Upgrading the postanalytics module¶
These instructions describe the steps to upgrade the postanalytics module installed on a separate server up to the latest 6.x version. Postanalytics module must be upgraded before Upgrading Wallarm NGINX modules.
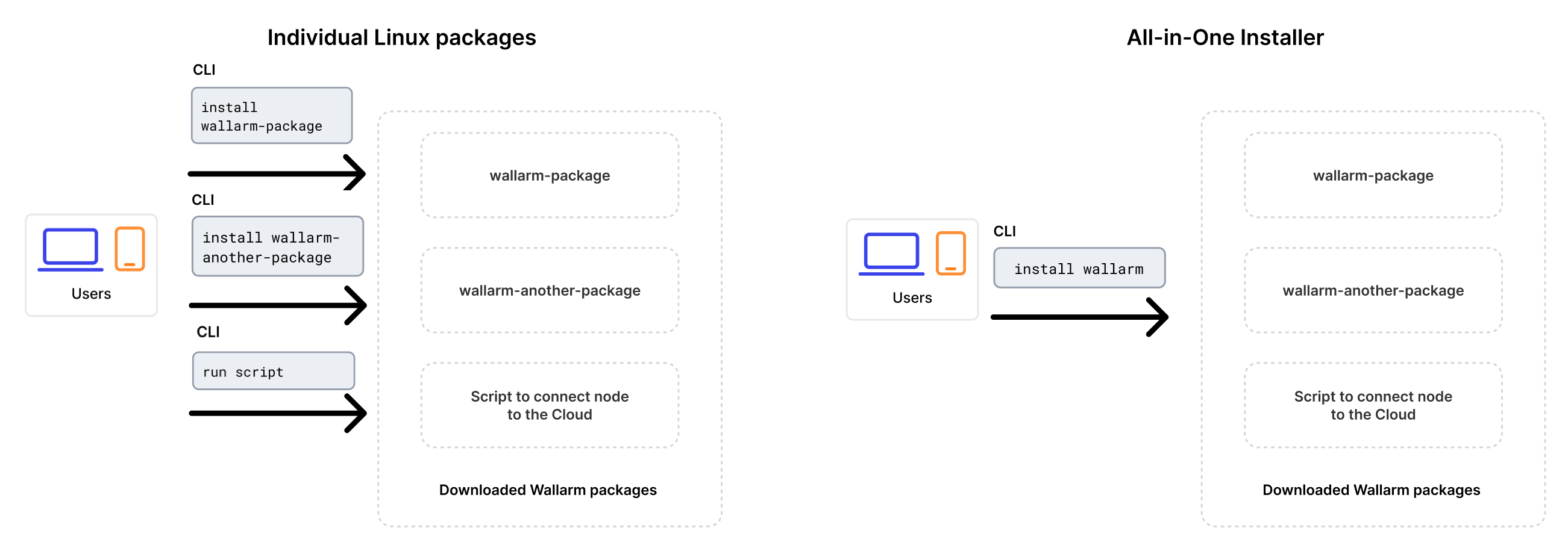
Upgrading with all-in-one installer
Since version 4.10, upgrading is performed using Wallarm's all-in-one installer as the individual Linux packages have been deprecated. This method simplifies the upgrade process and ongoing deployment maintenance compared to the previous approach.
The installer automatically performs the following actions:
- Checking your OS and NGINX version.
- Adding Wallarm repositories for the detected OS and NGINX version.
- Installing Wallarm packages from these repositories.
- Connecting the installed Wallarm module to your NGINX.
- Connecting the filtering node to Wallarm Cloud using the provided token.
To upgrade the end‑of‑life module (3.6 or lower), please use the different instructions.
Requirements¶
-
Access to the account with the Administrator role in Wallarm Console for the US Cloud or EU Cloud.
