Customizing Wallarm Sidecar¶
This article instructs you on safe and effective customization of the Wallarm Kubernetes Sidecar solution providing examples for some common customization use cases.
Configuration area¶
The Wallarm Sidecar solution is based on the standard Kubernetes components, thus the solution configuration is largely similar to the Kubernetes stack configuration. You can configure the Wallarm Sidecar solution globally via values.yaml and on a per-application pod basis via annotations.
Global settings¶
Global configuration options apply to all sidecar resources created by the Wallarm controller and are set in the default Helm chart values. You can override them during helm install or helm upgrade by providing custom values.yaml.
The number of available global configuration options is unlimited. Care should be taken when customizing the solution since it allows complete change of the resulting Pod and improper solution function as a result. Please rely on the Helm and Kubernetes documentation when changing global settings.
There is the list of Wallarm-specific chart values
Per-pod settings¶
Per-pod settings allow customizing the solution behavior for certain applications.
Per-application pod settings are set via application Pod's annotations. Annotations take precedence over global settings. If the same option is specified globally and via the annotation, the value from the annotation will be applied.
The supported annotation set is limited but the nginx-*-include and nginx-*-snippet annotations allow any custom NGINX configuration to be used by the solution.
There is the list of supported per-pod's annotations
Configuration use cases¶
As mentioned above, you can customize the solution in many ways to fit your infrastructure and requirements to the security solution. To make the most common customization options easier to implement, we have described them considering related best practices.
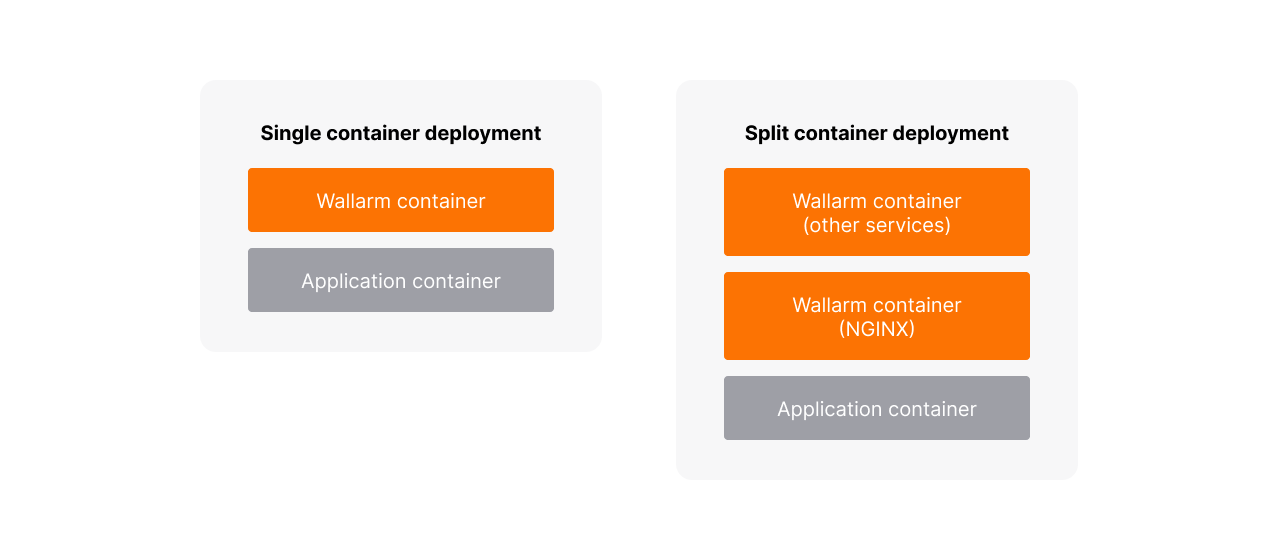
Single and split deployment of containers¶
Wallarm provides two options for deployment of Wallarm containers to a Pod:
-
Single deployment (by default)
-
Split deployment
You can set the container deployment options both on the global and per-pod basis:
-
Globally by setting the Helm chart value
config.injectionStrategy.schematosingle(default) orsplit. -
On a per-pod basis by setting the appropriate application Pod's annotation
sidecar.wallarm.io/sidecar-injection-schemato"single"or"split".
Postanalytics module
Please note that the postanalytics module container runs separately, the described deployment options are related only to other containers.
