Heroku üzerinde Wallarm'ı çalıştırma¶
Wallarm, Heroku bulut platformunda dağıtılan web uygulamalarını ve API'leri koruyabilir. Bu kılavuz, trafiği gerçek zamanlı analiz etmek için Wallarm düğümünü Heroku üzerinde çalıştırma sürecini adım adım açıklar.
Şu anda Wallarm tarafından Heroku için resmi bir Docker imajı bulunmamaktadır. Bu nedenle bu kılavuz, all-in-one installer kullanılarak kendi imajınızı nasıl oluşturup çalıştıracağınızı açıklar.
Gereksinimler¶
-
Ana sisteminizde yüklü Docker
-
Heroku Wallarm Docker imajını göndermek için Docker hesabı
-
Ana sisteminizde yüklü Heroku CLI
-
Heroku web dyno’larında çalışan uygulamalar veya API’ler
-
US Cloud veya EU Cloud ortamlarında Wallarm Console üzerinde yönetici erişimi
-
all-in-one Wallarm installer’ı indirmek için
https://meganode.wallarm.comerişimi -
US Wallarm Cloud ile çalışmak için
https://us1.api.wallarm.comveya EU Wallarm Cloud ile çalışmak içinhttps://api.wallarm.comerişimi -
Saldırı tespit kuralları ve API spesifikasyonları güncellemelerini indirmek ve allowlist'e, denylist'e veya graylist'e aldığınız ülkeler, bölgeler veya veri merkezleri için kesin IP’leri almak amacıyla aşağıdaki IP adreslerine erişim
Adım 1: Wallarm Docker yapılandırmasını hazırlayın¶
Wallarm’ın Docker imajını Heroku’da dağıtmak için, öncelikle imajı oluşturma sürecinde gerekli yapılandırma dosyalarını oluşturun. Şu adımları izleyin:
-
Yerel sisteminizde, Wallarm Docker yapılandırmaları için özel bir dizin oluşturun ve bu dizine geçin.
-
NGINX ve Wallarm yapılandırmalarını içeren bir
nginx.confdosyası hazırlayın. Docker imajı NGINX-uyumlu all-in-one installer üzerine inşa edileceğinden, NGINX’in uygun şekilde yapılandırıldığından emin olun.Aşağıda, Wallarm düğümünü monitoring modunda çalıştıran temel bir yapılandırma şablonu bulunmaktadır:
daemon off; worker_processes auto; load_module /usr/lib/nginx/modules/ngx_http_wallarm_module.so; pid /tmp/nginx.pid; include /etc/nginx/modules-enabled/*.conf; events { worker_connections 768; use epoll; accept_mutex on; } http { gzip on; gzip_comp_level 2; gzip_min_length 512; gzip_proxied any; # Heroku yönlendiricisi Via başlığını gönderir proxy_temp_path /tmp/proxy_temp; client_body_temp_path /tmp/client_temp; fastcgi_temp_path /tmp/fastcgi_temp; uwsgi_temp_path /tmp/uwsgi_temp; scgi_temp_path /tmp/scgi_temp; sendfile on; tcp_nopush on; tcp_nodelay on; keepalive_timeout 65; types_hash_max_size 2048; server_tokens off; # server_names_hash_bucket_size 64; # server_name_in_redirect off; include /etc/nginx/mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log; error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log; # Ana Heroku uygulaması server { listen $PORT default_server; server_name _; wallarm_mode monitoring; location / { proxy_pass