Running Wallarm on Heroku¶
Wallarm can protect web applications and APIs deployed on the Heroku cloud platform. This guide walks you through the process of running the Wallarm node on Heroku to analyze traffic in real-time.
At present, there is no official Docker image for Heroku from Wallarm. So, this guide explains how to create and run your own using our all-in-one installer.
Requirements¶
-
Docker installed on your host system
-
Docker account for pushing Heroku Wallarm Docker image
-
Heroku CLI installed on your host system
-
Applications or APIs running on Heroku web dynos
-
Administrator access to Wallarm Console in the US Cloud or EU Cloud
-
Access to
https://meganode.wallarm.comto download all-in-one Wallarm installer -
Access to
https://us1.api.wallarm.comfor working with US Wallarm Cloud or tohttps://api.wallarm.comfor working with EU Wallarm Cloud -
Access to the IP addresses below for downloading updates to attack detection rules and API specifications, as well as retrieving precise IPs for your allowlisted, denylisted, or graylisted countries, regions, or data centers
Step 1: Prepare Wallarm Docker configuration¶
To deploy Wallarm's Docker image on Heroku, start by creating the necessary configuration files for the image build process. Follow these steps:
-
On your local system, create a directory specifically for Wallarm Docker configurations and proceed to it.
-
Craft an
nginx.conffile that includes NGINX and Wallarm configurations. Since the Docker image will be based on the NGINX-compatible all-in-one installer, ensure NGINX is configured appropriately.Here is the template with a basic configuration that runs the Wallarm node in the monitoring mode:
daemon off; worker_processes auto; load_module /usr/lib/nginx/modules/ngx_http_wallarm_module.so; pid /tmp/nginx.pid; include /etc/nginx/modules-enabled/*.conf; events { worker_connections 768; use epoll; accept_mutex on; } http { gzip on; gzip_comp_level 2; gzip_min_length 512; gzip_proxied any; # Heroku router sends Via header proxy_temp_path /tmp/proxy_temp; client_body_temp_path /tmp/client_temp; fastcgi_temp_path /tmp/fastcgi_temp; uwsgi_temp_path /tmp/uwsgi_temp; scgi_temp_path /tmp/scgi_temp; sendfile on; tcp_nopush on; tcp_nodelay on; keepalive_timeout 65; types_hash_max_size 2048; server_tokens off; # server_names_hash_bucket_size 64; # server_name_in_redirect off; include /etc/nginx/mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log; error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log; # Main Heroku app server { listen $PORT default_server; server_name _; wallarm_mode monitoring; location / { proxy_pass http://unix:/tmp/nginx.socket; # Heroku apps are always behind a load balancer, which is why we trust all IPs set_real_ip_from 0.0.0.0/0; real_ip_header X-Forwarded-For; real_ip_recursive off; proxy_redirect off; proxy_set_header Host $http_host; proxy_set_header "Connection" ""; } error_page 403 /403.html; location = /403.html { root /usr/share/nginx/html; internal; } } # Wallarm status helper (localhost-only) server { listen 127.0.0.8:$PORT; server_name localhost; allow 127.0.0.0/8; deny all; wallarm_mode off; disable_acl "on"; access_log off; location ~/wallarm-status$ { wallarm_status on; } } } -
Create the following