Single deployment (by default)¶
With the single deployment of Wallarm containers, only one container will run in a Pod, apart from the optional init container with iptables.
As a result, there are two running containers:
-
sidecar-init-iptablesis the init container running iptables. By default, this container starts but you can disable it. -
sidecar-proxyruns NGINX proxy with the Wallarm modules and some helper services. All these processes are run and managed by supervisord.
Split deployment¶
With the split deployment of Wallarm containers, two additional containers will run in a Pod, apart from two init containers.
This option moves all helper services out from the sidecar-proxy container and remains only NGINX services to be started by the container.
Split container deployment provides more granular control over resources consumed by NGINX and helper services. It is the recommended option for highly loaded applications where dividing the CPU/Memory/Storage namespaces between the Wallarm and helper containers is necessary.
As a result, there are four running containers:
-
sidecar-init-iptablesis the init container running iptables. By default, this container starts but you can disable it. -
sidecar-init-helperis the init container with helper services tasked with connecting the Wallarm node to the Wallarm Cloud. -
sidecar-proxyis the container with NGINX services. -
sidecar-helperis the container with some other helper services.
Application container port auto-discovery¶
The protected application port can be configured in many ways. To handle and forward incoming traffic properly, the Wallarm sidecar must be aware of the TCP port the application container accepts incoming requests.
By default, the sidecar controller automatically discovers the port in the following priority order:
-
If the port is defined via the
sidecar.wallarm.io/application-portpod's annotation, the Wallarm controller uses this value. -
If there is the port defined under the
name: httpapplication container setting, the Wallarm controller uses this value. -
If there is no port defined under the
name: httpsetting, the Wallarm controller uses the port value found first in the application container settings. -
If there are no ports defined in the application container settings, the Wallarm controller uses the value of
config.nginx.applicationPortfrom the Wallarm Helm chart.
If application container port auto-discovery does not work as expected, explicitly specify the port using the 1st or the 4th option.
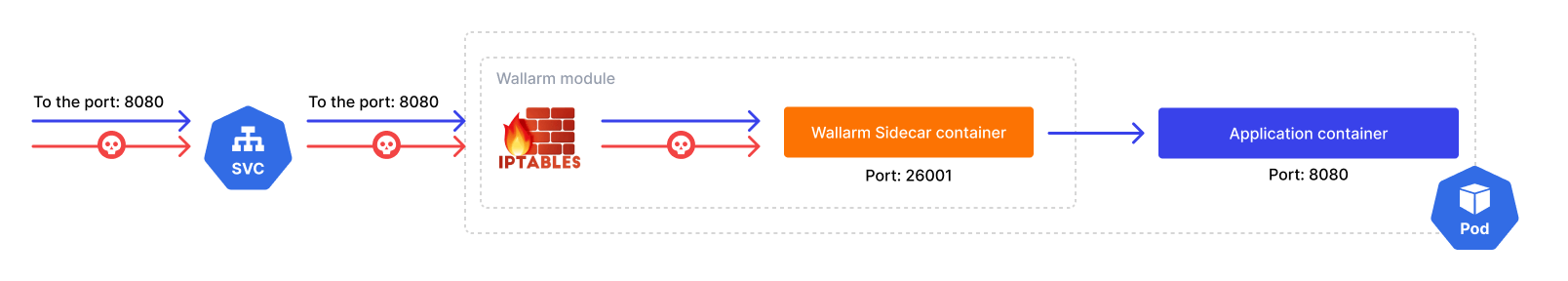
Capturing incoming traffic (port forwarding)¶
By default, the Wallarm sidecar controller routes traffic as follows:
-
Captures incoming traffic coming to the attached Pod's IP and application container port.
-
Redirects this traffic to the sidecar container using the built-in iptables features.
-
Sidecar mitigates malicious requests and forwards legitimate traffic to the application container.
Incoming traffic capture is implemented using the init container running iptables which is the best practice for automatic port forwarding. This container is run as privileged, with the NET_ADMIN capability.
However, this approach is incompatible with the service mesh like Istio since Istio already has iptables-based traffic capture implemented. In this case, you can disable iptables and port forwarding will work as follows:
Unprotected application container
If iptables is disabled, an exposed application container will not be protected by Wallarm. As a result, malicious "east-west" traffic may reach the application container if its IP address and port are known to an attacker.
East/west traffic is traffic flowing around the Kubernetes cluster (e.g. service-to-service).
You can change the default behavior as follows:
-
Disable iptables in one of the ways:
- Globally by setting the Helm chart value
config.injectionStrategy.iptablesEnableto"false" - On a per-pod basis by setting the Pod's annotation
sidecar.wallarm.io/sidecar-injection-iptables-enableto"false"
- Globally by setting the Helm chart value
-
Update the
spec.ports.targetPortsetting in your Service manifest to point to theproxyport.If iptables-based traffic capture is disabled, the Wallarm sidecar container will publish a port with the name
proxy. For incoming traffic to come from Kubernetes service to theproxyport, thespec.ports.targetPortsetting in your Service manifest should point to this port:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: myapp
namespace: default
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: myapp
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: myapp
wallarm-sidecar: enabled
annotations:
sidecar.wallarm.io/sidecar-injection-iptables-enable: "false"
spec:
containers:
- name: application
image: kennethreitz/httpbin
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 80
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: myapp-svc
namespace: default
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: proxy
protocol: TCP
name: http
selector:
app: myapp
SSL/TLS termination¶
By default, the Sidecar solution only accepts HTTP traffic and forwards plain HTTP traffic to the application pods. It is assumed that SSL/TLS termination is performed by an infrastructure component located before the sidecar solution (such as Ingress/Application Gateway), allowing the sidecar solution to process plain HTTP.
However, there may be cases where the existing infrastructure does not support SSL/TLS termination. In such cases, you can enable SSL/TLS termination at the Wallarm sidecar level. This feature is supported starting from the Helm chart 4.6.1.
The Sidecar solution supports either SSL or plain HTTP traffic processing
The Wallarm Sidecar solution supports either SSL/TLS or plain HTTP traffic processing. Enabling SSL/TLS termination means that the sidecar solution will not process plain HTTP traffic, while disabling SSL/TLS termination will result in only HTTPS traffic being processed.
To enable SSL/TLS termination:
-
Obtain the server certificate (public key) and private key associated with the server for which the Sidecar will terminate SSL/TLS.
-
In the namespace of the application pod, create a TLS secret containing the server certificate and private key.
-
In the
values.yamlfile, add theconfig.profiles sectionfor secret mounting. The example below shows multiple certificate mounting configurations.Customize the code based on the comments to meet your needs. Remove any unnecessary certificate mounting configurations if you only require one certificate.
config: wallarm: api: token: "<NODE_TOKEN>" host: "us1.api.wallarm.com" # or empty string if using the EU Cloud # Other Wallarm settings https://docs.wallarm.com/installation/kubernetes/sidecar-proxy/helm-chart-for-wallarm/ profiles: tls-profile: # Set any desired TLS profile name here sidecar: volumeMounts: - name: nginx-certs-example-com # Name of the volume containing example.com keys mountPath: /etc/nginx/certs/example.com # Path to mount example.com keys in the container readOnly: true - name: nginx-certs-example-io # Name of the volume containing example.io keys mountPath: /etc/nginx/certs/example.io # Path to mount example.io keys in the container readOnly: true volumes: - name: nginx-certs-example-com # Name of the volume containing example.com keys secret: secretName: example-com-certs # Name of the secret created for the example.com backend, containing public and private keys - name: nginx-certs-example-io # Name of the volume containing example.io keys secret: secretName: example-io-certs # Name of the secret created for the example.io backend, containing public and private keys nginx: # NGINX SSL module configuration specific to your TLS/SSL termination procedure. # Refer to https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_ssl_module.html. # This configuration is required for the Sidecar to perform traffic termination. servers: - listen: "ssl http2" include: - "server_name example.com www.example.com" - "ssl_protocols TLSv1.3" - "ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/certs/example.com/tls.crt" - "ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/certs/example.com/tls.key" - "ssl_ciphers ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384" - "ssl_conf_command Ciphersuites TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256:TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384:TLS_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256" - listen: "ssl" include: - "server_name example.io www.example.io" - "ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3" - "ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/certs/example.io/tls.crt" - "ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/certs/example.io/tls.key" -
Apply the changes from
values.yamlto the Sidecar solution using the following command: -
Apply the
sidecar.wallarm.io/profile: tls-profileannotation to the application pod. -
Once the configuration is applied, you can test the solution by following the steps described here, replacing HTTP with HTTPS protocol.
The sidecar solution will accept TLS/SSL traffic, terminate it, and forward plain HTTP traffic to the application pod.
Certificates for the admission webhook¶
Starting with release 4.10.7, you have the option to issue and use your own certificates for the admission webhook.
By default, the solution automatically generates certificates for the admission webhook using certgen.
To use your own certificates, the following options are available:
-
Using cert-manager: If you use
cert-managerin your cluster and prefer it for generating the admission webhook certificate, update yourvalues.yamlas follows.This will automatically disable
certgen. -
Manual certificate upload: You can manually upload certificates by adding the following configuration to
values.yaml. This will automatically disablecertgen.
If you are upgrading from version 4.10.6 or earlier, please follow the specific upgrade instructions. This update introduces a breaking change, requiring solution re-installation.
Enabling additional NGINX modules¶
Docker image of the Wallarm sidecar is distributed with the following additional NGINX modules disabled by default:
You can enable additional modules only on a per-pod basis by setting Pod's annotation sidecar.wallarm.io/nginx-extra-modules.
The format of annotation's value is an array. Example with additional modules enabled:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: myapp
namespace: default
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: myapp
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: myapp
wallarm-sidecar: enabled
annotations:
sidecar.wallarm.io/nginx-extra-modules: "['ngx_http_brotli_filter_module.so','ngx_http_brotli_static_module.so', 'ngx_http_opentracing_module.so']"
spec:
containers:
- name: application
image: kennethreitz/httpbin
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 80
Using custom NGINX configuration¶
If there are no dedicated pod annotations for some NGINX settings, you can specify them via per-pod snippets and includes.
Snippet¶
Snippets is a convenient way to add one-line changes to the NGINX configuration. For more complex changes, includes is a recommended option.
To specify custom settings via snippets, use the following per-pod's annotations:
| NGINX config section | Annotation |
|---|---|
| http | sidecar.wallarm.io/nginx-http-snippet |
| server | sidecar.wallarm.io/nginx-server-snippet |
| location | sidecar.wallarm.io/nginx-location-snippet |
Example of the annotation changing the disable_acl NGINX directive value:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: myapp
namespace: default
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: myapp
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: myapp
wallarm-sidecar: enabled
annotations:
sidecar.wallarm.io/wallarm-mode: block
sidecar.wallarm.io/nginx-location-snippet: "disable_acl on"
spec:
containers:
- name: application
image: kennethreitz/httpbin
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 80
To specify more than one directive, use the ; symbol, e.g.:
Include¶
To mount an additional NGINX configuration file to the Wallarm sidecar container, you can create ConfigMap or Secret resource from this file and use the created resource in the container.
Once the ConfigMap or Secret resource is created, you can mount it to the container via the Volume and VolumeMounts components by using the following per-pod's annotations:
| Item | Annotation | Value type |
|---|---|---|
| Volumes | sidecar.wallarm.io/proxy-extra-volumes | JSON |
| Volume mounts | sidecar.wallarm.io/proxy-extra-volume-mounts | JSON |
Once the resource is mounted to the container, specify the NGINX context to add the configuration by passing the path to the mounted file in the corresponding annotation:
| NGINX config section | Annotation | Value type |
|---|---|---|
| http | sidecar.wallarm.io/nginx-http-include | Array |
| server | sidecar.wallarm.io/nginx-server-include | Array |
| location | sidecar.wallarm.io/nginx-location-include | Array |
Below is the example with mounted configuration file included on the http level of NGINX config. This example assumes that the nginx-http-include-cm ConfigMap was created in advance and contains valid NGINX configuration directives.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: myapp
namespace: default
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: myapp
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: myapp
wallarm-sidecar: enabled
annotations:
sidecar.wallarm.io/proxy-extra-volumes: '[{"name": "nginx-http-extra-config", "configMap": {"name": "nginx-http-include-cm"}}]'
sidecar.wallarm.io/proxy-extra-volume-mounts: '[{"name": "nginx-http-extra-config", "mountPath": "/nginx_include/http.conf", "subPath": "http.conf"}]'
sidecar.wallarm.io/nginx-http-include: "['/nginx_include/http.conf']"
spec:
containers:
- name: application
image: kennethreitz/httpbin
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 80
Configuring Wallarm features¶
In addition to the listed general solution settings, we also recommend you to learn best practices for attack prevention with Wallarm.
This configuration is performed via annotations and the Wallarm Console UI.
Other configurations via annotations¶
In addition to the listed configuration use cases, you can fine-tune the Wallarm sidecar solution for application pods using many other annotations.