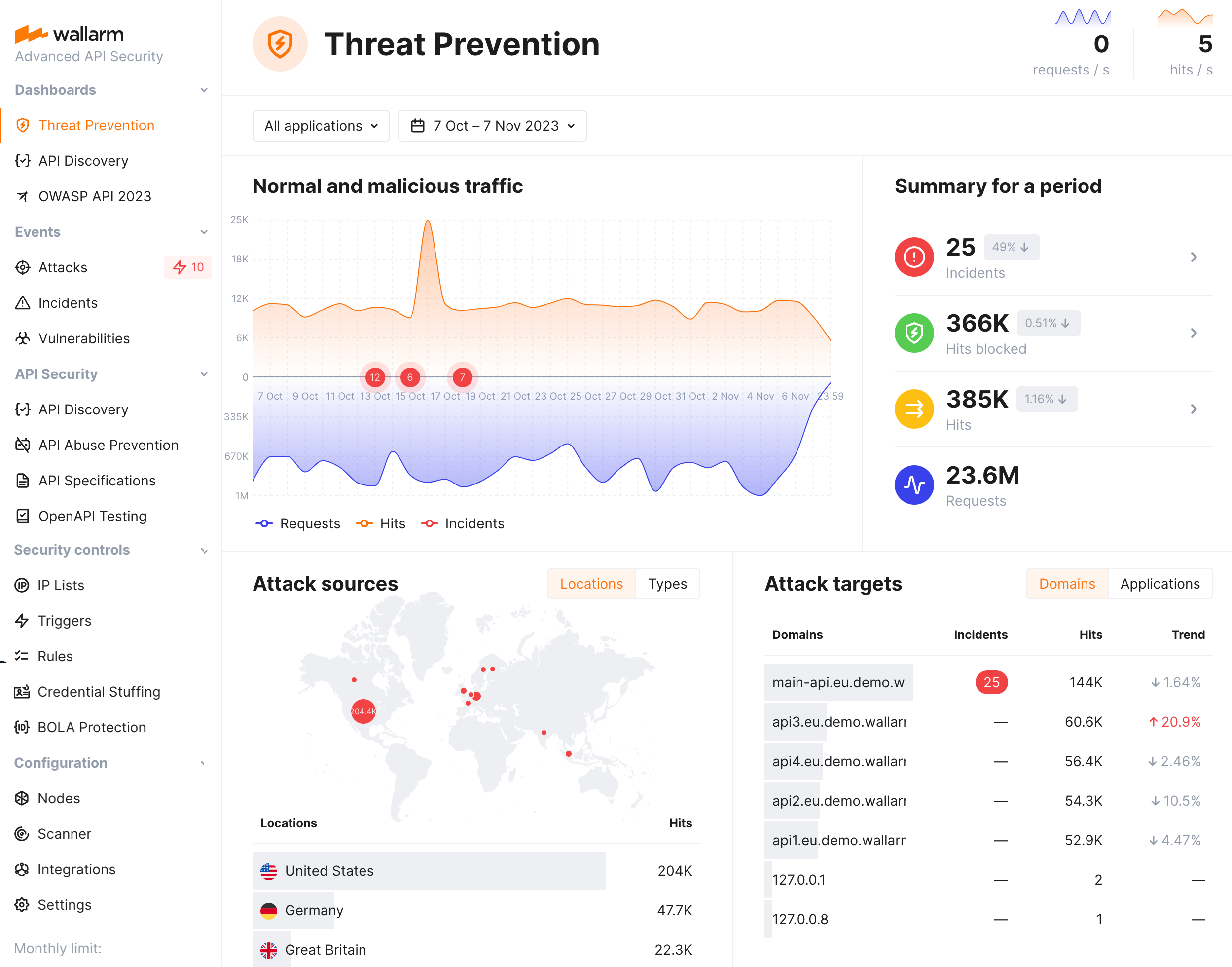
Wallarm provides comprehensive dashboards to help you analyze detected attacks.
Wallarm's Threat Prevention dashboard provides general metrics on your system's security posture, including multi-aspect information about attacks: their sources, targets, types and protocols.
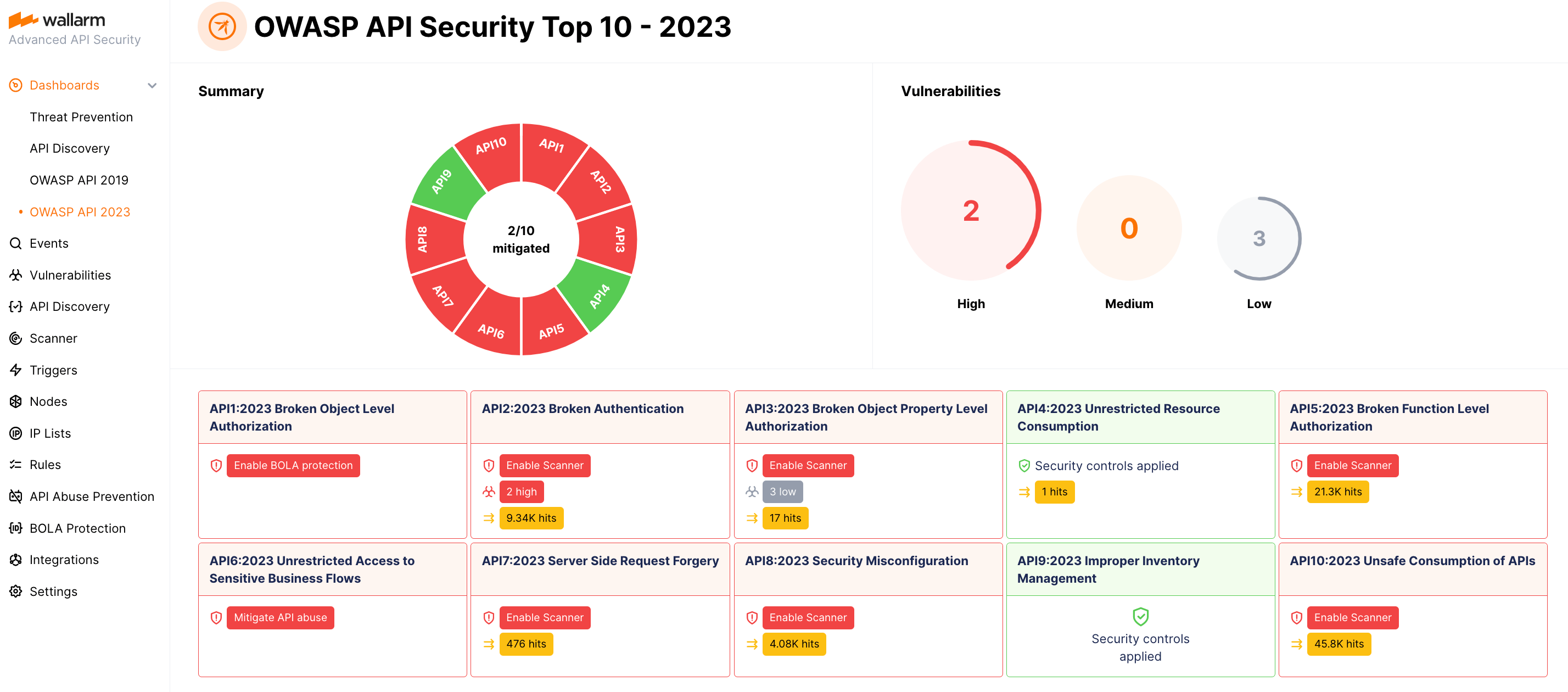
The OWASP API Security Top 10 dashboard provides detailed visibility into your system's security posture against the OWASP API Top 10 threats, including attack information.
Notifications¶
Wallarm can send you notifications on detected attacks, hits and malicious payloads. It allows you to be aware of attempts to attack your system and analyze detected malicious traffic promptly. Analyzing malicious traffic includes reporting false positives, allowlisting IPs originating legitimate requests and denylisting IPs of attack sources.
To configure notifications:
-
Configure native integrations with the systems to send notifications (e.g. PagerDuty, Opsgenie, Splunk, Slack, Telegram).
-
Set the conditions for sending notifications:
-
To get notifications on each detected hit, select the appropriate option in the integration settings.
See the example of the notification about detected hit in the JSON format
[ { "summary": "[Wallarm] New hit detected", "details": { "client_name": "TestCompany", "cloud": "EU", "notification_type": "new_hits", "hit": { "domain": "www.example.com", "heur_distance": 0.01111, "method": "POST", "parameter": "SOME_value", "path": "/news/some_path", "payloads": [ "say ni" ], "point": [ "post" ], "probability": 0.01, "remote_country": "PL", "remote_port": 0, "remote_addr4": "8.8.8.8", "remote_addr6": "", "tor": "none", "request_time": 1603834606, "create_time": 1603834608, "response_len": 14, "response_status": 200, "response_time": 5, "stamps": [ 1111 ], "regex": [], "stamps_hash": -22222, "regex_hash": -33333, "type": "sqli", "block_status": "monitored", "id": [ "hits_production_999_202010_v_1", "c2dd33831a13be0d_AC9" ], "object_type": "hit", "anomaly": 0 } } } ] -
To set the threshold of attack, hit or malicious payload number and get notifications when the threshold is exceeded, configure appropriate triggers.
-
API calls¶
To get the attack details, you can call the Wallarm API directly besides using the Wallarm Console UI. Below is the example of the API call for getting the first 50 attacks detected in the last 24 hours.
Please replacing TIMESTAMP with the date 24 hours ago converted to the Unix Timestamp format.
curl -v -X POST "https://us1.api.wallarm.com/v1/objects/attack" -H "X-WallarmApi-Token: <YOUR_TOKEN>" -H "accept: application/json" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d "{ \"filter\": { \"clientid\": [YOUR_CLIENT_ID], \"time\": [[TIMESTAMP, null]] }, \"offset\": 0, \"limit\": 50, \"order_by\": \"last_time\", \"order_desc\": true}"
curl -v -X POST "https://api.wallarm.com/v1/objects/attack" -H "X-WallarmApi-Token: <YOUR_TOKEN>" -H "accept: application/json" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d "{ \"filter\": { \"clientid\": [YOUR_CLIENT_ID], \"time\": [[TIMESTAMP, null]] }, \"offset\": 0, \"limit\": 50, \"order_by\": \"last_time\", \"order_desc\": true}"
Getting 100 or more attacks
For attack and hit sets containing 100 or more records, it is best to retrieve them in smaller pieces rather than fetching large datasets all at once, in order to optimize performance. Explore the corresponding request example