entrypoint.shfile with directives for the Wallarm Docker image:#!/bin/bash set -e log() { local msg="$1" local level="$2" if [ -z "$level" ]; then level="INFO" fi echo "[$(date '+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')] [$level] $msg" } log "Script execution started." # Ensure necessary directories exist log "Ensuring necessary directories exist for supervisord." mkdir -p /opt/wallarm/var/log/wallarm mkdir -p /opt/wallarm/run/supervisor if [ ! -z "$WALLARM_API_TOKEN" ]; then log "WALLARM_API_TOKEN is set, checking configuration." if [[ $DYNO == web.* ]]; then log "Heroku dyno type [$DYNO] is 'web', proceeding with Wallarm configuration." # Propagate env vars log "Propagating environment variables from /opt/wallarm/env.list." set -a source /opt/wallarm/env.list if [ -s /etc/wallarm-override/env.list ]; then log "Propagating environment variables from /etc/wallarm-override/env.list." source /etc/wallarm-override/env.list fi set +a # Register Wallarm node in the Cloud log "Registering Wallarm node in the cloud." /opt/wallarm/register-node # Configure PORT in nginx config log "Replacing \$PORT in Nginx configuration with value $PORT." sed -i "s/\$PORT/${PORT}/g" /etc/nginx/nginx.conf # Verify that PORT was replaced successfully log "Checking if the PORT in Nginx configuration was successfully replaced." if cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf | grep -q "listen ${PORT}"; then log "Successfully replaced PORT in Nginx configuration with value $PORT." else log "Failed to replace PORT in Nginx configuration!" "ERROR" exit 1 fi # Export $PORT as $NGINX_PORT (required for the `export-metrics` script) log "Exporting PORT as NGINX_PORT for Wallarm metrics." export NGINX_PORT="$PORT" # Start all Wallarm services and NGINX under supervisord log "Starting all Wallarm services and NGINX under supervisord." /opt/wallarm/usr/bin/python3.10 /opt/wallarm/usr/bin/supervisord -c /opt/wallarm/etc/supervisord.conf --loglevel=debug # Check if supervisord started successfully log "Checking if supervisord process is running." if pgrep -f "supervisord" > /dev/null; then log "supervisord process started successfully." else log "Failed to start supervisord process!" "ERROR" exit 1 fi # Check the status of services managed by supervisord log "Checking the status of all services managed by supervisord every 10s during 3 minutes." timeout=0 while (/opt/wallarm/usr/bin/supervisorctl -c /opt/wallarm/etc/supervisord.conf status | grep -qv "RUNNING"); do log "One or more services failed to start!" "ERROR" log "Waiting 10s and check it again" sleep 10s timeout=$(( timeout + 10 )) if [ $timeout -ge 180 ]; then log "One or more services failed to start!" "ERROR" /opt/wallarm/usr/bin/supervisorctl -c /opt/wallarm/etc/supervisord.conf status exit 1 fi done log "All services are running successfully." log "Wallarm configuration completed." else log "Heroku dyno type [$DYNO] is not 'web', skipping Wallarm configuration." fi else log "WALLARM_API_TOKEN is not set, executing CMD." fi # Execute the CMD command log "Executing command: $@" exec "$@" log "Script execution finished." -
Set the
entrypoint.shfile permissions to-rwxr-xr-xby executing the following command: -
Design a
403.htmlfile that displays a well-structured page for requests that Wallarm will block. You can copy the following:<!doctype html> <html> <head> <meta charset=utf-8> <meta content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1.0,minimum-scale=1.0,maximum-scale=1.0,user-scalable=no" name=viewport> <title>Forbidden</title> <link rel="shortcut icon" type="image/x-icon" href="https://www.herokucdn.com/favicon.ico"> <style>html, body { font-family: sans-serif; -ms-text-size-adjust: 100%; -webkit-text-size-adjust: 100%; background-color: #F7F8FB; height: 100%; -webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased; } body { margin: 0; padding: 0; display: flex; flex-direction: column; align-items: center; justify-content: center; } .message { text-align: center; align-self: center; display: flex; flex-direction: column; align-items: center; padding: 0px 20px; max-width: 450px; } .message__title { font-size: 22px; font-weight: 100; margin-top: 15px; color: #47494E; margin-bottom: 8px; } p { -webkit-margin-after: 0px; -webkit-margin-before: 0px; font-size: 15px; color: #7F828B; line-height: 21px; margin-bottom: 4px; } .btn { text-decoration: none; padding: 8px 15px; border-radius: 4px; margin-top: 10px; font-size: 14px; color: #7F828B; border: 1px solid #7F828B; } .hk-logo, .app-icon { fill: #DBE1EC; } .info { fill: #9FABBC; } body.friendly { background: -webkit-linear-gradient(-45deg, #8363a1 0%, #74a8c3 100%); background: linear-gradient(135deg, #8363a1 0%, #74a8c3 100%); } body.friendly .message__title { color: #fff; } body.friendly p { color: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.6); } body.friendly .hk-logo, body.friendly .app-icon { fill: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.9); } body.friendly .info { fill: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.9); } body.friendly .btn { color: #fff; border: 1px solid rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.9); } .info_area { position: fixed; right: 12px; bottom: 12px; } .logo { position: fixed; left: 12px; bottom: 12px; } </style> <base target=_parent /> </head> <body> <div class=spacer></div> <div class=message> <svg width=49 height=51 xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"><path d="M3.9468 10.0288L20.5548.995c2.4433-1.3267 5.45-1.3267 7.8936 0l16.6078 9.0338C47.4966 11.3585 49 13.8102 49 16.4666V34.534c0 2.6537-1.5034 5.1082-3.9438 6.438l-16.6078 9.0307c-2.4435 1.3297-5.4503 1.3297-7.8937 0L3.9467 40.972C1.5035 39.642 0 37.1876 0 34.534V16.4667c0-2.6564 1.5034-5.108 3.9468-6.4378z" class=app-icon fill-rule=evenodd /></svg> <div class=message__title> Your request has been blocked </div> <p> If you think this is a mistake, please get in touch with the app's support team. </p> </div> <div class=logo> <svg width=85 height=24 xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"><g class=info fill-rule=evenodd><path d="M27.8866 16.836h2.373v-3.504h2.919v3.504h2.373V8.164h-2.373v3.2227h-2.919V8.164h-2.373v8.672zm10.4888 0h6.4666V14.949h-4.0935v-1.6054h2.7764v-1.8282h-2.7765v-1.4062h3.8918V8.164h-6.265v8.672zm8.8396 0h2.3256V13.824h.6526L51.89 16.836h2.5154l-1.863-3.3165c1.151-.3867 1.7325-1.1718 1.7325-2.5312 0-2.086-1.3765-2.8242-3.631-2.8242h-3.429v8.672zm2.3256-4.793v-1.9805h1.0204c.973 0 1.4.2578 1.4.9844 0 .7264-.427.996-1.4.996h-1.0204zM60.8363 17c2.112 0 4.307-1.3242 4.307-4.5 0-3.1758-2.195-4.5-4.307-4.5-2.124 0-4.319 1.3242-4.319 4.5 0 3.1758 2.195 4.5 4.319 4.5zm0-1.875c-1.2458 0-1.946-1.0313-1.946-2.625 0-1.5938.7002-2.5664 1.946-2.5664 1.234 0 1.934.9726 1.934 2.5664 0 1.5938-.7 2.625-1.934 2.625zm6.7157 1.711h2.373v-2.6954l.6764-.7734 2.0764 3.4687h2.6816l-3.2155-5.25 2.9543-3.422h-2.7527l-2.4205 3.1407V8.164h-2.373v8.672zm13.4552.1288c2.563 0 3.6782-1.3125 3.6782-3.6093V8.164H82.36v5.1798c0 1.1953-.3798 1.7343-1.329 1.7343-.9493 0-1.3408-.539-1.3408-1.7342V8.164h-2.373v5.1915c0 2.2968 1.127 3.6093 3.69 3.6093zM2.4444 0C.9214 0 0 .8883 0 2.3226v19.3548C0 23.1068.9215 24 2.4444 24h17.1112C21.0736 24 22 23.1117 22 21.6774V2.3226C21.995.8883 21.0735 0 19.5556 0H2.4444zm16.8973 1.9c.4025.0045.7583.3483.7583.7214v18.7572c0 .3776-.3558.7214-.7583.7214H2.6583c-.4025 0-.7583-.3438-.7583-.7214V2.6214c0-.3777.3558-.7214.7583-.7214h16.6834z"/><path d="M16.43 20h-2.2527v-6.8048c0-.619-.1917-.838-.3786-.9666-1.131-.7667-4.3855-.0334-6.3458.7333l-1.553.6475L5.9048 4h2.2814v6.3333c.4314-.1333.973-.2714 1.524-.3857 2.4206-.5143 4.1987-.3762 5.3586.4048.6375.4286 1.3612 1.2714 1.3612 2.8428V20zM11.57 8h2.6675c1.4042-1.75 1.9732-3.35 2.1925-4h-2.6623c-.3967.95-1.1223 2.55-2.1977 4zM5.9 20v-5.6l2.43 2.8L5.9 20z"/></g></svg> </div> </body> </html> -
Create a
Dockerfileto describe the build process for Wallarm's Docker image:FROM ubuntu:22.04 ARG VERSION="6.2.0" ENV PORT=3000 ENV WALLARM_LABELS="group=heroku" ENV WALLARM_API_TOKEN= ENV WALLARM_API_HOST="us1.api.wallarm.com" RUN apt-get -qqy update && apt-get -qqy install nginx curl && apt-get clean # Download and unpack the Wallarm all-in-one installer RUN curl -o /install.sh "https://meganode.wallarm.com/$(echo "$VERSION" | cut -d '.' -f 1-2)/wallarm-$VERSION.x86_64-glibc.sh" \ && chmod +x /install.sh \ && /install.sh --noexec --target /opt/wallarm \ && rm -f /install.sh \ && cd /opt/wallarm \ && chmod +x pick-module.sh \ && SELECTED_MODULE="$(./pick-module.sh)" \ && echo "Selected module => $SELECTED_MODULE" \ # Copy wlrm-module into NGINX's module directory && cp "$SELECTED_MODULE" /usr/lib/nginx/modules/ngx_http_wallarm_module.so \ && mkdir -p /usr/local/lib \ && mv /opt/wallarm/modules/libwallarm.so* -t "/usr/local/lib/" \ && rm -rf /opt/wallarm/modules # Run supervisord in background. Our foreground process is the Heroku app itself RUN sed -i '/nodaemon=true/d' /opt/wallarm/etc/supervisord.conf # Add NGINX to supervisord RUN printf "\n\n[program:nginx]\ncommand=/usr/sbin/nginx\nautorestart=true\nstartretries=4294967295\n" | tee -a /opt/wallarm/etc/supervisord.conf # Heroku runs everything under an unprivileged user (dyno:dyno), so we need to grant it access to Wallarm directories RUN find /opt/wallarm -type d -exec chmod 777 {} \; # Copy NGINX configuration COPY nginx.conf /etc/nginx/nginx.conf # Herokuesque 403 error page COPY 403.html /usr/share/nginx/html/403.html # Add entrypoint.sh COPY entrypoint.sh /entrypoint.sh # Let entrypoint modify the config under dyno:dyno and redirect NGINX logs to console RUN chmod +x /entrypoint.sh \ && chmod 666 /etc/nginx/nginx.conf \ && chmod 777 /etc/nginx/ \ && ln -sf /dev/stdout /var/log/nginx/access.log \ && ln -sf /dev/stderr /var/log/nginx/error.log ENTRYPOINT ["/entrypoint.sh"]
Step 2: Build the Wallarm Docker image for Heroku¶
Execute the following commands within the previously created directory:
docker build -t wallarm-heroku:6.2.0 .
docker login
docker tag wallarm-heroku:6.2.0 <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/wallarm-heroku:6.2.0
docker push <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/wallarm-heroku:6.2.0
Step 3: Run the built Docker image on Heroku¶
To deploy the image on Heroku:
-
Navigate to the root of your application directory to perform the subsequent operations.
-
Construct a
Dockerfilewhich will include the installation of necessary dependencies specific to your app's runtime. For a Node.js application, use the following template:FROM <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/wallarm-heroku:6.2.0 ENV NODE_MAJOR=20 # Install NodeJS v20 from NodeSource RUN apt-get update \ && apt-get install -qqy ca-certificates curl gnupg \ && mkdir -p /etc/apt/keyrings \ && curl -fsSL https://deb.nodesource.com/gpgkey/nodesource-repo.gpg.key | gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/nodesource.gpg \ && echo "deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/nodesource.gpg] https://deb.nodesource.com/node_$NODE_MAJOR.x nodistro main" | tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nodesource.list \ && apt-get update \ && apt-get install nodejs -qqy \ && apt-get clean ADD . /opt/webapp WORKDIR /opt/webapp # Install dependencies and build the app RUN npm install --omit=dev ENV npm_config_prefix /opt/webapp # Note that in private spaces the `run` section of heroku.yml is ignored # See: https://devcenter.heroku.com/articles/build-docker-images-heroku-yml#known-issues-and-limitations CMD ["npm", "run", "start"] -
Create a
heroku.ymlconfiguration file with the following content: -
Adapt your application to listen on
/tmp/nginx.socketrather than$PORTbecause$PORTis utilized by NGINX. For instance, the configuration may look as follows:// app.js const app = require('express')() let port = process.env.PORT || 3000 // If Wallarm is not configured, listen on $PORT if(process.env.WALLARM_API_TOKEN) port = '/tmp/nginx.socket' // Wallarm is configured app.listen(port, (err) => { if (err) throw err console.log(`> App is listening on ${port}`) }) app.get('/', (req, res) => { res.send('This app is protected by Wallarm') }) -
Generate a filtering node token of the appropriate type to link the Wallarm node instance to the Wallarm Cloud:
-
Establish the parameters for connecting the node to the Cloud within the relevant variables:
-
Push your application to trigger a restart, thereby deploying the Wallarm node:
Step 4: Test the deployment¶
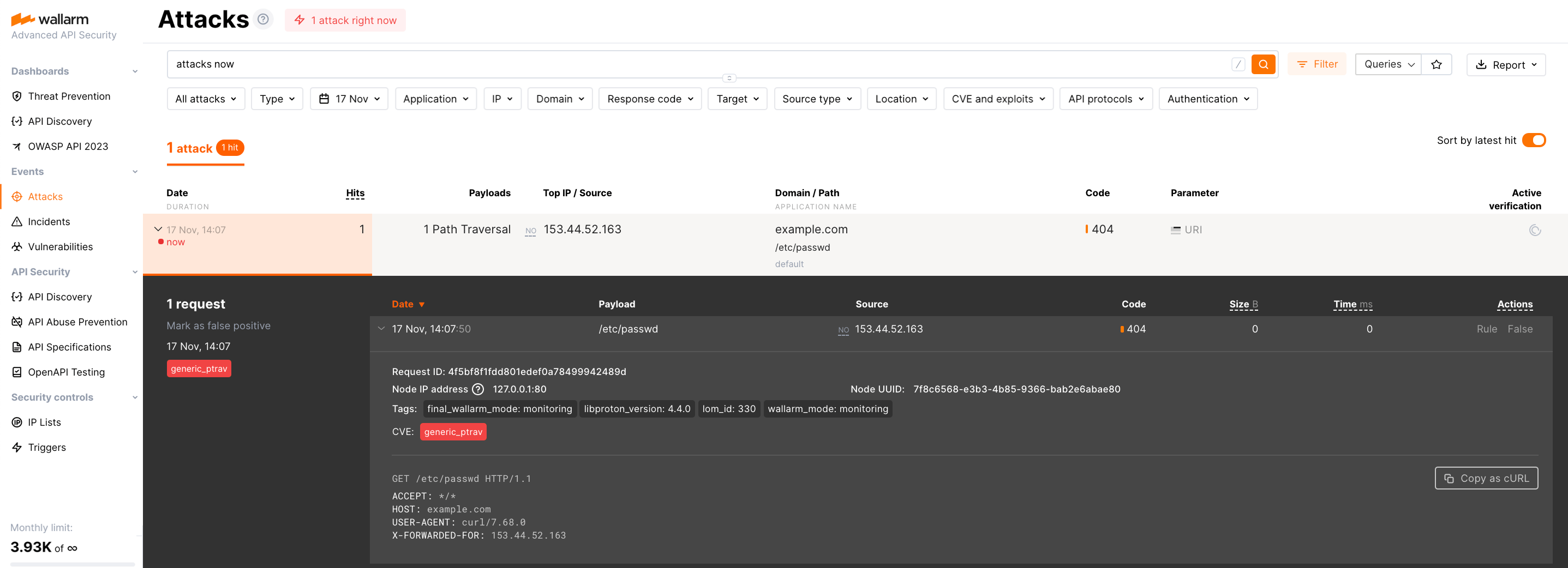
To confirm that the deployment is functional, initiate a test attack using the Path Traversal exploit:
Since the node operates in the monitoring filtration mode by default, the Wallarm node will not block the attack but will register it. To check that the attack has been registered, proceed to Wallarm Console → Attacks:
Debug¶
Should you face any difficulties with the Wallarm base Docker image, inspect the Heroku logs for potential error messages:
If you need assistance during the deployment, contact the Wallarm support team.