Deploying Wallarm OOB for NGINX, Envoy and Similar Mirroring using Terraform Module¶
This article demonstrates the example on how to deploy Wallarm to AWS as an Out-of-Band solution using the Wallarm Terraform module. It is expected that NGINX, Envoy, Istio and/or Traefik provides traffic mirroring.
Use cases¶
Among all supported Wallarm deployment options, Terraform module is recommended for Wallarm deployment on AWS VPC in these use cases:
-
Your existing infrastructure resides on AWS.
-
You leverage the Infrastructure as Code (IaC) practice. Wallarm's Terraform module allows for the automated management and provisioning of the Wallarm node on AWS, enhancing efficiency and consistency.
Requirements¶
-
Terraform 1.0.5 or higher installed locally
-
Access to the account with the Administrator role in Wallarm Console in the US or EU Cloud
-
Access to
https://us1.api.wallarm.comif working with US Wallarm Cloud or tohttps://api.wallarm.comif working with EU Wallarm Cloud. Please ensure the access is not blocked by a firewall
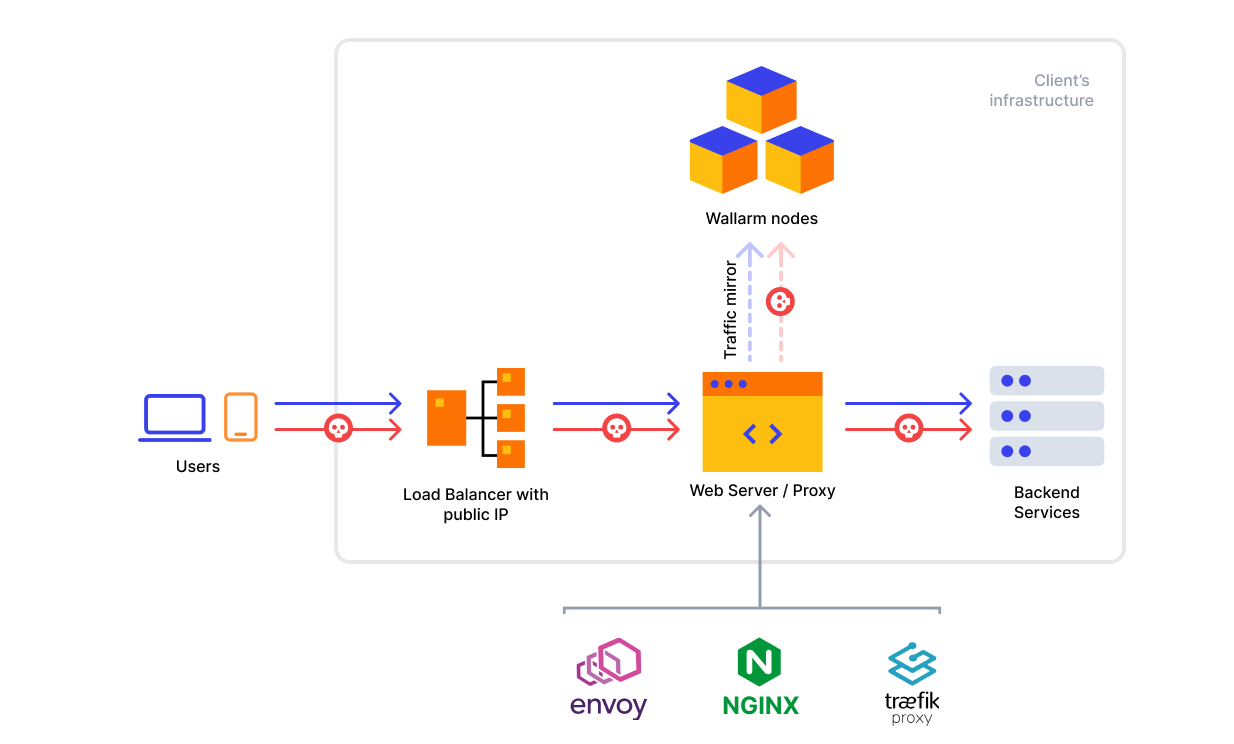
Solution architecture¶
This example Wallarm solution has the following components:
-
Internet-facing load balancer routing traffic to the Wallarm node instances. It is expected that a load balancer has been already deployed, the
wallarmmodule will not create this resource. -
Any web or proxy server (e.g. NGINX, Envoy) serving traffic from a load balancer and mirroring HTTP requests to an internal ALB endpoint and backend services. It is expected that a the component used for traffic mirroring has been already deployed, the
wallarmmodule will not create this resource. -
An internal ALB accepting mirrored HTTPS requests from a web or proxy server and forwarding them to the Wallarm node instances.
-
Wallarm node analyzing requests from an internal ALB and sending malicious traffic data to the Wallarm Cloud.
The example runs the Wallarm nodes in the monitoring mode that drives the described behavior. If you switch the mode to another value, nodes continue to only monitor the traffic as the OOB approach does not allow attack blocking.
The last two components will be deployed by the provided wallarm example module.
Code components¶
This example has the following code components:
main.tf: the main configuration of thewallarmmodule to be deployed as a mirror solution. The configuration produces an internal AWS ALB and Wallarm instances.
Running the example Wallarm mirror solution¶
To run the example Wallarm mirror solution, you need to configure HTTP request mirroring and then deploy the solution.
1. Configuring HTTP request mirroring¶
Traffic mirroring is a feature provided by many web and proxy servers. The link provides the documentation on how to configure traffic mirroring with some of them.
2. Deploy the example Wallarm mirror solution¶
-
Open Wallarm Console → Nodes and create the node of the Wallarm node type.
-
Copy the generated node token.
-
Clone the repository containing the example code to your machine:
-
Set variable values in the
defaultoptions in theexamples/mirror/variables.tffile of the cloned repository and save changes. -
Deploy the stack by executing the following commands from the
examples/mirrordirectory:
To remove the deployed environment, use the following command: