Running Docker NGINX‑based Image¶
The Wallarm NGINX-based filtering node can be deployed using a Docker image. This node supports both x86_64 and ARM64 architectures, which are automatically identified during installation. This article provides guidance on how to run the node from the Docker image for inline traffic filtration.
The Docker image is based on Alpine Linux and the NGINX version provided by Alpine. Currently, the latest image uses Alpine Linux version 3.22, which includes NGINX stable 1.28.0.
Use cases¶
Among all supported Wallarm deployment options, NGINX-based Docker image is recommended for Wallarm deployment in these use cases:
-
If your organization utilizes Docker-based infrastructure, Wallarm Docker image is the ideal choice. It integrates effortlessly into your existing setup, whether you are employing a microservice architecture running on AWS ECS, Alibaba ECS, or other similar services. This solution also applies to those using virtual machines seeking a more streamlined management through Docker containers.
-
If you require fine-grained control over each container, the Docker image excels. It affords a greater level of resource isolation than typically possible with traditional VM-based deployments.
For more information on running Wallarm's NGINX-based Docker image on popular public cloud container orchestration services, refer to our guides: AWS ECS, GCP GCE, Azure Container Instances, Alibaba ECS.
Requirements¶
-
Docker installed on your host system
-
Access to
https://hub.docker.com/r/wallarm/nodeto download the Docker image. Please ensure the access is not blocked by a firewall -
Access to the account with the Administrator role in Wallarm Console in the US Cloud or EU Cloud
-
Access to
https://us1.api.wallarm.comif working with US Wallarm Cloud or tohttps://api.wallarm.comif working with EU Wallarm Cloud. Please ensure the access is not blocked by a firewall -
Access to the IP addresses below for downloading updates to attack detection rules and API specifications, as well as retrieving precise IPs for your allowlisted, denylisted, or graylisted countries, regions, or data centers
Options for running the container¶
The filtering node configuration parameters should be passed to the deployed Docker container in one of the following ways:
-
In the environment variables. This option allows for the configuration of only basic filtering node parameters. Most directives cannot be configured through environment variables.
-
In the mounted configuration file. This option allows full filtering node configuration via any directives. With this configuration method, environment variables with the filtering node and Wallarm Cloud connection settings are also passed to the container.
Run the container passing the environment variables¶
To run the container:
-
Get Wallarm token of the appropriate type:
-
Run the container with the node:
You can pass the following basic filtering node settings to the container via the option -e:
| Environment variable | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
WALLARM_API_TOKEN | Wallarm node or API token. | Yes |
WALLARM_LABELS | Available starting from node 4.6. Works only if
...will place node instance into the | Yes (for API tokens) |
NGINX_BACKEND | Domain or IP address of the resource to protect with the Wallarm solution. | Yes |
WALLARM_API_HOST | Wallarm API server:
api.wallarm.com. | No |
WALLARM_MODE | Node mode:
monitoring.Detailed description of filtration modes → | No |
WALLARM_APPLICATION | Unique identifier of the protected application to be used in the Wallarm Cloud. The value can be a positive integer except for 0.Default value (if the variable is not passed to the container) is -1 which indicates the default application displayed in Wallarm Console → Settings → Application.More details on setting up applications → | No |
SLAB_ALLOC_ARENA (TARANTOOL_MEMORY_GB NGINX Node 5.x and earlier) | Amount of memory allocated to wstore. The value can be a float (a dot . is a decimal separator). By default: 1.0 (1 gygabyte). | No |
NGINX_PORT | Sets a port that NGINX will use inside the Docker container. Starting from the Docker image 4.0.2-1, the wallarm-status service automatically runs on the same port as NGINX.Default value (if the variable is not passed to the container) is 80.Syntax is NGINX_PORT='443'. | No |
WALLARM_STATUS_ALLOW | Custom CIDRs that are allowed to access the /wallarm-status endpoint from outside the Docker container. Example value: 10.0.0.0/8. If you need to pass several values, use a comma , as a separator. To access the service externally, use the Docker container's IP, specifying the /wallarm-status endpoint path. | No |
DISABLE_IPV6 | The variable with any value except for an empty one deletes the listen [::]:80 default_server ipv6only=on; line from the NGINX configuration file which will stop NGINX from IPv6 connection processing.If the variable is not specified explicitly or has an empty value "", NGINX processes both IPv6 and IPv4 connections. | No |
WALLARM_APIFW_ENABLE | This setting toggles API Specification Enforcement on or off, available from release 4.10 onwards. Please note that activating this feature does not substitute for the required subscription and configuration through the Wallarm Console UI. Its default value is true, enabling the functionality. | No |
WALLARM_APID_ONLY (5.3.7 and higher) | In this mode, attacks detected in your traffic are blocked locally by the node (if enabled) but not exported to Wallarm Cloud. Meanwhile, API Discovery and some other features remain fully functional, detecting your API inventory and uploading it to the Cloud for visualization. This mode is for those who want to review their API inventory and identify sensitive data first, and plan controlled attack data export accordingly. However, disabling attack export is rare, as Wallarm securely processes attack data and provides sensitive attack data masking if needed. More details By default: false. | No |
The command does the following:
-
Creates the file
default.confwith minimal NGINX configuration and passes filtering node configuration in the/etc/nginx/http.dcontainer directory. -
Creates files with filtering node credentials to access the Wallarm Cloud in the
/opt/wallarm/etc/wallarmcontainer directory:node.yamlwith filtering node UUID and secret keyprivate.keywith Wallarm private key
-
Protects the resource
http://NGINX_BACKEND:80.
Run the container mounting the configuration file¶
You can mount the prepared configuration file to the Docker container via the -v option. The file must contain the following settings:
To run the container:
-
Get Wallarm token of the appropriate type:
-
Run the container with the node:
-
The
-eoption passes the following required environment variables to the container:Environment variable Description Required WALLARM_API_TOKENWallarm node or API token. Yes WALLARM_API_HOSTWallarm API server: us1.api.wallarm.comfor the US Cloudapi.wallarm.comfor the EU Cloud
api.wallarm.com.No WALLARM_LABELSAvailable starting from node 4.6. Works only if
WALLARM_API_TOKENis set to API token with theDeployrole. Sets thegrouplabel for node instance grouping, for example:WALLARM_LABELS="group=<GROUP>"...will place node instance into the
<GROUP>instance group (existing, or, if does not exist, it will be created).Yes (for API tokens) SLAB_ALLOC_ARENA(TARANTOOL_MEMORY_GBNGINX Node 5.x and earlier)Amount of memory allocated to wstore. The value can be a float (a dot .is a decimal separator). By default: 1.0 (1 gygabyte).No WALLARM_APID_ONLY(5.3.7 and higher)In this mode, attacks detected in your traffic are blocked locally by the node (if enabled) but not exported to Wallarm Cloud. Meanwhile, API Discovery and some other features remain fully functional, detecting your API inventory and uploading it to the Cloud for visualization. This mode is for those who want to review their API inventory and identify sensitive data first, and plan controlled attack data export accordingly. However, disabling attack export is rare, as Wallarm securely processes attack data and provides sensitive attack data masking if needed. More details
By default:false.No -
The
-voption mounts the directory with the configuration filedefault.confto the/etc/nginx/http.dcontainer directory.See the example
/etc/nginx/http.d/default.confminimal contentserver { listen 80 default_server; listen [::]:80 default_server ipv6only=on; #listen 443 ssl; server_name localhost; #ssl_certificate cert.pem; #ssl_certificate_key cert.key; root /usr/share/nginx/html; index index.html index.htm; wallarm_mode monitoring; location / { proxy_pass http://example.com; include proxy_params; } }Mounting other configuration files
The container directories used by NGINX:
-
/etc/nginx/nginx.conf- This is the main NGINX configuration file. If you decide to mount this file, additional steps are necessary for proper Wallarm functionality:-
In
nginx.conf, add the following setting at the top level: -
In
nginx.conf, add thewallarm_srv_include /etc/nginx/wallarm-apifw-loc.conf;directive in thehttpblock. This specifies the path to the configuration file for API Specification Enforcement. -
Mount the
wallarm-apifw-loc.conffile to the specified path. The content should be:location ~ ^/wallarm-apifw(.*)$ { wallarm_mode off; proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8088$1; error_page 404 431 = @wallarm-apifw-fallback; error_page 500 502 503 504 = @wallarm-apifw-fallback; allow 127.0.0.8/8; deny all; } location @wallarm-apifw-fallback { wallarm_mode off; return 500 "API FW fallback"; } -
Mount the
/etc/nginx/conf.d/wallarm-status.conffile with the content below. It is crucial not to modify any lines from the provided configuration as this may interfere with the successful upload of node metrics to the Wallarm cloud. -
Within your NGINX configuration file, set up the following configuration for the
/wallarm-statusendpoint:
-
-
/etc/nginx/conf.d— common settings /etc/nginx/http.d— virtual host settings/opt/wallarm/usr/share/nginx/html— static files
If required, you can mount any files to the listed container directories. The filtering node directives should be described in the
/etc/nginx/http.d/default.conffile. -
-
The command does the following:
-
Mounts the file
default.confinto the/etc/nginx/http.dcontainer directory. -
Creates files with filtering node credentials to access Wallarm Cloud in the
/opt/wallarm/etc/wallarmcontainer directory:node.yamlwith filtering node UUID and secret keyprivate.keywith Wallarm private key
-
Protects the resource
http://example.com.
Logging configuration¶
The logging is enabled by default. The log directories are:
-
/var/log/nginx— NGINX logs -
/opt/wallarm/var/log/wallarm— Wallarm node logs
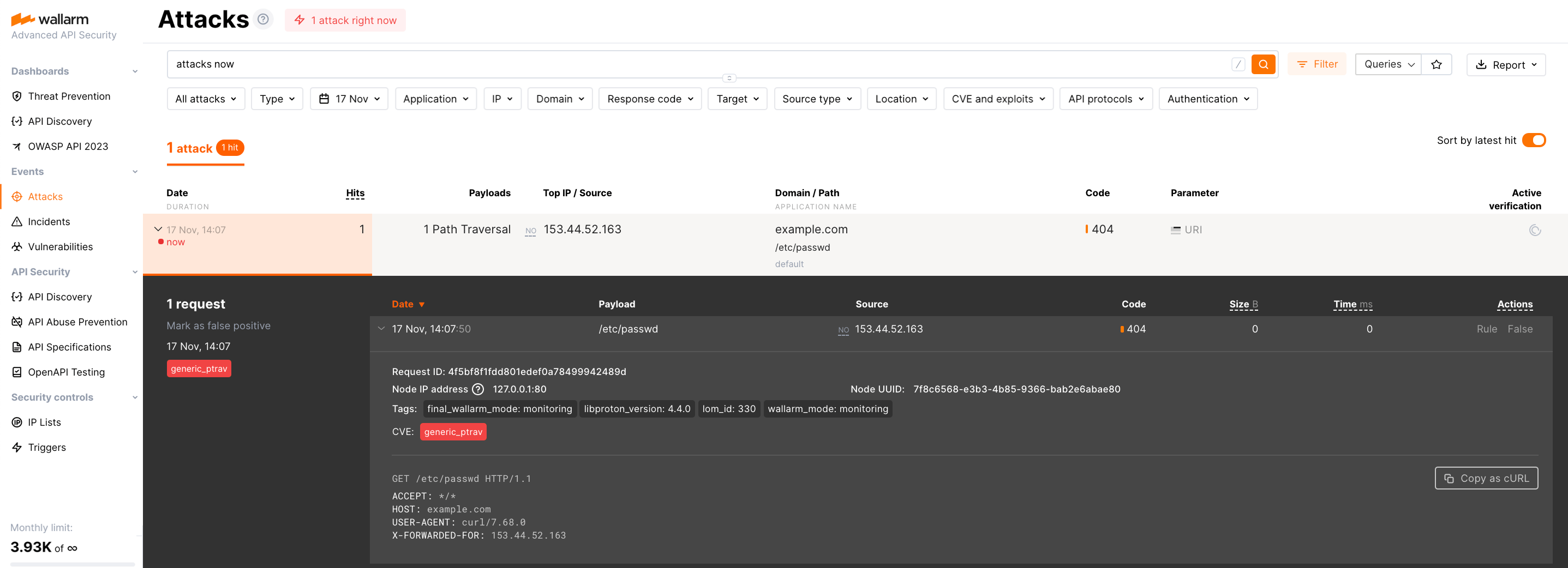
Testing Wallarm node operation¶
-
Send the request with test Path Traversal attack to a protected resource address:
If traffic is configured to be proxied to
example.com, include the-H "Host: example.com"header in the request. -
Open Wallarm Console → Attacks section in the US Cloud or EU Cloud and make sure the attack is displayed in the list.
-
Optionally, [test][link-wallarm-health-check] other aspects of the node functioning.
Configuring the use cases¶
The configuration file mounted to the Docker container should describe the filtering node configuration in the available directive. Below are some commonly used filtering node configuration options: