Cache Rules in Security Edge Inline  ¶
¶
Cache rules are settings that define how the Security Edge Inline node stores and reuses responses from specific hosts and locations.
When cache rules are configured, the system stores and reuses responses to frequent requests instead of reprocessing them. This reduces load on your backend servers, lowers response times, and improves user experience — especially for endpoints that return the same data repeatedly (e.g., configuration files or static content).
Cache rules give you fine-grained control over caching by defining:
-
Which hosts and locations to cache
-
How long responses stay in the cache (TTL)
-
Memory limits and size estimates for better resource management
Requirements¶
Cache rules are supported starting from Edge Node version 6.6.1.
Cache processing details¶
-
Automatic cleanup of unused data: cached responses that have not been used for 30 minutes are automatically removed from memory.
-
Maximum cache size per location: by default, each location has a maximum cache size of 1 GiB. When this limit is reached, older cached responses are automatically removed to make room for new ones.
-
Serving stale responses during updates: when a cached response is being refreshed (e.g., after its TTL has expired), the system temporarily serves the previous (stale) cached version of the response.
This ensures that users continue to receive responses without delays while the cache is updated in the background. Once the new response is fetched, it replaces the old one in the cache automatically.
-
Cache revalidation: the system does not immediately delete a cached response after its TTL expires. Instead, it checks with the backend to see if the data has changed. This process is called revalidation. If the backend confirms that the data is still the same, the cached response continues to be used. If the data has changed, the cache is refreshed.
This check happens automatically via conditional GET requests that use the
If-Modified-SinceandIf-None-MatchHTTP headers.
Creating a cache rule¶
You can add cache rules during or after Edge Node deployment.
-
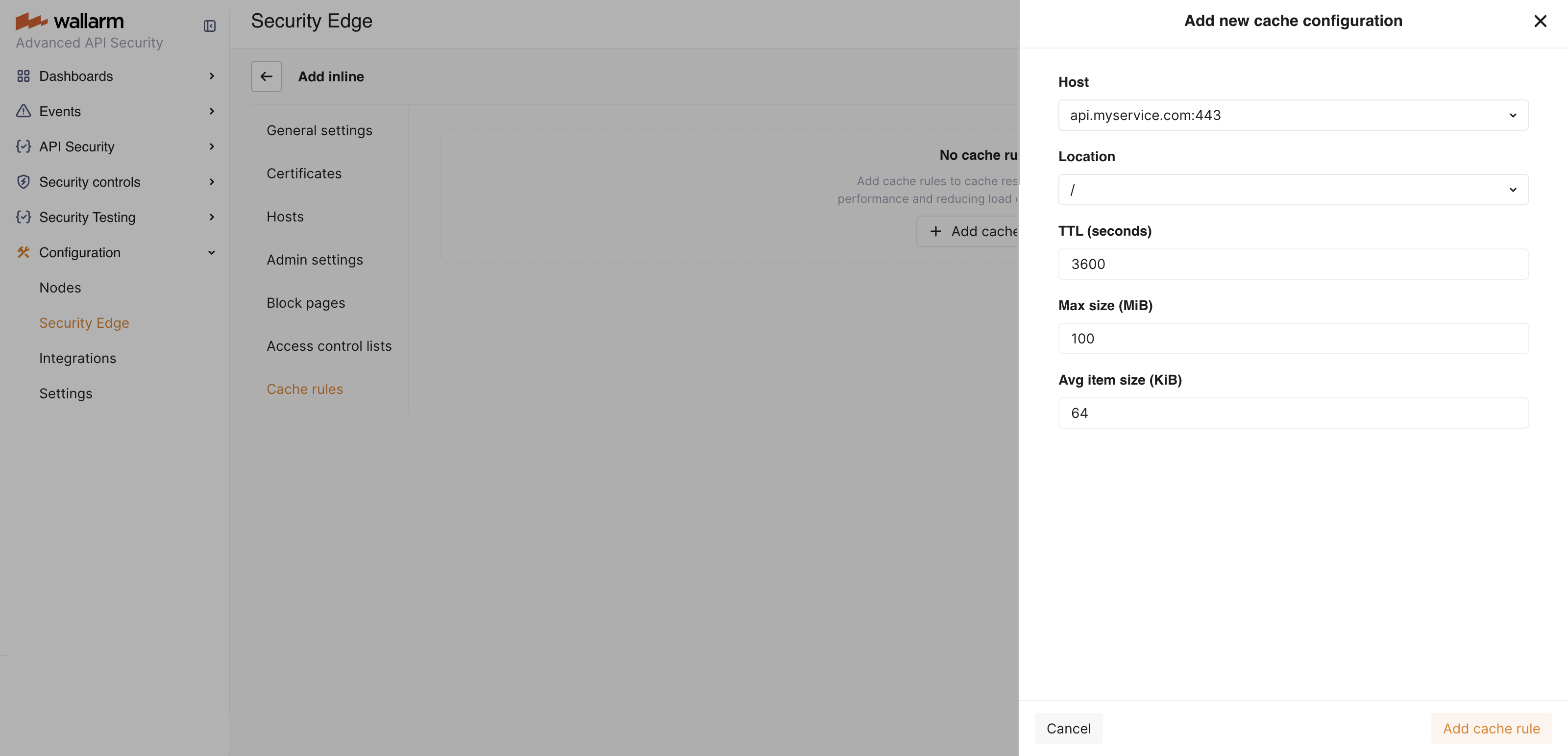
Go to Wallarm Console → Security Edge → Inline → Configure → Cache rules and click Add cache rule.
-
In the dropdown lists, select the host and location the rule will apply to.
-
Under TTL (seconds), specify how long to store each cached response (e.g.,
3600).Use shorter TTLs for locations with frequently changing data and longer TTLs for static or rarely updated content.
-
Click Add cache rule.
The added rule appears in the list of cache rules and is automatically activated.
Clearing a cache rule¶
Clearing a cache rule removes all cached responses for this rule without deleting or deactivating it.
It is useful in the following situations:
-
Backend data has changed, and users need to immediately receive fresh responses instead of outdated cached ones.
-
Host or location behavior has changed (e.g., a new API version or an updated response format).
-
You need to temporarily free up cache memory without changing rule settings.
After clearing, new responses are cached again automatically as matching requests arrive.
-
Go to Wallarm Console → Security Edge → Inline → Configure → Cache rules.
-
Click the
 icon next to the rule you want to clear, and then click Clear.
icon next to the rule you want to clear, and then click Clear.
Deactivating a cache rule¶
If you no longer need a cache rule, you can deactivate it temporarily and activate it again later.
-
Go to Wallarm Console → Security Edge → Inline → Configure → Cache rules.
-
Under Active, toggle off the rule you want to deactivate.
Deleting a cache rule¶
If you no longer need a cache rule permanently, you can delete it. To use the same configuration later, you will need to recreate the rule.