http://unix:/tmp/nginx.socket; # Heroku uygulamaları her zaman bir yük dengeleyicinin arkasındadır, bu nedenle tüm IP'lere güveniyoruz set_real_ip_from 0.0.0.0/0; real_ip_header X-Forwarded-For; real_ip_recursive off; proxy_redirect off; proxy_set_header Host $http_host; proxy_set_header "Connection" ""; } error_page 403 /403.html; location = /403.html { root /usr/share/nginx/html; internal; } } # Wallarm durum yardımcı sayfası (yalnızca localhost) server { listen 127.0.0.8:$PORT; server_name localhost; allow 127.0.0.0/8; deny all; wallarm_mode off; disable_acl "on"; access_log off; location ~/wallarm-status$ { wallarm_status on; } } } -
Wallarm Docker imajı için yönergeler içeren aşağıdaki
entrypoint.shdosyasını oluşturun:#!/bin/bash set -e log() { local msg="$1" local level="$2" if [ -z "$level" ]; then level="INFO" fi echo "[$(date '+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')] [$level] $msg" } log "Script execution started." # Gerekli dizinlerin mevcut olduğundan emin olun log "Ensuring necessary directories exist for supervisord." mkdir -p /opt/wallarm/var/log/wallarm mkdir -p /opt/wallarm/run/supervisor if [ ! -z "$WALLARM_API_TOKEN" ]; then log "WALLARM_API_TOKEN is set, checking configuration." if [[ $DYNO == web.* ]]; then log "Heroku dyno type [$DYNO] is 'web', proceeding with Wallarm configuration." # Ortam değişkenlerini aktar log "Propagating environment variables from /opt/wallarm/env.list." set -a source /opt/wallarm/env.list if [ -s /etc/wallarm-override/env.list ]; then log "Propagating environment variables from /etc/wallarm-override/env.list." source /etc/wallarm-override/env.list fi set +a # Wallarm düğümünü Cloud'da kaydet log "Registering Wallarm node in the cloud." /opt/wallarm/register-node # NGINX yapılandırmasında PORT değerini ayarla log "Replacing \$PORT in Nginx configuration with value $PORT." sed -i "s/\$PORT/${PORT}/g" /etc/nginx/nginx.conf # PORT'un başarıyla değiştirildiğini doğrula log "Checking if the PORT in Nginx configuration was successfully replaced." if cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf | grep -q "listen ${PORT}"; then log "Successfully replaced PORT in Nginx configuration with value $PORT." else log "Failed to replace PORT in Nginx configuration!" "ERROR" exit 1 fi # $PORT'u $NGINX_PORT olarak dışa aktar (export-metrics script'i için gereklidir) log "Exporting PORT as NGINX_PORT for Wallarm metrics." export NGINX_PORT="$PORT" # Tüm Wallarm servislerini ve NGINX'i supervisord altında başlat log "Starting all Wallarm services and NGINX under supervisord." /opt/wallarm/usr/bin/python3.10 /opt/wallarm/usr/bin/supervisord -c /opt/wallarm/etc/supervisord.conf --loglevel=debug # supervisord'in başarıyla başladığını kontrol et log "Checking if supervisord process is running." if pgrep -f "supervisord" > /dev/null; then log "supervisord process started successfully." else log "Failed to start supervisord process!" "ERROR" exit 1 fi # supervisord tarafından yönetilen servislerin durumunu kontrol et log "Checking the status of all services managed by supervisord every 10s during 3 minutes." timeout=0 while (/opt/wallarm/usr/bin/supervisorctl -c /opt/wallarm/etc/supervisord.conf status | grep -qv "RUNNING"); do log "One or more services failed to start!" "ERROR" log "Waiting 10s and check it again" sleep 10s timeout=$(( timeout + 10 )) if [ $timeout -ge 180 ]; then log "One or more services failed to start!" "ERROR" /opt/wallarm/usr/bin/supervisorctl -c /opt/wallarm/etc/supervisord.conf status exit 1 fi done log "All services are running successfully." log "Wallarm configuration completed." else log "Heroku dyno type [$DYNO] is not 'web', skipping Wallarm configuration." fi else log "WALLARM_API_TOKEN is not set, executing CMD." fi # CMD komutunu çalıştır log "Executing command: $@" exec "$@" log "Script execution finished." -
entrypoint.shdosyasının izinlerini aşağıdaki komutla-rwxr-xr-xolarak ayarlayın: -
Wallarm tarafından engellenecek istekler için düzgün yapılandırılmış bir sayfa gösteren bir
403.htmldosyası tasarlayın. Aşağıdakini kopyalayabilirsiniz:<!doctype html> <html> <head> <meta charset=utf-8> <meta content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1.0,minimum-scale=1.0,maximum-scale=1.0,user-scalable=no" name=viewport> <title>Forbidden</title> <link rel="shortcut icon" type="image/x-icon" href="https://www.herokucdn.com/favicon.ico"> <style>html, body { font-family: sans-serif; -ms-text-size-adjust: 100%; -webkit-text-size-adjust: 100%; background-color: #F7F8FB; height: 100%; -webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased; } body { margin: 0; padding: 0; display: flex; flex-direction: column; align-items: center; justify-content: center; } .message { text-align: center; align-self: center; display: flex; flex-direction: column; align-items: center; padding: 0px 20px; max-width: 450px; } .message__title { font-size: 22px; font-weight: 100; margin-top: 15px; color: #47494E; margin-bottom: 8px; } p { -webkit-margin-after: 0px; -webkit-margin-before: 0px; font-size: 15px; color: #7F828B; line-height: 21px; margin-bottom: 4px; } .btn { text-decoration: none; padding: 8px 15px; border-radius: 4px; margin-top: 10px; font-size: 14px; color: #7F828B; border: 1px solid #7F828B; } .hk-logo, .app-icon { fill: #DBE1EC; } .info { fill: #9FABBC; } body.friendly { background: -webkit-linear-gradient(-45deg, #8363a1 0%, #74a8c3 100%); background: linear-gradient(135deg, #8363a1 0%, #74a8c3 100%); } body.friendly .message__title { color: #fff; } body.friendly p { color: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.6); } body.friendly .hk-logo, body.friendly .app-icon { fill: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.9); } body.friendly .info { fill: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.9); } body.friendly .btn { color: #fff; border: 1px solid rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.9); } .info_area { position: fixed; right: 12px; bottom: 12px; } .logo { position: fixed; left: 12px; bottom: 12px; } </style> <base target=_parent /> </head> <body> <div class=spacer></div> <div class=message> <svg width=49 height=51 xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"><path d="M3.9468 10.0288L20.5548.995c2.4433-1.3267 5.45-1.3267 7.8936 0l16.6078 9.0338C47.4966 11.3585 49 13.8102 49 16.4666V34.534c0 2.6537-1.5034 5.1082-3.9438 6.438l-16.6078 9.0307c-2.4435 1.3297-5.4503 1.3297-7.8937 0L3.9467 40.972C1.5035 39.642 0 37.1876 0 34.534V16.4667c0-2.6564 1.5034-5.108 3.9468-6.4378z" class=app-icon fill-rule=evenodd /></svg> <div class=message__title> Your request has been blocked </div> <p> If you think this is a mistake, please get in touch with the app's support team. </p> </div> <div class=logo> <svg width=85 height=24 xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"><g class=info fill-rule=evenodd><path d="M27.8866 16.836h2.373v-3.504h2.919v3.504h2.373V8.164h-2.373v3.2227h-2.919V8.164h-2.373v8.672zm10.4888 0h6.4666V14.949h-4.0935v-1.6054h2.7764v-1.8282h-2.7765v-1.4062h3.8918V8.164h-6.265v8.672zm8.8396 0h2.3256V13.824h.6526L51.89 16.836h2.5154l-1.863-3.3165c1.151-.3867 1.7325-1.1718 1.7325-2.5312 0-2.086-1.3765-2.8242-3.631-2.8242h-3.429v8.672zm2.3256-4.793v-1.9805h1.0204c.973 0 1.4.2578 1.4.9844 0 .7264-.427.996-1.4.996h-1.0204zM60.8363 17c2.112 0 4.307-1.3242 4.307-4.5 0-3.1758-2.195-4.5-4.307-4.5-2.124 0-4.319 1.3242-4.319 4.5 0 3.1758 2.195 4.5 4.319 4.5zm0-1.875c-1.2458 0-1.946-1.0313-1.946-2.625 0-1.5938.7002-2.5664 1.946-2.5664 1.234 0 1.934.9726 1.934 2.5664 0 1.5938-.7 2.625-1.934 2.625zm6.7157 1.711h2.373v-2.6954l.6764-.7734 2.0764 3.4687h2.6816l-3.2155-5.25 2.9543-3.422h-2.7527l-2.4205 3.1407V8.164h-2.373v8.672zm13.4552.1288c2.563 0 3.6782-1.3125 3.6782-3.6093V8.164H82.36v5.1798c0 1.1953-.3798 1.7343-1.329 1.7343-.9493 0-1.3408-.539-1.3408-1.7342V8.164h-2.373v5.1915c0 2.2968 1.127 3.6093 3.69 3.6093zM2.4444 0C.9214 0 0 .8883 0 2.3226v19.3548C0 23.1068.9215 24 2.4444 24h17.1112C21.0736 24 22 23.1117 22 21.6774V2.3226C21.995.8883 21.0735 0 19.5556 0H2.4444zm16.8973 1.9c.4025.0045.7583.3483.7583.7214v18.7572c0 .3776-.3558.7214-.7583.7214H2.6583c-.4025 0-.7583-.3438-.7583-.7214V2.6214c0-.3777.3558-.7214.7583-.7214h16.6834z"/><path d="M16.43 20h-2.2527v-6.8048c0-.619-.1917-.838-.3786-.9666-1.131-.7667-4.3855-.0334-6.3458.7333l-1.553.6475L5.9048 4h2.2814v6.3333c.4314-.1333.973-.2714 1.524-.3857 2.4206-.5143 4.1987-.3762 5.3586.4048.6375.4286 1.3612 1.2714 1.3612 2.8428V20zM11.57 8h2.6675c1.4042-1.75 1.9732-3.35 2.1925-4h-2.6623c-.3967.95-1.1223 2.55-2.1977 4zM5.9 20v-5.6l2.43 2.8L5.9 20z"/></g></svg> </div> </body> </html> -
Wallarm’ın Docker imajını oluşturma sürecini tanımlamak için bir
Dockerfileoluşturun:FROM ubuntu:22.04 ARG VERSION="6.5.1" ENV PORT=3000 ENV WALLARM_LABELS="group=heroku" ENV WALLARM_API_TOKEN= ENV WALLARM_API_HOST="us1.api.wallarm.com" RUN apt-get -qqy update && apt-get -qqy install nginx curl && apt-get clean # Wallarm all-in-one installer’ı indirip aç RUN curl -o /install.sh "https://meganode.wallarm.com/$(echo "$VERSION" | cut -d '.' -f 1-2)/wallarm-$VERSION.x86_64-glibc.sh" \ && chmod +x /install.sh \ && /install.sh --noexec --target /opt/wallarm \ && rm -f /install.sh \ && cd /opt/wallarm \ && chmod +x pick-module.sh \ && SELECTED_MODULE="$(./pick-module.sh)" \ && echo "Selected module => $SELECTED_MODULE" \ # wlrm-modülünü NGINX'in modül dizinine kopyala && cp "$SELECTED_MODULE" /usr/lib/nginx/modules/ngx_http_wallarm_module.so \ && mkdir -p /usr/local/lib \ && mv /opt/wallarm/modules/libwallarm.so* -t "/usr/local/lib/" \ && rm -rf /opt/wallarm/modules # supervisord’u arka planda çalıştır. Ön plandaki süreç Heroku uygulamasının kendisidir RUN sed -i '/nodaemon=true/d' /opt/wallarm/etc/supervisord.conf # NGINX’i supervisord’a ekle RUN printf "\n\n[program:nginx]\ncommand=/usr/sbin/nginx\nautorestart=true\nstartretries=4294967295\n" | tee -a /opt/wallarm/etc/supervisord.conf # Heroku her şeyi ayrıcalıksız bir kullanıcı (dyno:dyno) altında çalıştırır, bu yüzden Wallarm dizinlerine erişim vermemiz gerekir RUN find /opt/wallarm -type d -exec chmod 777 {} \; # NGINX yapılandırmasını kopyala COPY nginx.conf /etc/nginx/nginx.conf # Heroku tarzı 403 hata sayfası COPY 403.html /usr/share/nginx/html/403.html # entrypoint.sh ekle COPY entrypoint.sh /entrypoint.sh # entrypoint’ın yapılandırmayı dyno:dyno altında değiştirmesine izin ver ve NGINX loglarını konsola yönlendir RUN chmod +x /entrypoint.sh \ && chmod 666 /etc/nginx/nginx.conf \ && chmod 777 /etc/nginx/ \ && ln -sf /dev/stdout /var/log/nginx/access.log \ && ln -sf /dev/stderr /var/log/nginx/error.log ENTRYPOINT ["/entrypoint.sh"]
Adım 2: Heroku için Wallarm Docker imajını oluşturun¶
Önceden oluşturduğunuz dizin içinde aşağıdaki komutları çalıştırın:
docker build -t wallarm-heroku:6.5.1 .
docker login
docker tag wallarm-heroku:6.5.1 <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/wallarm-heroku:6.5.1
docker push <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/wallarm-heroku:6.5.1
Adım 3: Oluşturduğunuz Docker imajını Heroku’da çalıştırın¶
İmajı Heroku’da dağıtmak için:
-
Aşağıdaki işlemleri gerçekleştirmek üzere uygulamanızın kök dizinine gidin.
-
Uygulamanızın çalışma zamanına özel gerekli bağımlılıkların kurulumunu içeren bir
Dockerfileoluşturun. Bir Node.js uygulaması için aşağıdaki şablonu kullanın:FROM <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/wallarm-heroku:6.5.1 ENV NODE_MAJOR=20 # NodeSource üzerinden NodeJS v20 kur RUN apt-get update \ && apt-get install -qqy ca-certificates curl gnupg \ && mkdir -p /etc/apt/keyrings \ && curl -fsSL https://deb.nodesource.com/gpgkey/nodesource-repo.gpg.key | gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/nodesource.gpg \ && echo "deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/nodesource.gpg] https://deb.nodesource.com/node_$NODE_MAJOR.x nodistro main" | tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nodesource.list \ && apt-get update \ && apt-get install nodejs -qqy \ && apt-get clean ADD . /opt/webapp WORKDIR /opt/webapp # Bağımlılıkları yükle ve uygulamayı derle RUN npm install --omit=dev ENV npm_config_prefix /opt/webapp # Özel alanlarda (private spaces) heroku.yml içindeki `run` bölümü yok sayılır # Bkz: https://devcenter.heroku.com/articles/build-docker-images-heroku-yml#known-issues-and-limitations CMD ["npm", "run", "start"] -
Aşağıdaki içerikle bir
heroku.ymlyapılandırma dosyası oluşturun: -
Uygulamanızı, NGINX
$PORTdeğerini kullandığı için$PORTyerine/tmp/nginx.socketüzerinde dinleyecek şekilde uyarlayın. Örneğin yapılandırma aşağıdaki gibi olabilir:// app.js const app = require('express')() let port = process.env.PORT || 3000 // Wallarm yapılandırılmamışsa $PORT üzerinde dinleyin if(process.env.WALLARM_API_TOKEN) port = '/tmp/nginx.socket' // Wallarm yapılandırılmışsa app.listen(port, (err) => { if (err) throw err console.log(`> App is listening on ${port}`) }) app.get('/', (req, res) => { res.send('This app is protected by Wallarm') }) -
Wallarm düğümü örneğini Wallarm Cloud’a bağlamak için uygun türde bir filtreleme düğümü belirteci (token) oluşturun:
-
Düğümün Cloud’a bağlanma parametrelerini ilgili değişkenlerde belirleyin:
-
Wallarm düğümünün dağıtımını tetikleyecek bir yeniden başlatma için uygulamanızı gönderin:
Adım 4: Dağıtımı test edin¶
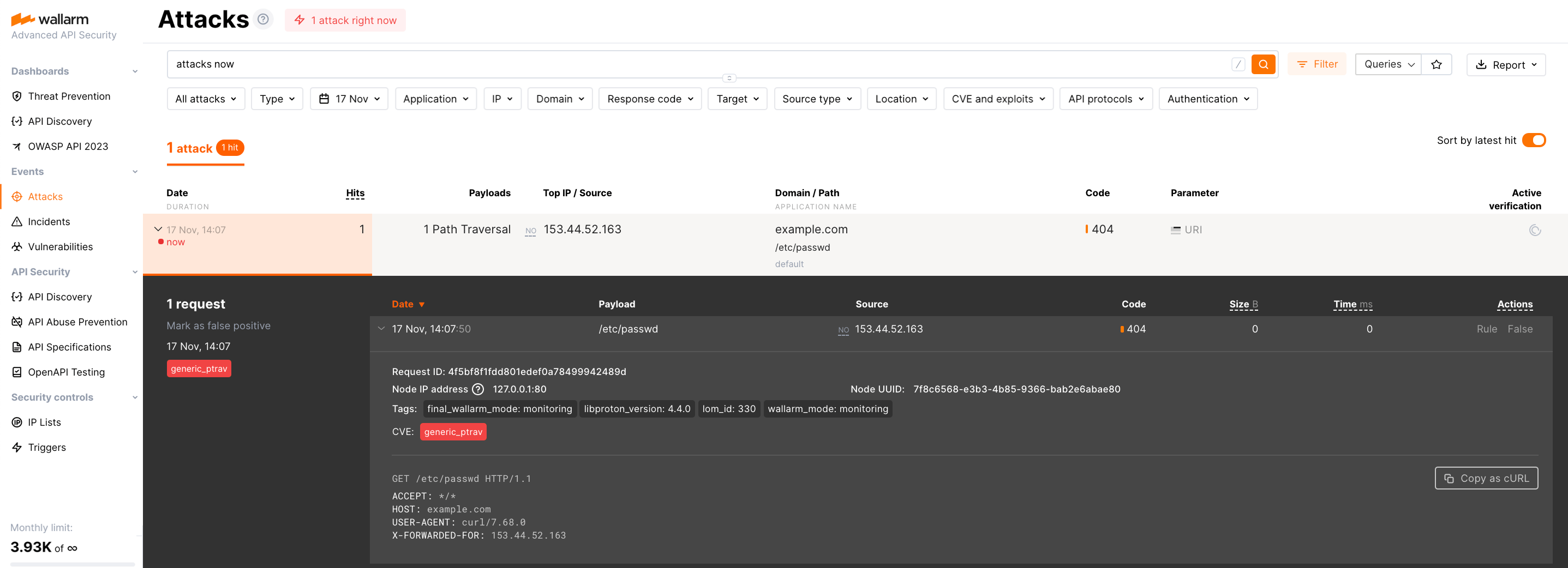
Dağıtımın çalıştığını doğrulamak için Path Traversal istismarını kullanarak bir test saldırısı başlatın:
Düğüm varsayılan olarak monitoring filtration mode içinde çalıştığından, Wallarm düğümü saldırıyı engellemeyecek ancak kaydedecektir. Saldırının kaydedildiğini doğrulamak için Wallarm Console → Attacks bölümüne gidin:
Hata ayıklama¶
Wallarm temel Docker imajıyla ilgili sorun yaşarsanız, olası hata mesajları için Heroku loglarını inceleyin:
Dağıtım sırasında yardıma ihtiyaç duyarsanız, Wallarm destek ekibi ile iletişime geçin.