What is New in Wallarm Node 6.x and 0.14.x¶
This changelog covers updates for NGINX Node 6.x and Native Node 0.14.x+. If upgrading from an older version, refer to this document.
For the detailed changelog on minor versions of the Wallarm Node, refer to the NGINX Node artifact inventory or Native Node artifact inventory.
This release introduces key architectural improvements aimed at enhancing performance and maintainability of the Wallarm Node. These updates also lay the groundwork for upcoming features.
Replacing Tarantool with wstore for postanalytics¶
Wallarm Node now uses wstore, a Wallarm-developed service, instead of Tarantool for local postanalytics processing.
As a result, the following changes have been introduced to NGINX Node:
-
All-in-one installer, AWS/GCP images:
-
The NGINX directive
wallarm_tarantool_upstream, which defines the postanalytics module server address when deployed separately from other NGINX services, has been renamed towallarm_wstore_upstream.Backward compatibility preserved with a deprecation warning:
-
Log file renamed:
/opt/wallarm/var/log/wallarm/tarantool-out.log→/opt/wallarm/var/log/wallarm/wstore-out.log. - The new wstore configuration file
/opt/wallarm/wstore/wstore.yamlreplaces obsolete Tarantool configuration files such as/etc/default/wallarm-tarantoolor/etc/sysconfig/wallarm-tarantool. - The
tarantoolsection in/opt/wallarm/etc/wallarm/node.yamlis nowwstore. Backward compatibility preserved with a deprecation warning.
-
-
- All the above changes are applied within the container.
- Previously, memory for Tarantool was allocated via the
TARANTOOL_MEMORY_GBenvironment variable. Now, memory allocation follows the same principle but uses a new variable:TARANTOOL_MEMORY_GB→SLAB_ALLOC_ARENA. -
Adjusted the container's directory structure to align with Alpine Linux conventions. Specifically:
- Content from
/etc/nginx/modules-availableand/etc/nginx/modules-enabledhas been moved to/etc/nginx/modules. - Content from
/etc/nginx/sites-availableand/etc/nginx/sites-enabledhas been moved to/etc/nginx/http.d.
- Content from
-
The default
allowvalue, specifying permitted IP addresses for the/wallarm-statusservice, is now 127.0.0.0/8 instead of 127.0.0.8/8.
-
Kubernetes Ingress Controller:
- Tarantool is no longer a separate pod, wstore runs within the main
<CHART_NAME>-wallarm-ingress-controller-xxxpod. - Helm values renamed:
controller.wallarm.tarantool→controller.wallarm.postanalytics.
- Tarantool is no longer a separate pod, wstore runs within the main
-
Kubernetes Sidecar Controller:
- Helm values renamed:
postanalytics.tarantool.*→postanalytics.wstore.*. -
The following Docker images have been removed from the Helm chart for Sidecar deployment:
These images have been replaced by the wallarm/node-helpers image, which now runs the relevant services.
- Helm values renamed:
The described changes are incorporated into the Node upgrade instructions provided below.
Removal of collectd¶
The collectd service, previously installed on all filtering nodes, has been removed along with its related plugins. Metrics are now collected and sent using Wallarm's built-in mechanisms, reducing dependencies on external tools.
Use the /wallarm-status endpoint, which replaces collectd by providing the same metrics in Prometheus and JSON formats.
As a result of this change, also the following changed in the configuration rules:
-
The
/opt/wallarm/etc/collectd/wallarm-collectd.conf.d/wallarm-tarantool.confcollectd configuration file is no longer used. -
If you previously used collectd to forward metrics via a network plugin, such as:
LoadPlugin network <Plugin "network"> Server "<Server IPv4/v6 address or FQDN>" "<Server port>" </Plugin>you should now switch to scraping
/wallarm-statusvia Prometheus.