-
Access to
https://meganode.wallarm.comto download all-in-one Wallarm installer. Ensure the access is not blocked by a firewall. -
Access to
https://us1.api.wallarm.comfor working with US Wallarm Cloud or tohttps://api.wallarm.comfor working with EU Wallarm Cloud. If access can be configured only via the proxy server, then use the instructions. -
Executing all commands as a superuser (e.g.
root). -
Access to the IP addresses below for downloading updates to attack detection rules and API specifications, as well as retrieving precise IPs for your allowlisted, denylisted, or graylisted countries, regions, or data centers.
Step 1: Prepare clean machine¶
When upgrading modules with all-in-one installer, you cannot upgrade an old package installation - instead you need to use a clean machine. Thus, as step 1, prepare a machine with one of the supported OS:
-
Debian 10, 11 and 12.x
-
Ubuntu LTS 18.04, 20.04, 22.04
-
CentOS 7, 8 Stream, 9 Stream
-
Alma/Rocky Linux 9
-
RHEL 8.x
-
RHEL 9.x
-
Oracle Linux 8.x
-
Oracle Linux 9.x
-
Redox
-
SuSe Linux
-
Others (the list is constantly widening, contact Wallarm support team to check if your OS is in the list)
Using new clean machine will lead to that at some moment you will have both old and new node, which is good: you can test the new one working properly without stopping the old one.
Step 2: Prepare Wallarm token¶
To install node, you will need a Wallarm token of the appropriate type. To prepare a token:
Step 3: Download all-in-one Wallarm installer¶
Wallarm suggests all-in-one installations for the following processors:
-
x86_64
-
ARM64 (beta)
To download all-in-one Wallarm installation script, execute the command:
Step 4: Run all-in-one Wallarm installer to install postanalytics¶
To install postanalytics separately with all-in-one installer, use:
# If using the x86_64 version:
sudo env WALLARM_LABELS='group=<GROUP>' sh wallarm-6.3.0.x86_64-glibc.sh postanalytics
# If using the ARM64 version:
sudo env WALLARM_LABELS='group=<GROUP>' sh wallarm-6.3.0.aarch64-glibc.sh postanalytics
The WALLARM_LABELS variable sets group into which the node will be added (used for logical grouping of nodes in the Wallarm Console UI).
Step 5: Upgrade the NGINX-Wallarm module on a separate server¶
Once the postanalytics module is installed on the separate server, upgrade its related NGINX-Wallarm module running on a different server.
Step 6: Re-connect the NGINX-Wallarm module to the postanalytics module¶
On the machine with the NGINX-Wallarm module, in the NGINX configuration file (typically located at /etc/nginx/nginx.conf), specify the postanalytics module server address:
http {
# omitted
upstream wallarm_wstore {
server <ip1>:3313 max_fails=0 fail_timeout=0 max_conns=1;
server <ip2>:3313 max_fails=0 fail_timeout=0 max_conns=1;
keepalive 2;
}
wallarm_wstore_upstream wallarm_wstore;
# omitted
}
-
max_connsvalue must be specified for each of the upstream wstore servers to prevent the creation of excessive connections. -
keepalivevalue must not be lower than the number of the wstore servers. -
The
# wallarm_wstore_upstream wallarm_wstore;string is commented by default - please delete#.
Once the configuration file changed, restart NGINX/NGINX Plus on the NGINX-Wallarm module server:
Step 7: Check the NGINX‑Wallarm and separate postanalytics modules interaction¶
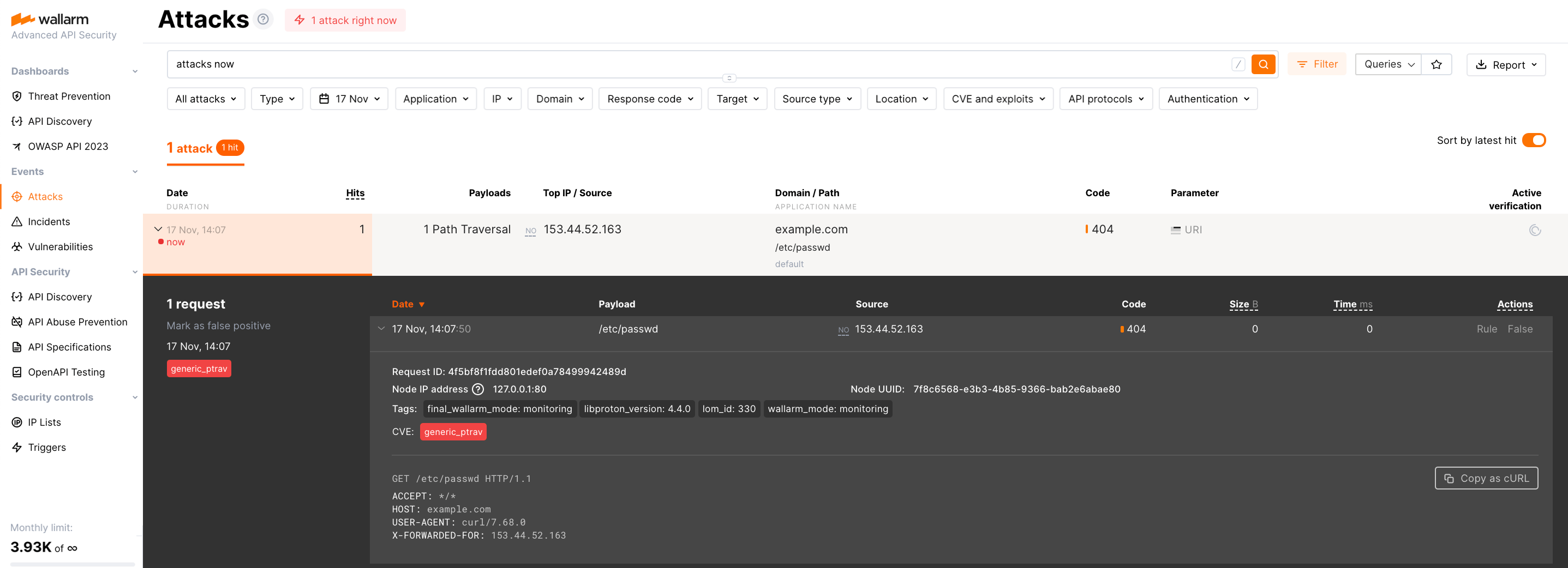
To check the NGINX‑Wallarm and separate postanalytics modules interaction, you can send the request with test attack to the address of the protected application:
If the NGINX‑Wallarm and separate postanalytics modules are configured properly, the attack will be uploaded to the Wallarm Cloud and displayed in the Attacks section of Wallarm Console:
If the attack was not uploaded to the Cloud, please check that there are no errors in the services operation:
-
Analyze the postanalytics module logs
If there is the record like
SystemError binary: failed to bind: Cannot assign requested address, make sure that the server accepts connection on specified address and port. -
On the server with the NGINX‑Wallarm module, analyze the NGINX logs:
If there is the record like
[error] wallarm: <address> connect() failed, make sure that the address of separate postanalytics module is specified correctly in the NGINX‑Wallarm module configuration files and separate postanalytics server accepts connection on specified address and port. -
On the server with the NGINX‑Wallarm module, get the statistics on processed requests using the command below and make sure that the value of
tnt_errorsis 0Description of all parameters returned by the statistics service →
Step 8: Remove old postanalytics module¶
-
Delete old postanalytics module in Wallarm Console → Nodes by selecting your postanalytics module node and clicking Delete.
-
Confirm the action.
When the postanalytics module node is deleted from Cloud, it will stop participation in filtration of requests to your applications. Deleting cannot be undone. The postanalytics module node will be deleted from the list of nodes permanently.
-
Delete machine with the old postanalytics module or just clean it from Wallarm postanalytics module components: