Amazon İmajından Wallarm OOB Dağıtımı¶
Bu makale, AWS üzerinde Wallarm OOB'nin, resmi Amazon Machine Image (AMI) kullanılarak dağıtılması için talimatları sunmaktadır. Burada anlatılan çözüm, bir web veya proxy sunucusu tarafından aynalanan trafiği analiz etmek üzere tasarlanmıştır.
Kullanım Durumları¶
Among all supported Wallarm deployment options, AMI is recommended for Wallarm deployment in these use cases:
-
Your existing infrastructure resides on AWS.
-
You aim to deploy a security solution as a separate cloud instance, rather than installing it directly on frontend systems like NGINX.
Requirements¶
-
An AWS account
-
Understanding of AWS EC2, Security Groups
-
Any AWS region of your choice, there are no specific restrictions on the region for the Wallarm node deployment
Wallarm supports both single availability zone (AZ) and multi availability zone deployments. In multi-AZ setups, Wallarm Nodes can be launched in separate availability zones and placed behind a Load Balancer for high availability.
-
Access to the account with the Administrator role in Wallarm Console for the US Cloud or EU Cloud
-
Executing all commands on a Wallarm instance as a superuser (e.g.
root)
Installation¶
1. Launch a Wallarm Node instance¶
Launch an EC2 instance using the Wallarm NGINX Node AMI.
Recommended configuration:
-
Latest available [AMI version][latest-node-version]
-
Any preferred AWS region
-
EC2 instance type:
t3.medium(for testing) orm4.xlarge(for production), [see cost guidance for details][aws-costs] -
SSH key pair for accessing the instance
-
Appropriate VPC and subnet based on your infrastructure
-
Security Group inbound access to ports 22, 80, and 443
Using a security group preconfigured by Wallarm
When you deploy the instance and create a security group, AWS prompts you to use the one preconfigured by Wallarm. This group already has all the necessary ports open for inbound access.
![!Preconfigured security group][img-security-group]
-
Security Group outbound access to:
https://meganode.wallarm.comto download the Wallarm installerhttps://us1.api.wallarm.comfor working with US Wallarm Cloud or tohttps://api.wallarm.comfor working with EU Wallarm Cloud. If access can be configured only via the proxy server, then use the instructions-
IP addresses below for downloading updates to attack detection rules and API specifications, as well as retrieving precise IPs for your allowlisted, denylisted, or graylisted countries, regions, or data centers
2. Connect to the Wallarm Node instance via SSH¶
Use the selected SSH key to connect to your running EC2 instance:
You need to use the admin username to connect to the instance.
3. Generate a token to connect an instance to the Wallarm Cloud¶
The Wallarm node needs to connect to the Wallarm Cloud using a Wallarm token of the appropriate type. An API token allows you to create a node group in the Wallarm Console UI, helping you organize your node instances more effectively.
Generate a token as follows:
6. Örneği Wallarm Cloud'a Bağlayın¶
Bulut örneğinin düğümü, cloud-init.py betiği aracılığıyla Wallarm Cloud'a bağlanır. Bu betik, sağlanan token ile düğümü Wallarm Cloud'a kaydeder, global olarak izleme modu'na ayarlar ve NGINX'in location / bloğunda yalnızca aynalanan trafik kopyalarını analiz etmek üzere wallarm_force yönergelerini uygular. NGINX'in yeniden başlatılması kurulumu tamamlar.
Cloud imajından oluşturulan örnekte cloud-init.py betiğini aşağıdaki gibi çalıştırın:
-
WALLARM_LABELS='group=<GROUP>'ifadesi, bir düğüm grubu adı ayarlar (mevcutsa kullanılır, yoksa oluşturulur). Bu ayar yalnızca API token kullanıldığında geçerlidir. -
<TOKEN>, kopyalanan token değeridir.
7. Web veya Proxy Sunucunuzu Wallarm Düğümüne Aynalanan Trafiği Yansıtacak Şekilde Yapılandırın¶
-
Web veya proxy sunucunuzu (örneğin, NGINX, Envoy) gelen trafiği Wallarm düğümüne aynalamak üzere yapılandırın. Yapılandırma detayları için web veya proxy sunucusu dokümantasyonunuza başvurmanızı öneririz.
web-server-mirroring-examples bağlantısında, en popüler web ve proxy sunucuları (NGINX, Traefik, Envoy) için örnek yapılandırma bulabilirsiniz.
-
Aşağıdaki yapılandırmayı, düğümlü örnekteki
/etc/nginx/sites-enabled/defaultdosyasına ekleyin:location / { include /etc/nginx/presets.d/mirror.conf; # Aynalama sunucusunun adresi için 222.222.222.22 değerini değiştirin set_real_ip_from 222.222.222.22; real_ip_header X-Forwarded-For; }set_real_ip_fromvereal_ip_headeryönergeleri, Wallarm Console'un atak yapanların IP adreslerini görüntülemesi için gereklidir.
8. Wallarm Operasyonunu Test Edin¶
-
The request with test Path Traversal attack to an address of either the web or proxy server mirroring traffic or the machine with the Wallarm node:
-
Open Wallarm Console → Attacks section in the US Cloud or EU Cloud and make sure the attack is displayed in the list.
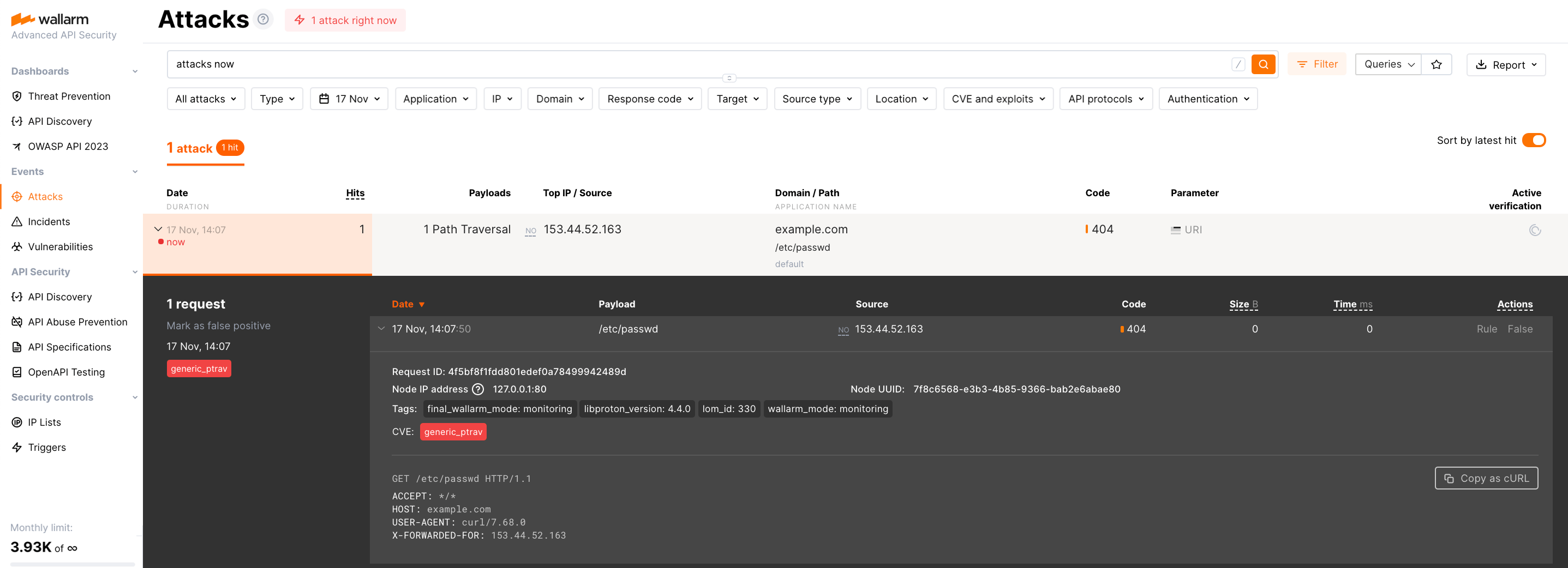
Since Wallarm OOB operates in the monitoring mode, the Wallarm node does not block the attack but registers it.
9. Dağıtılan Çözümü İnce Ayar Yapın¶
The deployment is now complete. The filtering node may require some additional configuration after deployment.
Wallarm settings are defined using the NGINX directives or the Wallarm Console UI. Directives should be set in the following files on the Wallarm instance:
-
/etc/nginx/sites-enabled/defaultdefines the configuration of NGINX -
/etc/nginx/conf.d/wallarm.confdefines the global configuration of Wallarm filtering node -
/etc/nginx/conf.d/wallarm-status.confdefines the filtering node monitoring service configuration -
/opt/wallarm/wstore/wstore.yamlwith the postanalytics service (wstore) settings
You can modify the listed files or create your own configuration files to define the operation of NGINX and Wallarm. It is recommended to create a separate configuration file with the server block for each group of the domains that should be processed in the same way (e.g. example.com.conf). To see detailed information about working with NGINX configuration files, proceed to the official NGINX documentation.
Creating a configuration file
When creating a custom configuration file, make sure that NGINX listens to the incoming connections on the free port.
Below there are a few of the typical settings that you can apply if needed:
To apply the settings, restart NGINX on the Wallarm instance:
Each configuration file change requires NGINX to be restarted to apply it.