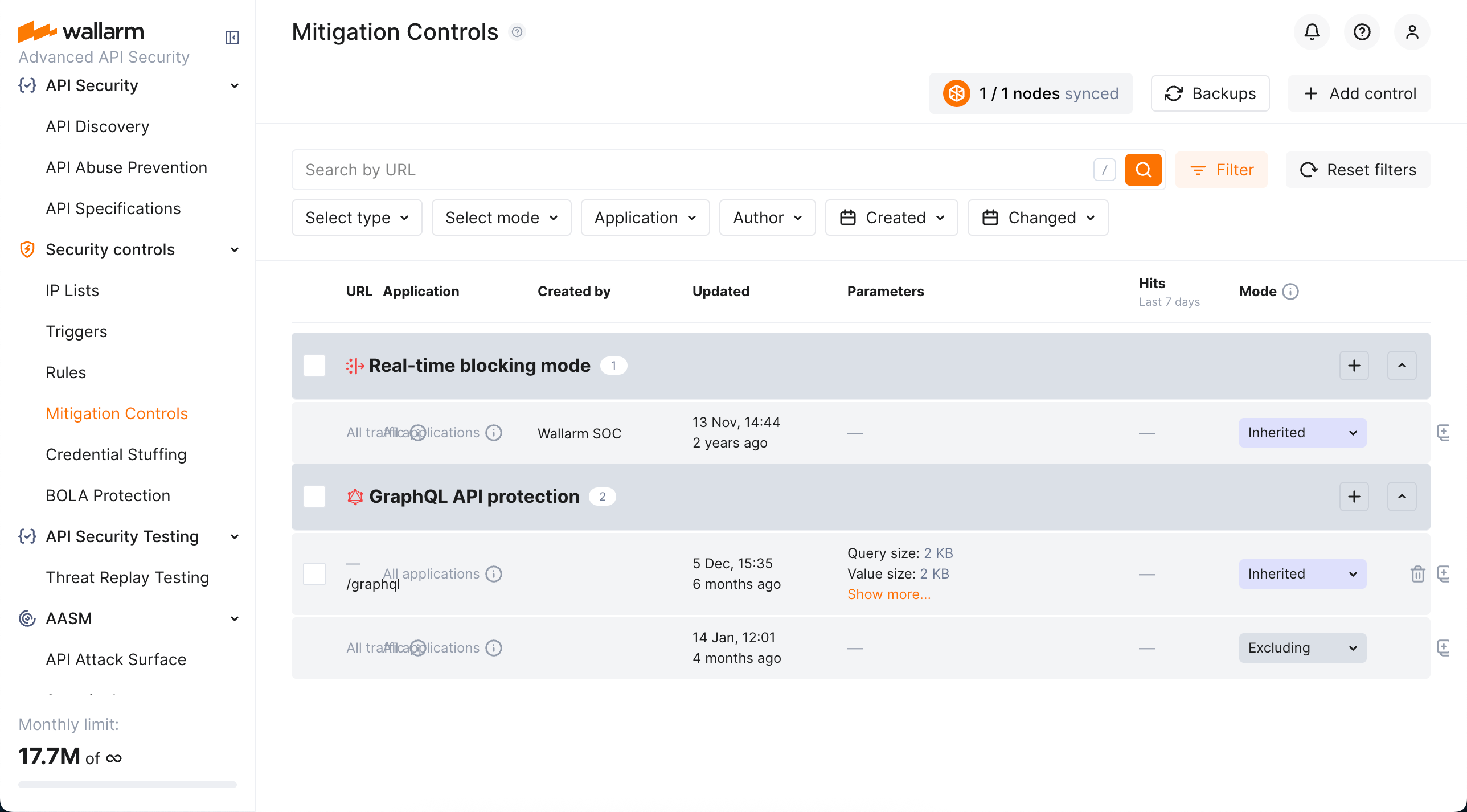
Mitigation Controls¶
We introduce a unified management center for all Wallarm attack mitigation settings - Mitigation Controls. With mitigation controls you can:
-
View and manage all Wallarm mitigation settings in one place.
-
Manage all in a unified way (all controls have similar configuration UI and options).
-
Easily overview the current mode of each control: is it active? is it just monitoring or also blocking?
-
Get quick overview of attacks caught by each control.
