Upgrading EOL Wallarm NGINX modules¶
These instructions describe the steps to upgrade the end‑of‑life Wallarm NGINX modules (version 3.6 and lower) to the latest version 6.x. Wallarm NGINX modules are the modules installed in accordance with one of the following instructions:
-
Individual packages for NGINX stable
-
Individual packages for NGINX Plus
-
Individual packages for distribution-provided NGINX
Wallarm nodes 3.6 and lower are not supported
You are recommended to upgrade the Wallarm nodes 3.6 and lower since these versions are not supported, they are end-of-life.
Node configuration and traffic filtration have been significantly simplified in the Wallarm node of the latest versions. Before upgrading the modules, please carefully review the list of changes and general recommendations. Please note that some settings of the latest node are incompatible with the nodes 3.6 and lower.
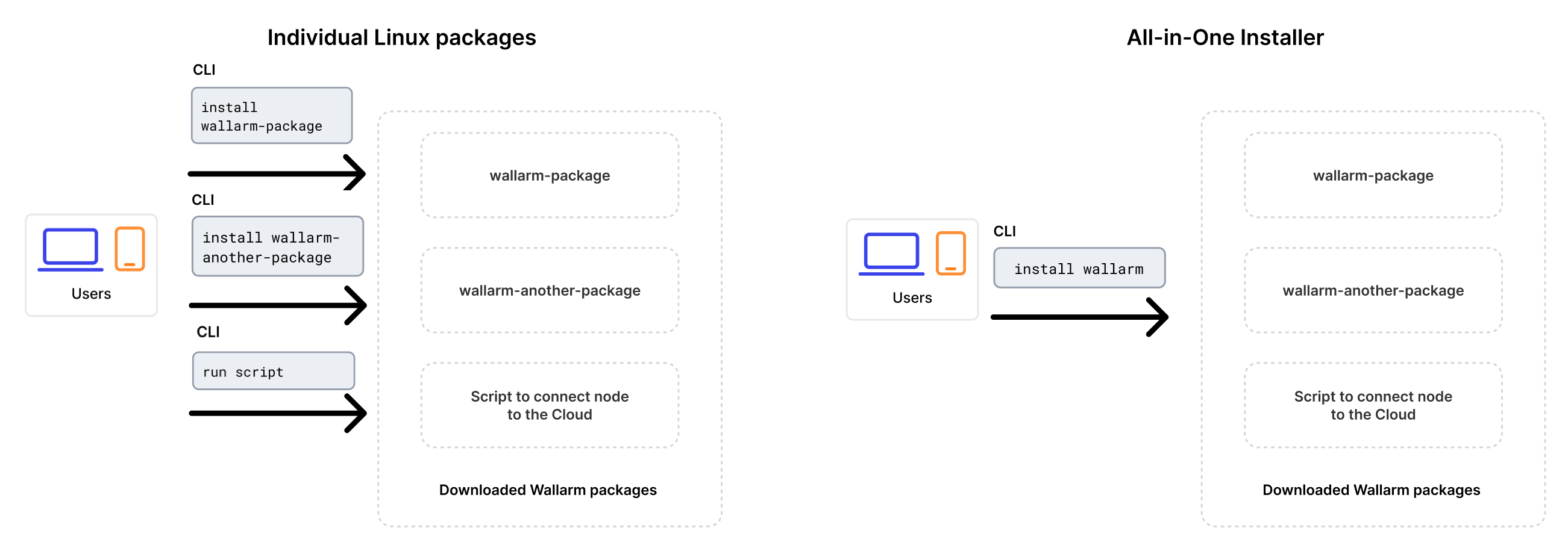
Upgrading with all-in-one installer
Upgrading is performed using Wallarm's all-in-one installer as the individual Linux packages have been deprecated. This method simplifies the upgrade process and ongoing deployment maintenance compared to the previous approach.
The installer automatically performs the following actions:
- Checking your OS and NGINX version.
- Adding Wallarm repositories for the detected OS and NGINX version.
- Installing Wallarm packages from these repositories.
- Connecting the installed Wallarm module to your NGINX.
-
Connecting the filtering node to Wallarm Cloud using the provided token.
Manual upgrade with individual Linux packages is not supported any more.
Inform Wallarm technical support that you are upgrading EOL node¶
If upgrading the end‑of‑life Wallarm NGINX modules (version 3.6 and lower) to version 6.x, inform Wallarm technical support about that and ask for assistance.
Besides any other help, ask to enable new IP lists logic for your Wallarm account. When new IP lists logic is enabled, please open Wallarm Console and ensure that the section IP lists is available.
Requirements¶
-
Access to the account with the Administrator role in Wallarm Console for the US Cloud or EU Cloud.
-
Access to
https://meganode.wallarm.comto download all-in-one Wallarm installer. Ensure the access is not blocked by a firewall. -
Access to
https://us1.api.wallarm.comfor working with US Wallarm Cloud or tohttps://api.wallarm.comfor working with EU Wallarm Cloud. If access can be configured only via the proxy server, then use the instructions. -
Executing all commands as a superuser (e.g.
root). -
Access to the IP addresses below for downloading updates to attack detection rules and API specifications, as well as retrieving precise IPs for your allowlisted, denylisted, or graylisted countries, regions, or data centers.
Upgrade procedure¶
-
If filtering node and postanalytics modules are installed on the same server, then follow the instructions below to upgrade all.
You will need to run a node of the newer version using all-in-one installer on a clean machine, test that it works well and stop the previous one and configure traffic to flow through the new machine instead of the previous one.
-
If filtering node and postanalytics modules are installed on different servers, first upgrade the postanalytics module and then the filtering module following these instructions.
Step 1: Disable the Threat Replay Testing module (if upgrading node 2.16 or lower)¶
If upgrading Wallarm node 2.16 or lower, please disable the Threat Replay Testing module in Wallarm Console → Vulnerabilities → Configure.
The module operation can cause false positives during the upgrade process. Disabling the module minimizes this risk.
Step 2: Prepare clean machine¶
When upgrading modules with all-in-one installer, you cannot upgrade an old package installation - instead you need to use a clean machine. Thus, as step 1, prepare a machine with one of the supported OS:
-
Debian 10, 11 and 12.x
-
Ubuntu LTS 18.04, 20.04, 22.04
-
CentOS 7, 8 Stream, 9 Stream
-
Alma/Rocky Linux 9
-
RHEL 8.x
-
RHEL 9.x
-
Oracle Linux 8.x
-
Oracle Linux 9.x
-
Redox
-
SuSe Linux
-
Others (the list is constantly widening, contact Wallarm support team to check if your OS is in the list)
Using new clean machine will lead to that at some moment you will have both old and new node, which is good: you can test the new one working properly without stopping the old one.
Step 3: Install NGINX and dependencies¶
Install the latest NGINX version of:
-
NGINX
stable(the latest supported version is v1.28.0) - see how to install it in the NGINX documentation. -
NGINX Mainline (the latest supported version is v1.27.5) - see how to install it in the NGINX documentation.
-
NGINX Plus (the latest supported version is NGINX Plus R33) - see how to install it in the NGINX documentation.
-
Distribution-Provided NGINX - to install, use the following commands:
Step 4: Prepare Wallarm token¶
To install node, you will need a Wallarm token of the appropriate type. To prepare a token:
Step 5: Download all-in-one Wallarm installer¶
Wallarm suggests all-in-one installations for the following processors:
-
x86_64
-
ARM64 (beta)
To download all-in-one Wallarm installation script, execute the command:
Step 6: Run all-in-one Wallarm installer¶
Filtering node and postanalytics on the same server¶
-
Run downloaded script:
# If using the x86_64 version: sudo env WALLARM_LABELS='group=<GROUP>' sh wallarm-6.3.0.x86_64-glibc.sh # If using the ARM64 version: sudo env WALLARM_LABELS='group=<GROUP>' sh wallarm-6.3.0.aarch64-glibc.shThe
WALLARM_LABELSvariable sets group into which the node will be added (used for logical grouping of nodes in the Wallarm Console UI). -
Enter Wallarm token.
Filtering node and postanalytics on different servers¶
Sequence of steps to upgrade the filtering node and postanalytics modules
If the filtering node and postanalytics modules are installed on different servers, then it is required to upgrade the postanalytics packages before updating the filtering node packages.
-
Upgrade postanalytics module following these instructions.
-
Upgrade filtering node:
# If using the x86_64 version: sudo env WALLARM_LABELS='group=<GROUP>' sh wallarm-6.3.0.x86_64-glibc.sh filtering # If using the ARM64 version: sudo env WALLARM_LABELS='group=<GROUP>' sh wallarm-6.3.0.aarch64-glibc.sh filteringThe
WALLARM_LABELSvariable sets group into which the node will be added (used for logical grouping of nodes in the Wallarm Console UI).
Step 7: Migrate allowlists and denylists from the previous Wallarm node version to 6.x (only if upgrading node 2.18 or lower)¶
If upgrading node 2.18 or lower, migrate allowlist and denylist configuration from previous Wallarm node version to the latest version.
Step 8: Transfer NGINX and postanalytics configuration from old node machine to new¶
Migrate the node-related NGINX and postanalytics configurations from the old machine to the new one by copying the necessary directives or files:
-
/etc/nginx/conf.d/default.confor/etc/nginx/nginx.confwith NGINX settings for thehttplevelIf the filtering and postanalytics nodes are on different servers, in the
httpblock of/etc/nginx/nginx.confon the filtering node machine, renamewallarm_tarantool_upstreamtowallarm_wstore_upstream. -
/etc/nginx/sites-available/defaultwith NGINX and Wallarm settings for traffic routing -
/etc/nginx/conf.d/wallarm-status.conf→ copy to/etc/nginx/wallarm-status.confon the new machineDetailed description is available within the link.
-
/etc/wallarm/node.yaml→ copy to/opt/wallarm/etc/wallarm/node.yamlon the new machineIf using a custom host and port on a separate postanalytics server, rename the
tarantoolsection towstorein the copied file on the postanalytics node machine.
Rename deprecated NGINX directives¶
Rename the following NGINX directives if they are explicitly specified in configuration files:
-
wallarm_instance→wallarm_application -
wallarm_local_trainingset_path→wallarm_custom_ruleset_path -
wallarm_global_trainingset_path→wallarm_protondb_path -
wallarm_ts_request_memory_limit→wallarm_general_ruleset_memory_limit -
wallarm_tarantool_upstream→wallarm_wstore_upstream
We only changed the names of the directives, their logic remains the same. Directives with former names will be deprecated soon, so you are recommended to rename them before.
Update the node logging variables¶
In the new node version the following changes to the node logging variables have been implemented:
-
The
wallarm_request_timevariable has been renamed towallarm_request_cpu_time.We only changed the variable name, its logic remains the same. The old name is temporarily supported as well, but still it is recommended to rename the variable.
-
The
wallarm_request_mono_timevariable has been added – place it in the configuration of the logging format if you need log information about total time being the sum of:- Time in the queue
- Time in seconds the CPU spent processing the request
Adjust Wallarm node filtration mode settings to changes released in the latest versions¶
-
Ensure that the expected behavior of settings listed below corresponds to the changed logic of the
offandmonitoringfiltration modes: -
If the expected behavior does not correspond to the changed filtration mode logic, please adjust the filtration mode settings to released changes using the instructions.
the overlimit_res attack detection configuration from directives to the rule¶
Starting from the version 3.6, you can fine-tune the overlimit_res attack detection using the rule in Wallarm Console.
Earlier, the wallarm_process_time_limit and wallarm_process_time_limit_block NGINX directives have been used. The listed directives are considered to be deprecated with the new rule release and will be deleted in future releases.
If the overlimit_res attack detection settings are customized via the listed directives, it is recommended to transfer them to the rule as follows:
-
Open Wallarm Console → Rules and proceed to the Limit request processing time rule setup.
-
Configure the rule as done via the NGINX directives:
- The rule condition should match the NGINX configuration block with the
wallarm_process_time_limitandwallarm_process_time_limit_blockdirectives specified. -
The time limit for the node to process a single request (milliseconds): the value of
wallarm_process_time_limit.Risk of running out of system memory
The high time limit and/or continuation of request processing after the limit is exceeded can trigger memory exhaustion or out-of-time request processing.
-
The node will either block or pass the
overlimit_resattack depending on the node filtration mode:- In the monitoring mode, the node forwards the original request to the application address. The application has the risk to be exploited by the attacks included in both processed and unprocessed request parts.
- In the safe blocking mode, the node blocks the request if it is originated from the graylisted IP address. Otherwise, the node forwards the original request to the application address. The application has the risk to be exploited by the attacks included in both processed and unprocessed request parts.
- In the block mode, the node blocks the request.
- The rule condition should match the NGINX configuration block with the
-
Delete the
wallarm_process_time_limitandwallarm_process_time_limit_blockNGINX directives from the NGINX configuration file.If the
overlimit_resattack detection is fine-tuned using both the directives and the rule, the node will process requests as the rule sets.
Update the wallarm-status.conf file contents¶
Update the /etc/nginx/conf.d/wallarm-status.conf contents as follows:
server {
listen 127.0.0.8:80;
server_name localhost;
allow 127.0.0.8/8; # Access is only available for loopback addresses of the filter node server
deny all;
wallarm_mode off;
disable_acl "on"; # Checking request sources is disabled, denylisted IPs are allowed to request the wallarm-status service. https://docs.wallarm.com/admin-en/configure-parameters-en/#disable_acl
wallarm_enable_apifw off;
access_log off;
location ~/wallarm-status$ {
wallarm_status on;
}
}
More details on the statistics service configuration
Update the Wallarm blocking page¶
In new node version, the Wallarm sample blocking page has been changed. The logo and support email on the page are now empty by default.
If the page &/usr/share/nginx/html/wallarm_blocked.html was configured to be returned in response to blocked requests, copy and customize the new version of a sample page.
Step 9: Update API port¶
Starting with version 4.0, the filtering node uploads data to the Cloud using the us1.api.wallarm.com:443 (US Cloud) and api.wallarm.com:443 (EU Cloud) API endpoints instead of us1.api.wallarm.com:444 and api.wallarm.com:444.
If you upgrade the node from the version 3.x or lower and your server with the deployed node has a limited access to the external resources and the access is granted to each resource separately, then after upgrade the synchronization between the filtering node and the Cloud will stop.
To restore the synchronization, in your configuration, change port 444 to 443 for API endpoint for each resource.
Step 10: Re-enable the Threat Replay Testing module (only if upgrading node 2.16 or lower)¶
Learn the recommendation on the Threat Replay Testing module setup and re-enable it if required.
After a while, ensure the module operation does not cause false positives. If discovering false positives, please contact the Wallarm technical support.
Step 11: Restart NGINX¶
Restart NGINX using the following command:
Step 12: Test Wallarm node operation¶
To test the new node operation:
-
Send the request with test SQLI and XSS attacks to the protected resource address:
-
Open the Wallarm Console → Attacks section in the US Cloud or EU Cloud and ensure attacks are displayed in the list.
-
As soon as your Cloud stored data (rules, IP lists) is synchronized to the new node, perform some test attacks to make sure your rules work as expected.
Step 13: Configure sending traffic to Wallarm node¶
Update targets of your load balancer to send traffic to the Wallarm instance. For details, please refer to the documentation on your load balancer.
Before full redirecting of the traffic to the new node, it is recommended to first redirect it partially and check that the new node behaves as expected.
Step 14: Remove old node¶
-
Delete old node in Wallarm Console → Nodes by selecting your node and clicking Delete.
-
Confirm the action.
When the node is deleted from Cloud, it will stop filtration of requests to your applications. Deleting the filtering node cannot be undone. The node will be deleted from the list of nodes permanently.
-
Delete machine with the old node or just clean it from Wallarm node components:
Settings customization¶
The Wallarm modules are updated to version 6.x. Previous filtering node settings will be applied to the new version automatically. To make additional settings, use the available directives.
Common customization options:
-
Using the balancer of the proxy server behind the filtering node
-
Limiting the single request processing time in the directive
wallarm_process_time_limit -
Limiting the server reply waiting time in the NGINX directive
proxy_read_timeout -
Limiting the maximum request size in the NGINX directive
client_max_body_size