Wallarm Ingress Controller Troubleshooting¶
This troubleshooting guide lists common issues you can face during the Wallarm NGINX-based Ingress controller deployment. If you did not find relevant details here, please contact Wallarm technical support.
How to check which clients' IP addresses are detected/used by the Ingress controller?¶
-
Take a look at the controller container’s log and find records about handled requests. In the default logging format the first reported field is the detected client IP address.
25.229.38.234is the detected IP address in the example below:
-
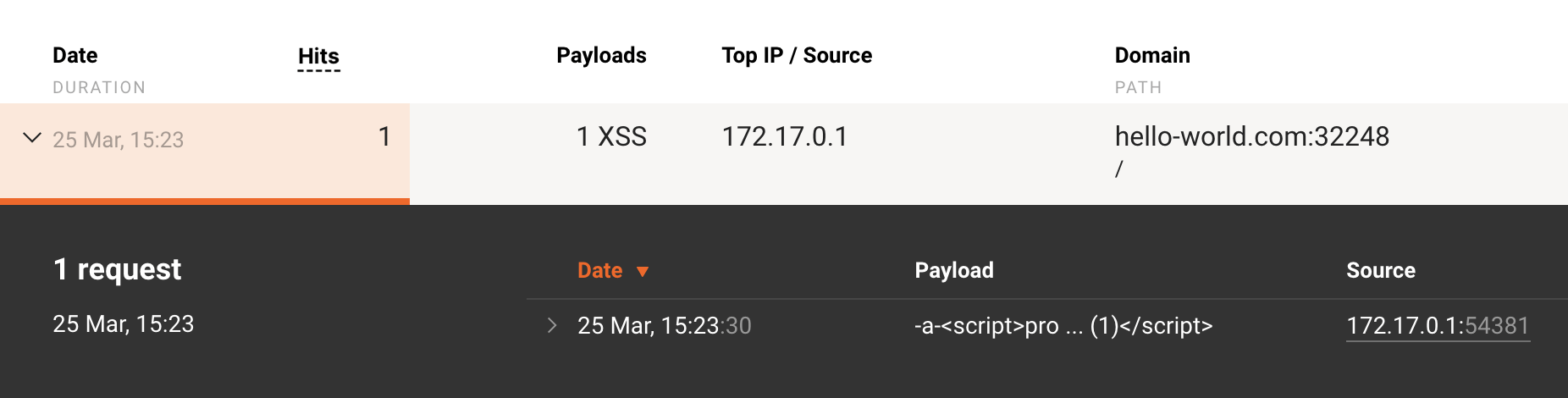
Go to your Wallarm Console for the US cloud or for the EU cloud → the Attacks section and expand request details. An IP address is displayed in the Source field. For example:
If the list of attacks is empty, you can send a test attack to the application protected by the Wallarm Ingress controller.
How to check that the Ingress controller is receiving the X-FORWARDED-FOR request header?¶
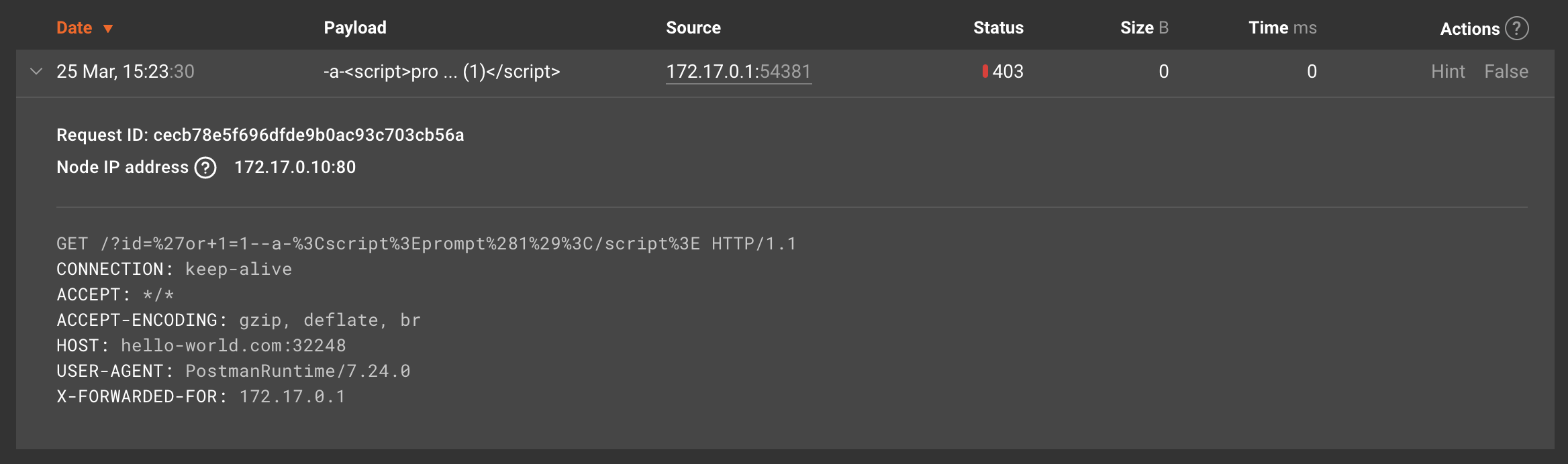
Please go to Wallarm Console for the US cloud or for the EU cloud → the Attacks section and expand the request details. In the displayed request details, pay attention to the X-FORWARDED-FOR header. For example:
If the list of attacks is empty, you can send a test attack to the application protected by the Wallarm Ingress controller.