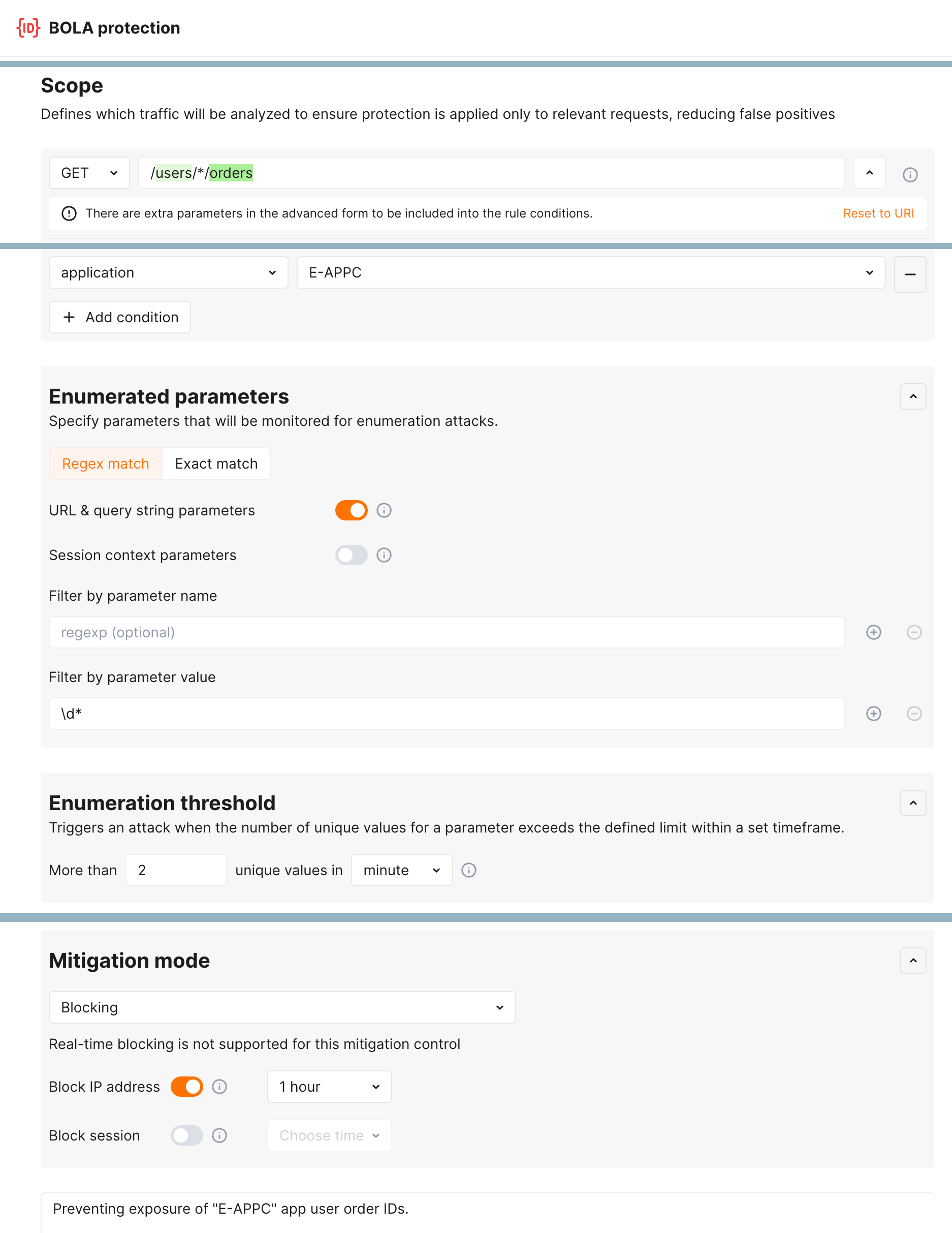
Enumeration attack protection¶
New level of protection from enumeration attacks comes with enumeration mitigation controls:
Comparing to triggers that were used for this protection before, mitigation controls:
-
Allow selecting which parameters will be monitored for enumeration attempts.
-
Allow advanced sophisticated filtering of which exact requests will be counted.
-
Provide deep integration with API Sessions: the detected attacks are displayed within a corresponding session, providing you with full context of what was happening and why the session activities were marked as attack and blocked.
