تثبيت كوحدة ديناميكية لنسخة NGINX المقدمة من التوزيع¶
هذه التعليمات توضح الخطوات لتثبيت عقدة تصفية Wallarm كوحدة ديناميكية لنسخة الكود المفتوح من NGINX المثبتة من مستودعات Debian/CentOS. ستقوم العقدة بتحليل حركة المرور بشكل مباشر.
التثبيت الشامل
ابتداءً من عقدة Wallarm 4.6، يُوصى باستخدام التثبيت الشامل الذي يُتيح أتمتة جميع الأنشطة المدرجة في الخطوات أدناه ويجعل نشر العقدة أسهل بكثير.
يمكن الحصول على NGINX الكود المفتوح من nginx.org أو المستودعات الافتراضية لـ Debian/CentOS حسب متطلباتك وتفضيلات إصدار NGINX وسياسات إدارة المستودعات. تقدم Wallarm حزمًا لكل من nginx.org والأٌصدارات التي يوفرها التوزيع. يركز هذا الدليل على NGINX من مستودعات Debian/CentOS.
حالات الاستخدام¶
Among all supported Wallarm deployment options, DEB/RPM packages for distribution-provided NGINX is recommended for Wallarm deployment in these use cases:
-
Your infrastructure is based on bare metal or virtual machines without using container-based methods. Typically, these setups are managed with Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools like Ansible or SaltStack.
-
Your services are built around distribution-provided NGINX. Wallarm can extend its functionalities using these packages.
المتطلبات¶
-
Access to the account with the Administrator role in Wallarm Console for the US Cloud or EU Cloud
-
SELinux disabled or configured upon the instructions
-
Executing all commands as a superuser (e.g.
root) -
Access to
https://repo.wallarm.comto download packages. Ensure the access is not blocked by a firewall -
Access to
https://us1.api.wallarm.comfor working with US Wallarm Cloud or tohttps://api.wallarm.comfor working with EU Wallarm Cloud. If access can be configured only via the proxy server, then use the instructions -
Access to the IP addresses and their corresponding hostnames (if any) listed below. This is needed for downloading updates to attack detection rules, as well as retrieving precise IPs for your allowlisted, denylisted, or graylisted countries, regions, or data centers
-
Installed text editor vim, nano, or any other. In the instruction, vim is used
1. Add Debian/CentOS repositories¶
sudo apt -y install dirmngr
curl -fSsL https://repo.wallarm.com/wallarm.gpg | sudo gpg --no-default-keyring --keyring gnupg-ring:/etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/wallarm.gpg --import
sudo chmod 644 /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/wallarm.gpg
sh -c "echo 'deb https://repo.wallarm.com/debian/wallarm-node bullseye/4.8/' | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/wallarm.list"
sudo apt update
2. Install NGINX with Wallarm packages¶
The command installs the following packages:
-
nginxfor NGINX -
libnginx-mod-http-wallarmornginx-mod-http-wallarmfor the NGINX-Wallarm module -
wallarm-nodefor the postanalytics module, Tarantool database, and additional NGINX-Wallarm packages
3. Connect the Wallarm module¶
Copy the configuration files for the system setup:
4. Connect the filtering node to Wallarm Cloud¶
The Wallarm filtering node interacts with the Wallarm Cloud. You need to connect the node to the Cloud.
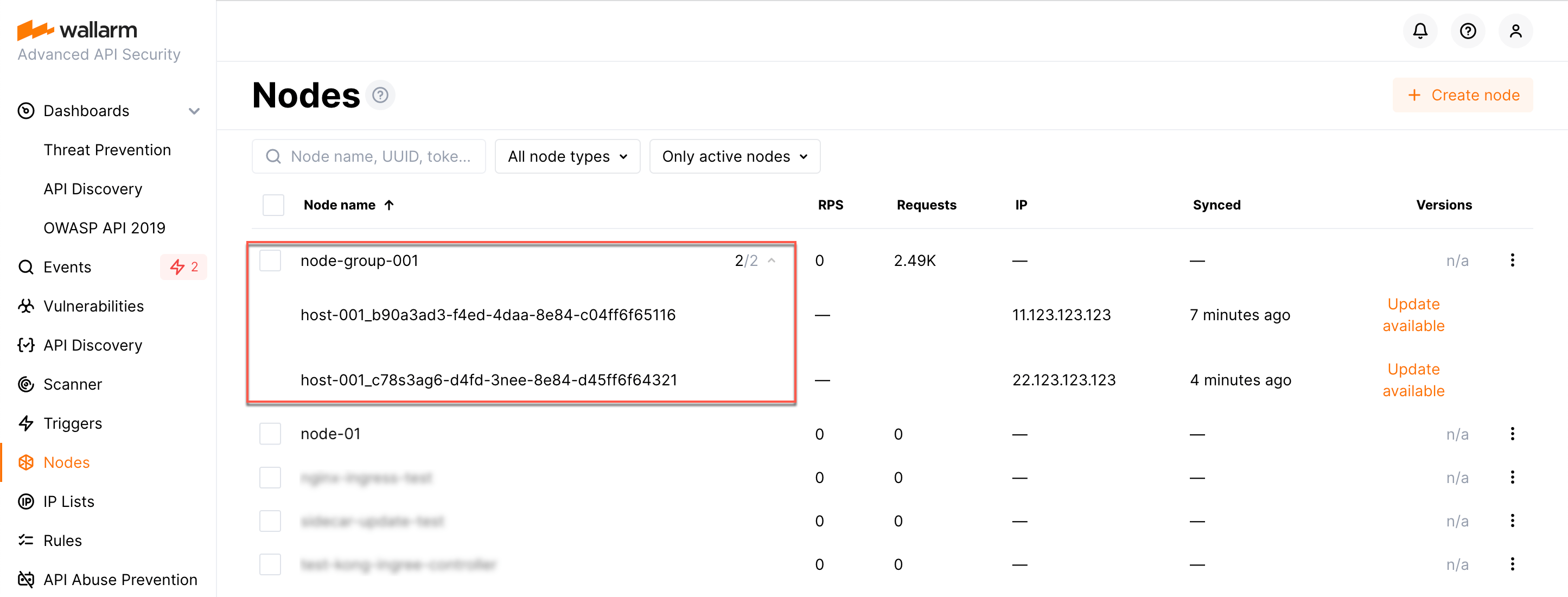
When connecting node to the Cloud, you can set the node name, under which it will be displayed in the Wallarm Console UI and put the node into the appropriate node group (used to logically organize nodes in UI).
To connect the node to the Cloud, use a Wallarm token of the appropriate type:
- Open Wallarm Console → Settings → API tokens in the US Cloud or EU Cloud.
- Find or create API token with the
Node deployment/Deploymentusage type. - Copy this token.
-
Run the
register-nodescript on a machine where you install the filtering node:<TOKEN>is the copied value of the API token with theDeployrole.--labels 'group=<GROUP>'parameter puts your node to the<GROUP>node group (existing, or, if does not exist, it will be created). If you are installing filtering and postanalytics modules separately, it is recommended to put them into the same group.
- Open Wallarm Console → Nodes in the US Cloud or EU Cloud.
- Do one of the following:
- Create the node of the Wallarm node type and copy the generated token.
- Use existing node group - copy token using node's menu → Copy token.
-
Run the
register-nodescript on a machine where you install the filtering node:
<TOKEN>is the copied value of the node token. If you are installing filtering and postanalytics modules separately, it is recommended to put them into the same group using the same node token.
- You may add
-n <HOST_NAME>parameter to set a custom name for your node instance. Final instance name will be:HOST_NAME_NodeUUID.
5. تمكين Wallarm لتحليل حركة المرور¶
By default, the deployed Wallarm Node does not analyze incoming traffic.
To enable traffic analysis and proxying of legitimate traffic, update the NGINX configuration file, typically located at /etc/nginx/sites-available/default.
The following minimal configuration adjustments are necessary:
-
Set the Wallarm Node to
wallarm_mode monitoring;. This mode is recommended for initial deployments and testing.Wallarm also supports more modes like blocking and safe blocking, which you can read more.
-
Determine where the node should forward legitimate traffic by adding the
proxy_passdirective in the required locations. This could be to the IP of an application server, a load balancer, or a DNS name. -
If present, remove the
try_filesdirective from the modified locations to ensure traffic is directed to Wallarm without local file interference.
server {
...
+ wallarm_mode monitoring;
location / {
+ proxy_pass http://example.com;
- # try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
}
...
}
6. إعادة تشغيل NGINX¶
Providing user with root permission
If you are running NGINX as a user that does not have root permission, then add this user to the wallarm group using the following command:
where <user_name> is the name of the user without root permission.
7. تكوين إرسال حركة المرور إلى عقدة Wallarm¶
Update targets of your load balancer to send traffic to the Wallarm instance. For details, please refer to the documentation on your load balancer.
8. اختبار تشغيل عقدة Wallarm¶
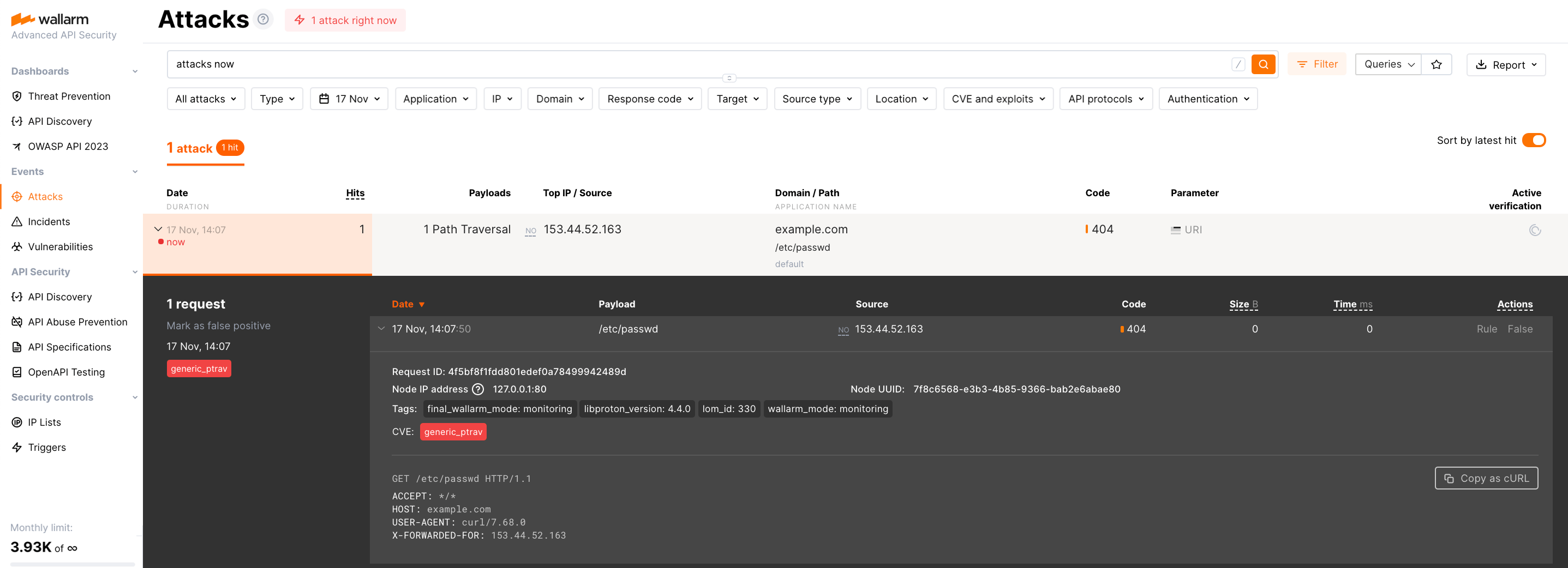
-
Send the request with test Path Traversal attack to a protected resource address:
If traffic is configured to be proxied to
example.com, include the-H "Host: example.com"header in the request. -
Open Wallarm Console → Attacks section in the US Cloud or EU Cloud and make sure the attack is displayed in the list.
-
Optionally, test other aspects of the node functioning.
9. الضبط الدقيق للحل المنشور¶
تم تثبيت الوحدة الديناميكية Wallarm بالإعدادات الافتراضية لـ NGINX stable. قد تتطلب عقدة التصفية بعض التجهيزات الإضافية بعد النشر.
تتم تعريف إعدادات Wallarm باستخدام التوجيهات NGINX أو واجهة مستخدم Wallarm Console. يجب ضبط التوجيهات في الملفات التالية على الجهاز الذي يحتوي على عقدة Wallarm:
-
/etc/nginx/conf.d/default.confمع إعدادات NGINX -
/etc/nginx/conf.d/wallarm.confمع إعدادات عقدة التصفية العالميةيُستخدم هذا الملف للإعدادات المُطبقة على جميع النطاقات. لتطبيق إعدادات مختلفة على مجموعات نطاقات مختلفة، استخدم الملف
default.confأو قم بإنشاء ملفات تكوين جديدة لكل مجموعة نطاقات (على سبيل المثال،example.com.confوtest.com.conf). لمزيد من المعلومات التفصيلية حول ملفات تكوين NGINX متوفرة في الوثائق الرسمية لـ NGINX. -
/etc/nginx/conf.d/wallarm-status.confمع إعدادات مراقبة عقدة Wallarm. الوصف التفصيلي متوفر ضمن الرابط -
/etc/default/wallarm-tarantoolأو/etc/sysconfig/wallarm-tarantoolمع إعدادات قاعدة البيانات Tarantool
فيما يلي بعض الإعدادات النموذجية التي يمكنك تطبيقها إذا لزم الأمر:
-
Using the balancer of the proxy server behind the filtering node
-
Limiting the single request processing time in the directive
wallarm_process_time_limit -
Limiting the server reply waiting time in the NGINX directive
proxy_read_timeout -
Limiting the maximum request size in the NGINX directive
client_max_body_size
القيود¶
- اكتشاف تعبئة بيانات الاعتماد غير مدعوم حاليًا، لأن الحزم لم يتم تحديثها إلى الإصدار 4.10 بعد