Upgrading an EOL Docker NGINX-based image¶
These instructions describe the steps to upgrade the running end‑of‑life Docker NGINX-based image (version 3.6 and lower) to the version 5.0.
Wallarm nodes 3.6 and lower are not supported
You are recommended to upgrade the Wallarm nodes 3.6 and lower since these versions are not supported, they are end-of-life.
Node configuration and traffic filtration have been significantly simplified in the Wallarm node of the latest versions. Before upgrading the modules, please carefully review the list of changes and general recommendations. Please note that some settings of the latest node are incompatible with the nodes 3.6 and lower.
Requirements¶
-
Docker installed on your host system
-
Access to
https://hub.docker.com/r/wallarm/nodeto download the Docker image. Please ensure the access is not blocked by a firewall -
Access to the account with the Administrator role in Wallarm Console in the US Cloud or EU Cloud
-
Access to
https://us1.api.wallarm.comif working with US Wallarm Cloud or tohttps://api.wallarm.comif working with EU Wallarm Cloud. Please ensure the access is not blocked by a firewall -
Access to the IP addresses below for downloading updates to attack detection rules and API specifications, as well as retrieving precise IPs for your allowlisted, denylisted, or graylisted countries, regions, or data centers
Step 1: Inform Wallarm technical support that you are upgrading filtering node modules (only if upgrading node 2.18 or lower)¶
If upgrading node 2.18 or lower, please inform Wallarm technical support that you are upgrading filtering node modules up to 5.0 and ask to enable new IP list logic for your Wallarm account. When new IP list logic is enabled, please ensure the section IP lists of Wallarm Console is available.
Step 2: Disable the Threat Replay Testing module (only if upgrading node 2.16 or lower)¶
If upgrading Wallarm node 2.16 or lower, please disable the Threat Replay Testing module in Wallarm Console → Vulnerabilities → Configure.
The module operation can cause false positives during the upgrade process. Disabling the module minimizes this risk.
Step 3: Update API port¶
Starting with version 4.0, the filtering node uploads data to the Cloud using the us1.api.wallarm.com:443 (US Cloud) and api.wallarm.com:443 (EU Cloud) API endpoints instead of us1.api.wallarm.com:444 and api.wallarm.com:444.
If you upgrade the node from the version 3.x or lower and your server with the deployed node has a limited access to the external resources and the access is granted to each resource separately, then after upgrade the synchronization between the filtering node and the Cloud will stop.
To restore the synchronization, in your configuration, change port 444 to 443 for API endpoint for each resource.
Step 4: Download the updated filtering node image¶
Step 5: Switch to the token-based connection to the Wallarm Cloud¶
Approach to connect the container to the Wallarm Cloud has been upgraded as follows:
-
The "email and password"-based approach has been deprecated. In this approach, the node was registered in the Wallarm Cloud automatically once the container started with correct credentials passed in the
DEPLOY_USERandDEPLOY_PASSWORDvariables. -
The token-based approach has been included. To connect the container to the Cloud, run the container with the
WALLARM_API_TOKENvariable containing the Wallarm API token copied from the Wallarm Console UI.
It is recommended to use the new approach to run the image 5.0. The "email and password"-based approach will be deleted in future releases, please migrate before.
To create a new Wallarm node and get its token:
-
Open Wallarm Console → Settings → API Tokens and generate a token with the Deploy role.
-
Copy the generated token.
Step 6: Migrate allowlists and denylists from the previous Wallarm node version to 5.0 (only if upgrading node 2.18 or lower)¶
If upgrading node 2.18 or lower, migrate allowlist and denylist configuration from previous Wallarm node version to 5.0.
Step 7: Switch from deprecated configuration options¶
There are the following deprecated configuration options:
-
The
WALLARM_ACL_ENABLEenvironment variable has been deprecated. If IP lists are migrated to the new node version, remove this variable from thedocker runcommand. -
The following NGINX directives have been renamed:
wallarm_instance→wallarm_applicationwallarm_local_trainingset_path→wallarm_custom_ruleset_pathwallarm_global_trainingset_path→wallarm_protondb_pathwallarm_ts_request_memory_limit→wallarm_general_ruleset_memory_limit
We only changed the names of the directives, their logic remains the same. Directives with former names will be deprecated soon, so you are recommended to rename them before.
Please check if the directives with former names are explicitly specified in the mounted configuration files. If so, rename them.
-
The
wallarm_request_timelogging variable has been renamed towallarm_request_cpu_time.We only changed the variable name, its logic remains the same. The old name is temporarily supported as well, but still it is recommended to rename the variable.
Step 8: Update the Wallarm blocking page (if upgrading NGINX-based image)¶
In new node version, the Wallarm sample blocking page has been changed. The logo and support email on the page are now empty by default.
If the Docker container was configured to return the &/usr/share/nginx/html/wallarm_blocked.html page to blocked requests, change this configuration as follows:
-
Copy and customize the new version of a sample page.
-
Mount the customized page and the NGINX configuration file to a new Docker container in the next step.
Step 9: Review recent architectural updates (for NGINX-based Docker image)¶
The latest update has introduced architectural changes that may impact users, especially those mounting custom configuration files during container initiation due to alterations in the paths of certain files. Please familiarize yourself with these changes to ensure proper configuration and usage of the new image.
Step 10: Transfer the overlimit_res attack detection configuration from directives to the rule¶
Starting from the version 3.6, you can fine-tune the overlimit_res attack detection using the rule in Wallarm Console.
Earlier, the following options have been used:
- The
wallarm_process_time_limitandwallarm_process_time_limit_blockNGINX directives
The listed directives and parameters are considered to be deprecated with the new rule release and will be deleted in future releases.
If the overlimit_res attack detection settings are customized via the listed parameters, it is recommended to transfer them to the rule as follows:
-
Open Wallarm Console → Rules and proceed to the Limit request processing time rule setup.
-
Configure the rule as done in the mounted configuration files:
* The time limit for the node to process a single request (milliseconds): the value ofwallarm_process_time_limitorprocess_time_limit.!!! warning "Risk of running out of system memory" The high time limit and/or continuation of request processing after the limit is exceeded can trigger memory exhaustion or out-of-time request processing.-
The node will either block or pass the
overlimit_resattack depending on the node filtration mode:- In the monitoring mode, the node forwards the original request to the application address. The application has the risk to be exploited by the attacks included in both processed and unprocessed request parts.
- In the safe blocking mode, the node blocks the request if it is originated from the graylisted IP address. Otherwise, the node forwards the original request to the application address. The application has the risk to be exploited by the attacks included in both processed and unprocessed request parts.
- In the block mode, the node blocks the request.
-
-
Delete the
wallarm_process_time_limit,wallarm_process_time_limit_blockNGINX directives from the mounted configuration file.If the
overlimit_resattack detection is fine-tuned using both the parameters and the rule, the node will process requests as the rule sets.
Step 11: Stop the running container¶
Step 12: Run the container using the updated image¶
Run the container using the updated image and making necessary adjustments to the paths for the mounted files if required by the recent changes to the image.
There are two options for running the container using the updated image:
Step 13: Adjust Wallarm node filtration mode settings to changes released in the latest versions (only if upgrading node 2.18 or lower)¶
-
Ensure that the expected behavior of settings listed below corresponds to the changed logic of the
offandmonitoringfiltration modes:- Environment variable
WALLARM_MODEor the directivewallarm_modeof the NGINX‑based Docker container
- General filtration rule configured in Wallarm Console
- Endpoint-targeted filtration rules configured in Wallarm Console
- Environment variable
-
If the expected behavior does not correspond to the changed filtration mode logic, please adjust the filtration mode settings to released changes using the instructions.
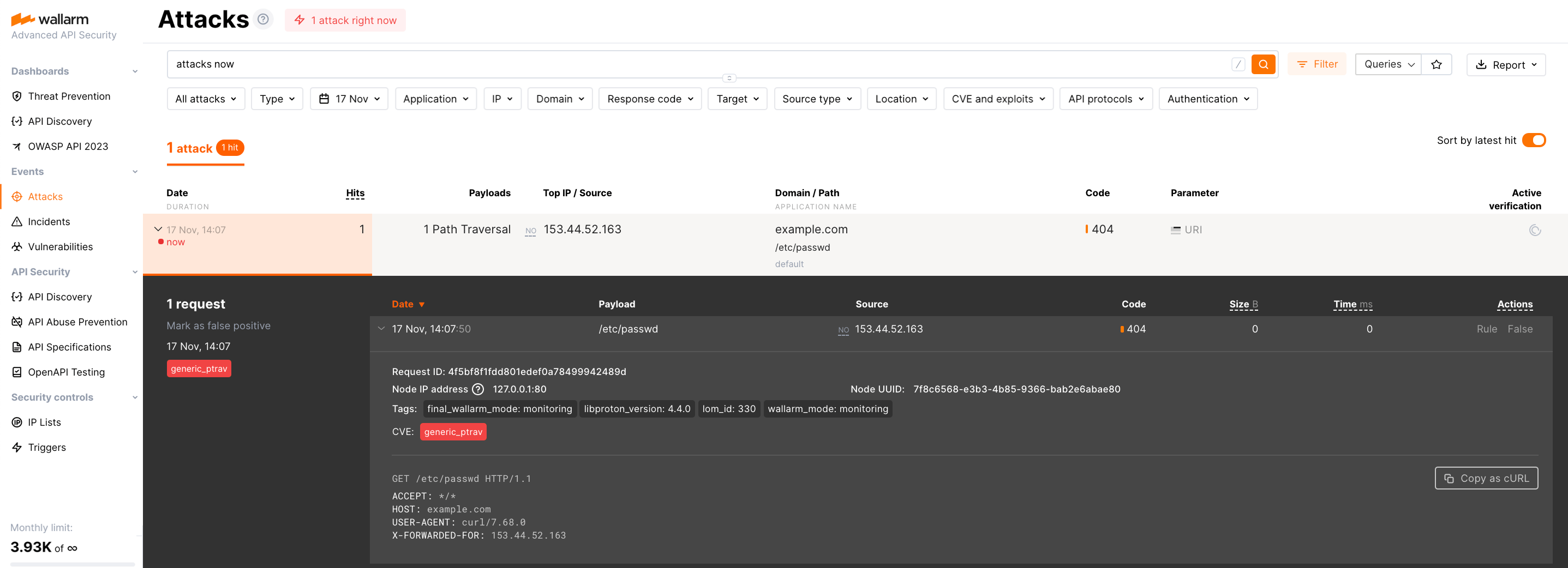
Step 14: Test the filtering node operation¶
-
Send the request with the test Path Traversal attack to the application address:
If traffic is configured to be proxied to
example.com, include the-H "Host: example.com"header in the request. -
Make sure the node of the new type processes the request in the same way as the regular node did, e.g.:
- Blocks the request if the appropriate filtration mode is configured.
- Returns the custom blocking page if it is configured.
-
Open Wallarm Console → Attacks in the EU Cloud or US Cloud and make sure that:
- The attack is displayed in the list.
- Hit details display the Wallarm node UUID.
Step 15: Delete the filtering node of the previous version¶
If the deployed image of the version 5.0 operates correctly, you can delete the filtering node of the previous version in the Wallarm Console → Nodes section.
Step 16: Re-enable the Threat Replay Testing module (only if upgrading node 2.16 or lower)¶
Learn the recommendation on the Threat Replay Testing module setup and re-enable it if required.
After a while, ensure the module operation does not cause false positives. If discovering false positives, please contact the Wallarm technical support.