Deployment of the Wallarm Docker Image to Azure¶
This quick guide provides the steps to deploy the Docker image of the NGINX-based Wallarm node to the Microsoft Azure cloud platform using the Azure Container Instances service.
The instructions limitations
These instructions do not cover the configuration of load balancing and node autoscaling. If setting up these components yourself, we recommend that you read the documentation on Azure Application Gateway.
Use cases¶
Among all supported Wallarm deployment options, Wallarm deployment on Azure Container Instances using the Docker image is recommended in these use cases:
-
If your applications leverage a microservices architecture, and are already containerized and operational on Azure Container Instances.
-
If you require fine-grained control over each container, the Docker image excels. It affords a greater level of resource isolation than typically possible with traditional VM-based deployments.
Requirements¶
-
Active Azure subscription
-
Access to the account with the Administrator role in Wallarm Console for the US Cloud or EU Cloud
-
Access to the IP addresses below for downloading updates to attack detection rules and API specifications, as well as retrieving precise IPs for your allowlisted, denylisted, or graylisted countries, regions, or data centers
Options for the Wallarm node Docker container configuration¶
The filtering node configuration parameters should be passed to the deployed Docker container in one of the following ways:
-
In the environment variables. This option allows for the configuration of only basic filtering node parameters. Most directives cannot be configured through environment variables.
-
In the mounted configuration file. This option allows full filtering node configuration via any directives. With this configuration method, environment variables with the filtering node and Wallarm Cloud connection settings are also passed to the container.
Deploying the Wallarm node Docker container configured through environment variables¶
To deploy the containerized Wallarm filtering node configured only through environment variables, you can use the following tools:
In these instructions, the container is deployed using the Azure CLI.
-
Get Wallarm token of the appropriate type:
-
Sign in to the Azure CLI by using the
az logincommand: -
Create a resource group by using the
az group createcommand. For example, create the groupmyResourceGroupin the East US region with the following command: -
Set the local environment variable with the Wallarm node token to be used to connect the instance to the Wallarm Cloud:
-
Create an Azure resource from the Wallarm node Docker container by using the
az container createcommand:az container create \ --resource-group myResourceGroup \ --name wallarm-node \ --dns-name-label wallarm \ --ports 80 \ --image registry-1.docker.io/wallarm/node:6.2.0 \ --environment-variables WALLARM_API_TOKEN=${WALLARM_API_TOKEN} NGINX_BACKEND='example.com' WALLARM_API_HOST='us1.api.wallarm.com' WALLARM_LABELS='group=<GROUP>'--resource-group: name of the resource group created in the second step.--name: name of the container.--dns-name-label: DNS name label for the container.--ports: port on which the filtering node listens.--image: name of the Wallarm node Docker image.-
--environment-variables: environment variables with the filtering node configuration (available variables are listed in the table below). Please note that it is not recommended to pass the value ofWALLARM_API_TOKENexplicitly.Environment variable Description Required WALLARM_API_TOKENWallarm node or API token. Yes WALLARM_LABELSAvailable starting from node 4.6. Works only if
WALLARM_API_TOKENis set to API token with theDeployrole. Sets thegrouplabel for node instance grouping, for example:WALLARM_LABELS="group=<GROUP>"...will place node instance into the
<GROUP>instance group (existing, or, if does not exist, it will be created).Yes (for API tokens) NGINX_BACKENDDomain or IP address of the resource to protect with the Wallarm solution. Yes WALLARM_API_HOSTWallarm API server: us1.api.wallarm.comfor the US Cloudapi.wallarm.comfor the EU Cloud
api.wallarm.com.No WALLARM_MODENode mode: blockto block malicious requestssafe_blockingto block only those malicious requests originated from graylisted IP addressesmonitoringto analyze but not block requestsoffto disable traffic analyzing and processing
monitoring.
Detailed description of filtration modes →No WALLARM_APPLICATIONUnique identifier of the protected application to be used in the Wallarm Cloud. The value can be a positive integer except for 0.
Default value (if the variable is not passed to the container) is-1which indicates the default application displayed in Wallarm Console → Settings → Application.
More details on setting up applications →No SLAB_ALLOC_ARENA(TARANTOOL_MEMORY_GBNGINX Node 5.x and earlier)Amount of memory allocated to wstore. The value can be a float (a dot .is a decimal separator). By default: 1.0 (1 gygabyte).No NGINX_PORTSets a port that NGINX will use inside the Docker container.
Starting from the Docker image4.0.2-1, thewallarm-statusservice automatically runs on the same port as NGINX.
Default value (if the variable is not passed to the container) is80.
Syntax isNGINX_PORT='443'.No WALLARM_STATUS_ALLOWCustom CIDRs that are allowed to access the /wallarm-statusendpoint from outside the Docker container. Example value:10.0.0.0/8. If you need to pass several values, use a comma,as a separator. To access the service externally, use the Docker container's IP, specifying the/wallarm-statusendpoint path.No DISABLE_IPV6The variable with any value except for an empty one deletes the listen [::]:80 default_server ipv6only=on;line from the NGINX configuration file which will stop NGINX from IPv6 connection processing.
If the variable is not specified explicitly or has an empty value"", NGINX processes both IPv6 and IPv4 connections.No WALLARM_APIFW_ENABLEThis setting toggles API Specification Enforcement on or off, available from release 4.10 onwards. Please note that activating this feature does not substitute for the required subscription and configuration through the Wallarm Console UI.
Its default value istrue, enabling the functionality.No WALLARM_APID_ONLY(5.3.7 and higher)In this mode, attacks detected in your traffic are blocked locally by the node (if enabled) but not exported to Wallarm Cloud. Meanwhile, API Discovery and some other features remain fully functional, detecting your API inventory and uploading it to the Cloud for visualization. This mode is for those who want to review their API inventory and identify sensitive data first, and plan controlled attack data export accordingly. However, disabling attack export is rare, as Wallarm securely processes attack data and provides sensitive attack data masking if needed. More details
By default:false.No
-
Open the Azure portal and ensure the created resource is displayed in the list of resources.
Deploying the Wallarm node Docker container configured through the mounted file¶
To deploy the containerized Wallarm filtering node configured through environment variables and mounted file, only Azure CLI can be used.
To deploy the container with environment variables and mounted configuration file:
-
Get Wallarm token of the appropriate type:
-
Sign in to the Azure CLI by using the
az logincommand: -
Create a resource group by using the
az group createcommand. For example, create the groupmyResourceGroupin the East US region with the following command: -
Create a configuration file with the filtering node settings locally. A example of the file with minimal settings:
server { listen 80 default_server; listen [::]:80 default_server ipv6only=on; #listen 443 ssl; server_name localhost; #ssl_certificate cert.pem; #ssl_certificate_key cert.key; root /usr/share/nginx/html; index index.html index.htm; wallarm_mode monitoring; # wallarm_application 1; location / { proxy_pass http://example.com; include proxy_params; } }Set of filtering node directives that can be specified in the configuration file →
-
Locate the configuration file in one of the ways suitable for mounting data volumes in Azure. All methods are described in the Mount data volumes section of the Azure documentation.
In these instructions, the configuration file is mounted from the Git repository.
-
Set the local environment variable with the Wallarm node token to be used to connect the instance to the Wallarm Cloud:
-
Create an Azure resource from the Wallarm node Docker container by using the