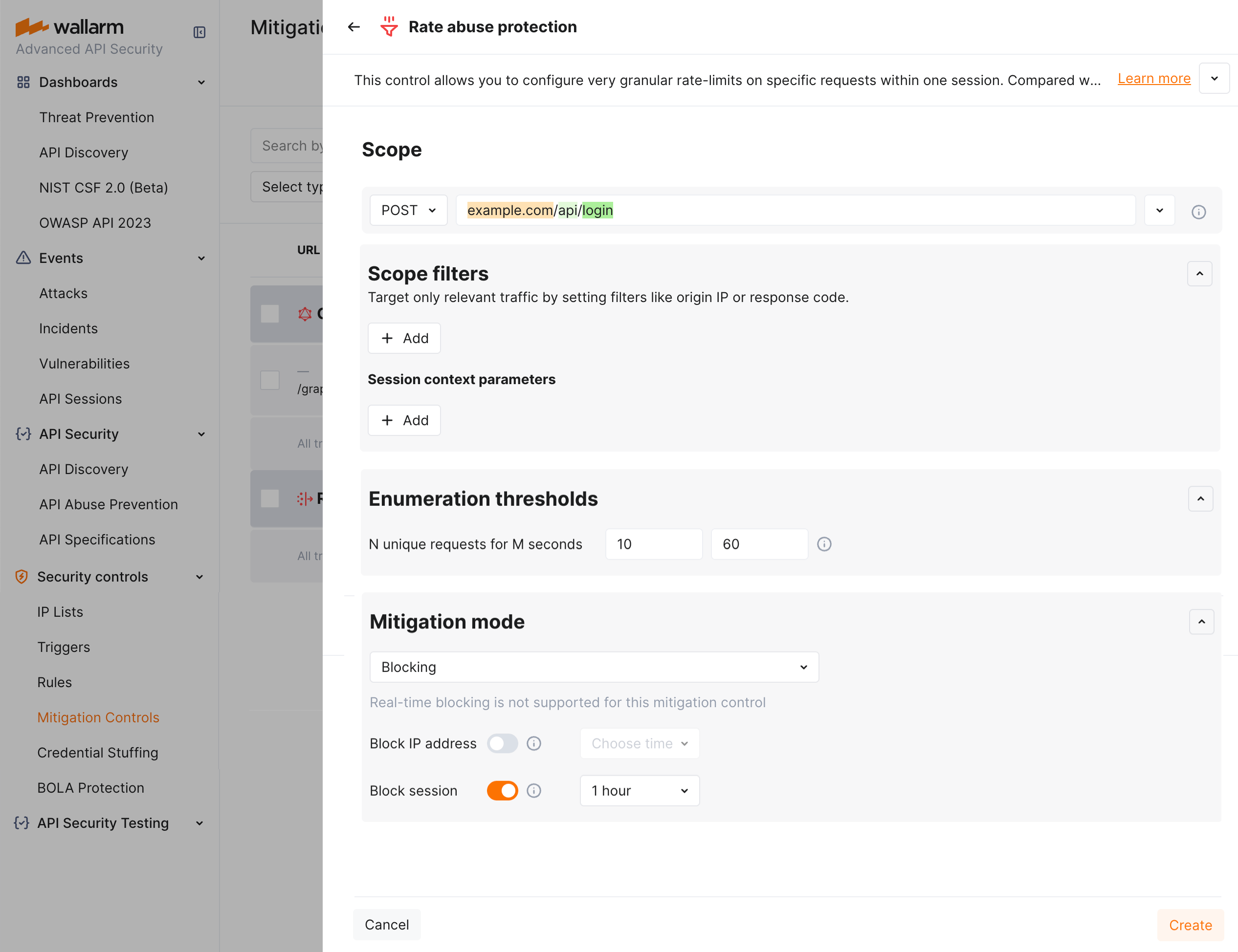
Rate abuse protection¶
The unrestricted resource consumption is included in the OWASP API Top 10 2023 list of most serious API security risks. Being a threat by itself (service slow-down or complete down by overload), this also serves as foundation to different attack types, for example, enumeration attacks. Allowing too many requests per time is one of the main causes of these risks.
Wallarm provides the new Rate abuse protection mitigation control to help prevent excessive traffic to your API.
Which Wallarm nodes are recommended to be upgraded?¶
-
Client and multi-tenant Wallarm NGINX Nodes of version 4.10 and 5.x to stay up to date with Wallarm releases and prevent installed module deprecation.
-
Client and multi-tenant Wallarm nodes of the unsupported versions (4.8 and lower).
If upgrading from the version 3.6 or lower, learn all changes from the separate list.
Upgrade process¶
-
Upgrade installed modules following the instructions for your Wallarm node deployment option: