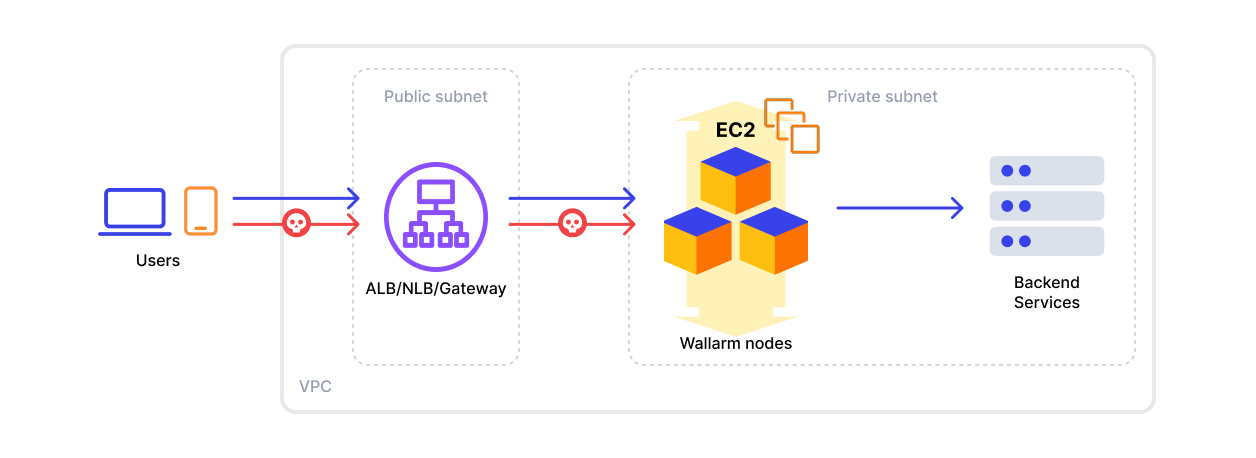
Amazon Machine ImageからのWallarmのデプロイ¶
本記事では、公式のAmazon Machine Image(AMI)を使用し、AWSでWallarmをインラインでデプロイする手順を説明します。
このイメージはDebianおよびDebianが提供するNGINXのバージョンをベースにしています。現在、最新のイメージはDebian 12を使用しており、NGINX stable 1.22.1を含みます。
AWS上のAMIからWallarmノードをデプロイする作業は通常約10分で完了します。
セキュリティに関する注意
このソリューションはAWSのセキュリティベストプラクティスに従うよう設計されています。デプロイにはAWSのルートアカウントの使用は避けることをおすすめします。代わりに、必要最小限の権限のみを付与したIAMユーザーまたはロールを使用してください。
デプロイプロセスは最小権限の原則を前提としており、Wallarmコンポーネントのプロビジョニングと運用に必要な最小限のアクセス権のみを付与します。
このデプロイに伴うAWSインフラストラクチャコストの見積もり方法については、AWSでWallarmをデプロイする際のコストガイダンスページをご覧ください。
ユースケース¶
Among all supported Wallarm deployment options, AMI is recommended for Wallarm deployment in these use cases:
-
Your existing infrastructure resides on AWS.
-
You aim to deploy a security solution as a separate cloud instance, rather than installing it directly on frontend systems like NGINX.
Requirements¶
-
An AWS account
-
Understanding of AWS EC2, Security Groups
-
Any AWS region of your choice, there are no specific restrictions on the region for the Wallarm node deployment
Wallarm supports both single availability zone (AZ) and multi availability zone deployments. In multi-AZ setups, Wallarm Nodes can be launched in separate availability zones and placed behind a Load Balancer for high availability.
-
Access to the account with the Administrator role in Wallarm Console for the US Cloud or EU Cloud
-
Executing all commands on a Wallarm instance as a superuser (e.g.
root) -
No system user named
wallarmexists
Installation¶
1. Launch a Wallarm Node instance¶
Launch an EC2 instance using the Wallarm NGINX Node AMI.
Recommended configuration:
-
Latest available AMI version
-
Any preferred AWS region
-
EC2 instance type:
t3.medium(for testing) orm4.xlarge(for production), see cost guidance for details -
SSH key pair for accessing the instance
-
Appropriate VPC and subnet based on your infrastructure
-
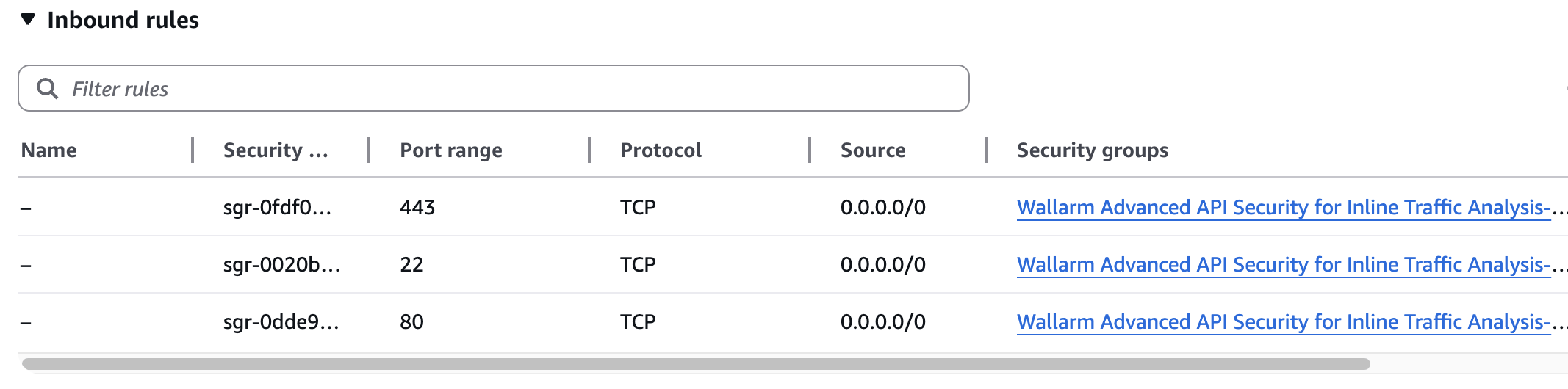
Security Group inbound access to ports 22, 80, and 443
-
Security Group outbound access to:
https://meganode.wallarm.comto download the Wallarm installerhttps://us1.api.wallarm.comfor working with US Wallarm Cloud or tohttps://api.wallarm.comfor working with EU Wallarm Cloud. If access can be configured only via the proxy server, then use the instructions-
IP addresses below for downloading updates to attack detection rules and API specifications, as well as retrieving precise IPs for your allowlisted, denylisted, or graylisted countries, regions, or data centers
2. Connect to the Wallarm Node instance via SSH¶
Use the selected SSH key to connect to your running EC2 instance:
You need to use the admin username to connect to the instance.
3. Generate a token to connect an instance to the Wallarm Cloud¶
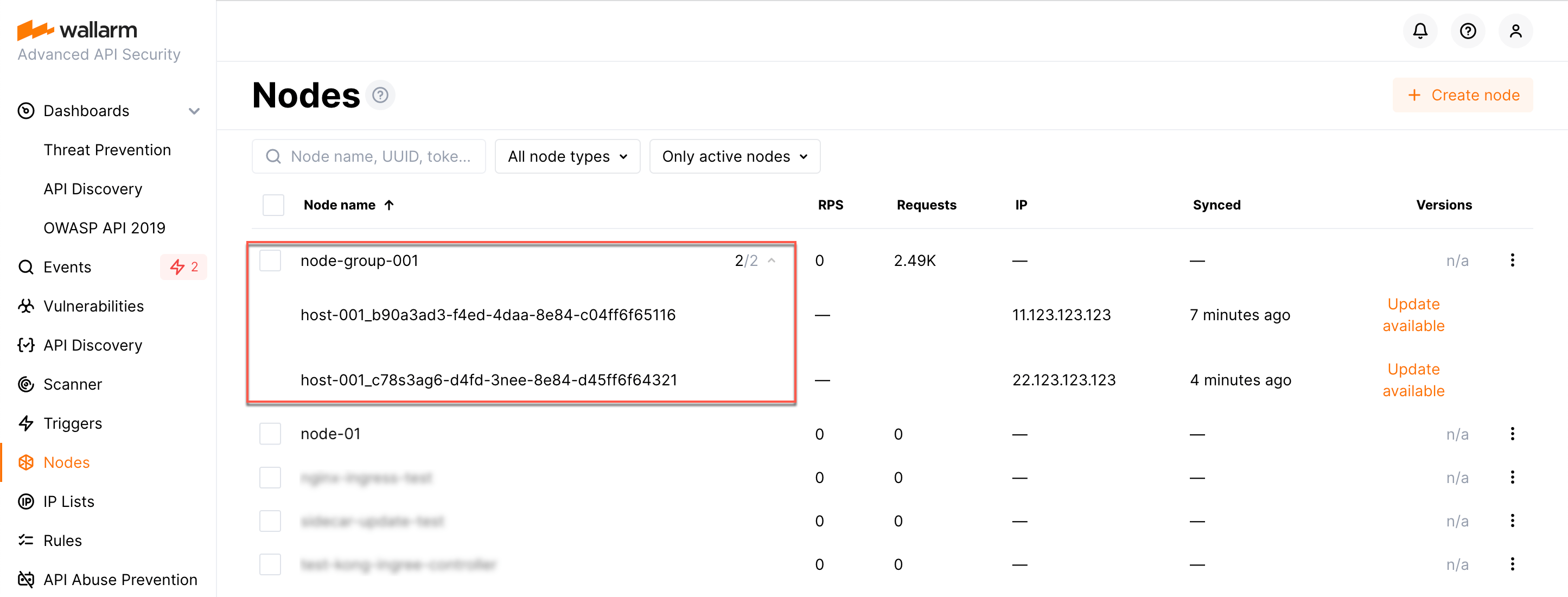
The Wallarm node needs to connect to the Wallarm Cloud using a Wallarm token of the appropriate type. An API token allows you to create a node group in the Wallarm Console UI, helping you organize your node instances more effectively.
Generate a token as follows:
6. インスタンスをWallarm Cloudに接続する¶
クラウドインスタンスのノードはcloud-init.pyスクリプトを介してWallarm Cloudに接続します。このスクリプトは、提供されたトークンを使用してノードをWallarm Cloudに登録し、グローバルに監視モードに設定し、--proxy-passフラグに基づいて正当なトラフィックを転送するようノードを構成します。NGINXを再起動すると設定が完了します。
クラウドイメージから作成したインスタンス上で次のようにcloud-init.pyスクリプトを実行します。
-
WALLARM_LABELS='group=<GROUP>'はノードグループ名を設定します(既存のグループ、または存在しない場合は作成されます)。APIトークンを使用する場合にのみ適用されます。 -
<TOKEN>はコピーしたトークンの値です。 -
<PROXY_ADDRESS>はWallarmノードが正当なトラフィックをプロキシ転送する宛先アドレスです。アーキテクチャに応じて、アプリケーションインスタンスのIP、ロードバランサー、DNS名などを指定できます。
7. Wallarmインスタンスにトラフィックを送信するよう構成する¶
Update targets of your load balancer to send traffic to the Wallarm instance. For details, please refer to the documentation on your load balancer.
8. Wallarmの動作をテストする¶
-
The request with test Path Traversal attack to an address of either the load balancer or the machine with the Wallarm node:
-
Open Wallarm Console → Attacks section in the US Cloud or EU Cloud and make sure the attack is displayed in the list.
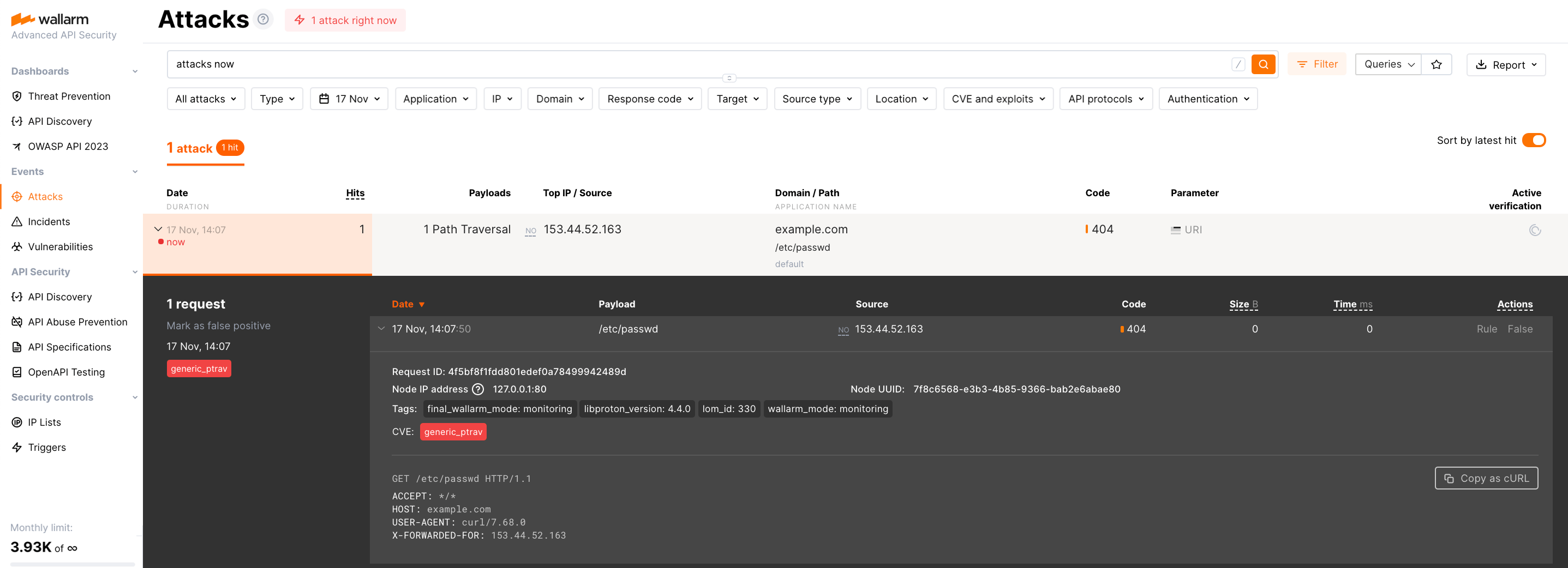
Since Wallarm operates in the monitoring mode, the Wallarm node does not block the attack but registers it.
-
Optionally, test other aspects of the node functioning.
9. デプロイ済みソリューションを微調整する¶
The deployment is now complete. The filtering node may require some additional configuration after deployment.
Wallarm settings are defined using the NGINX directives or the Wallarm Console UI. Directives should be set in the following files on the Wallarm instance:
-
/etc/nginx/sites-enabled/defaultdefines the configuration of NGINX -
/etc/nginx/conf.d/wallarm.confdefines the global configuration of Wallarm filtering node -
/etc/nginx/conf.d/wallarm-status.confdefines the filtering node monitoring service configuration -
/opt/wallarm/wstore/wstore.yamlwith the postanalytics service (wstore) settings
You can modify the listed files or create your own configuration files to define the operation of NGINX and Wallarm. It is recommended to create a separate configuration file with the server block for each group of the domains that should be processed in the same way (e.g. example.com.conf). To see detailed information about working with NGINX configuration files, proceed to the official NGINX documentation.
Creating a configuration file
When creating a custom configuration file, make sure that NGINX listens to the incoming connections on the free port.
Below there are a few of the typical settings that you can apply if needed:
To apply the settings, restart NGINX on the Wallarm instance:
Each configuration file change requires NGINX to be restarted to apply it.