az container createcommand:az container create \ --resource-group myResourceGroup \ --name wallarm-node \ --dns-name-label wallarm \ --ports 80 \ --image registry-1.docker.io/wallarm/node:6.2.0 \ --gitrepo-url <URL_OF_GITREPO> \ --gitrepo-mount-path /etc/nginx/http.d \ --environment-variables WALLARM_API_TOKEN=${WALLARM_API_TOKEN} WALLARM_API_HOST='us1.api.wallarm.com' WALLARM_LABELS='group=<GROUP>'az container create \ --resource-group myResourceGroup \ --name wallarm-node \ --dns-name-label wallarm \ --ports 80 \ --image registry-1.docker.io/wallarm/node:6.2.0 \ --gitrepo-url <URL_OF_GITREPO> \ --gitrepo-mount-path /etc/nginx/http.d \ --environment-variables WALLARM_API_TOKEN=${WALLARM_API_TOKEN} WALLARM_LABELS='group=<GROUP>'--resource-group: name of the resource group created in the 2nd step.--name: name of the container.--dns-name-label: DNS name label for the container.--ports: port on which the filtering node listens.--image: name of the Wallarm node Docker image.--gitrepo-url: URL of the Git repository containing the configuration file. If the file is located in the repository root, you need to pass only this parameter. If the file is located in a separate Git repository directory, please also pass the path to the directory in the--gitrepo-dirparameter (for example,--gitrepo-dir ./dir1).-
--gitrepo-mount-path: directory of the container to mount the configuration file to. Configuration files can be mounted to the following container directories used by NGINX:/etc/nginx/conf.d— common settings/etc/nginx/http.d— virtual host settings/var/www/html— static files
The filtering node directives should be described in the
/etc/nginx/http.d/default.conffile. -
--environment-variables: environment variables containing settings for the filtering node and Wallarm Cloud connection (available variables are listed in the table below). Please note that it is not recommended to explicitly pass the value ofWALLARM_API_TOKEN.Environment variable Description Required WALLARM_API_TOKENWallarm node or API token. Yes WALLARM_API_HOSTWallarm API server: us1.api.wallarm.comfor the US Cloudapi.wallarm.comfor the EU Cloud
api.wallarm.com.No WALLARM_LABELSAvailable starting from node 4.6. Works only if
WALLARM_API_TOKENis set to API token with theDeployrole. Sets thegrouplabel for node instance grouping, for example:WALLARM_LABELS="group=<GROUP>"...will place node instance into the
<GROUP>instance group (existing, or, if does not exist, it will be created).Yes (for API tokens) SLAB_ALLOC_ARENA(TARANTOOL_MEMORY_GBNGINX Node 5.x and earlier)Amount of memory allocated to wstore. The value can be a float (a dot .is a decimal separator). By default: 1.0 (1 gygabyte).No WALLARM_APID_ONLY(5.3.7 and higher)In this mode, attacks detected in your traffic are blocked locally by the node (if enabled) but not exported to Wallarm Cloud. Meanwhile, API Discovery and some other features remain fully functional, detecting your API inventory and uploading it to the Cloud for visualization. This mode is for those who want to review their API inventory and identify sensitive data first, and plan controlled attack data export accordingly. However, disabling attack export is rare, as Wallarm securely processes attack data and provides sensitive attack data masking if needed. More details
By default:false.No
-
Open the Azure portal and ensure the created resource is displayed in the list of resources.
Testing the filtering node operation¶
-
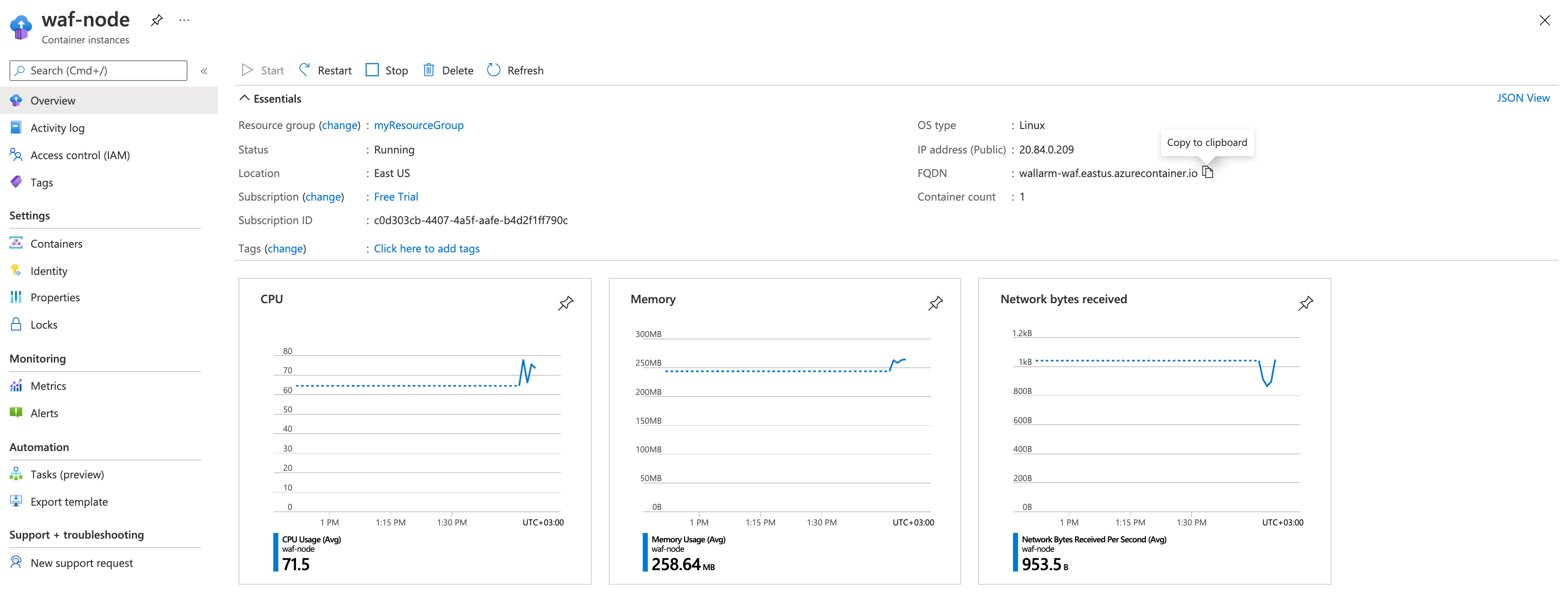
Open the created resource on the Azure portal and copy the FQDN value.
If the FQDN field is empty, please ensure the container is in the Running status.
-
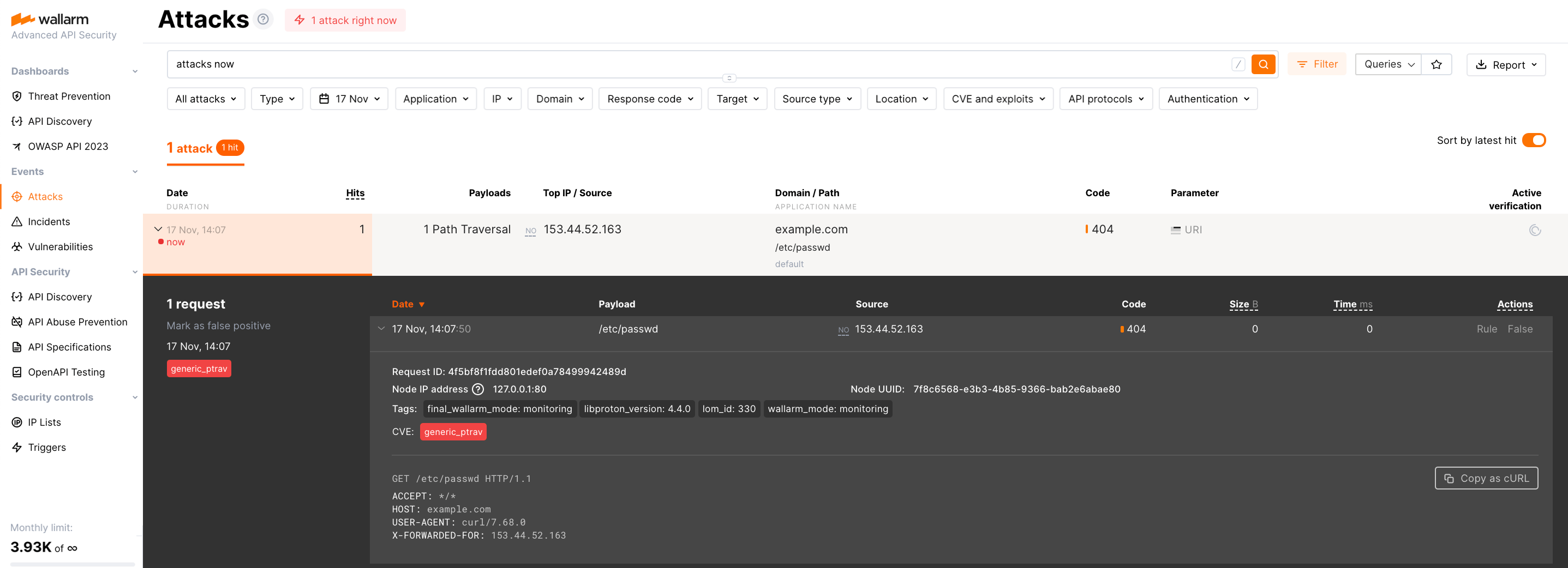
Send the request with the test Path Traversal attack to the copied domain:
-
Open Wallarm Console → Attacks in the US Cloud or EU Cloud and make sure the attack is displayed in the list.
-
Optionally, [test][link-docs-check-operation] other aspects of the node functioning.
Details on errors occurred during the container deployment are displayed on the Containers → Logs tab of the resource details on the Azure portal. If the resource is unavailable, please ensure required filtering node parameters with correct values are passed to the container.