تشغيل Wallarm على Heroku¶
يمكن لـ Wallarm حماية التطبيقات الويب وواجهات البرمجة للتطبيقات (APIs) المنتشرة على منصة السحابة Heroku. يوجهك هذا الدليل خلال عملية تشغيل العقدة Wallarm على Heroku لتحليل حركة المرور في الوقت الحقيقي.
حاليا، لا يوجد صورة Docker رسمية لـ Heroku من Wallarm. لذلك، يشرح هذا الدليل كيفية إنشاء وتشغيل الخاصة بك باستخدام برنامج التثبيت الكل في واحد الخاص بنا.
المتطلبات¶
-
تثبيت Docker على نظام الاستضافة الخاص بك
-
حساب Docker لدفع صورة Docker الخاصة بـ Heroku Wallarm
-
تثبيت واجهة الأوامر لـ Heroku CLI على نظام الاستضافة الخاص بك
-
التطبيقات أو واجهات برمجة التطبيقات تعمل على وحدات web dynos في Heroku
-
الوصول كمسؤول إلى وحدة التحكم Wallarm في السحابة الأمريكية أو السحابة الأوروبية
-
الوصول إلى
https://meganode.wallarm.comلتنزيل برنامج التثبيت الشامل لـ Wallarm -
الوصول إلى
https://us1.api.wallarm.comللعمل مع السحابة الأمريكية لـ Wallarm ، أو إلىhttps://api.wallarm.comللعمل مع السحابة الأوروبية لـ Wallarm -
Access to the IP addresses below for downloading updates to attack detection rules, as well as retrieving precise IPs for your allowlisted, denylisted, or graylisted countries, regions, or data centers
الخطوة 1: إعداد تكوين Docker لـ Wallarm¶
لنشر صورة Docker لـ Wallarm على Heroku، ابدأ بإنشاء الملفات التكوينية اللازمة لعملية بناء الصورة. اتبع هذه الخطوات:
-
على النظام المحلي الخاص بك, قم بإنشاء دليل خاص بتكوينات Docker الخاصة بـ Wallarm وانتقل إليه.
-
أنشئ ملف
nginx.confمع تفاصيل تكوين NGINX. نظرًا لأن الصورة Docker ستعتمد على البرنامج الكل في واحد المتوافق مع NGINX، فمن الهام تكوين NGINX على النحو الأمثل.daemon off; worker_processes auto; load_module /opt/wallarm/modules/bullseye-1180/ngx_http_wallarm_module.so; pid /tmp/nginx.pid; include /etc/nginx/modules-enabled/*.conf; events { worker_connections 768; # multi_accept on; } http { proxy_temp_path /tmp/proxy_temp; client_body_temp_path /tmp/client_temp; fastcgi_temp_path /tmp/fastcgi_temp; uwsgi_temp_path /tmp/uwsgi_temp; scgi_temp_path /tmp/scgi_temp; sendfile on; tcp_nopush on; tcp_nodelay on; keepalive_timeout 65; types_hash_max_size 2048; server_tokens off; # server_names_hash_bucket_size 64; # server_name_in_redirect off; include /etc/nginx/mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log; error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log; include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf; include /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/*; } -
قم بصياغة ملف
default.confمع تكوينات Wallarm. استخدم تعليمات أمر والارم لإنجينكس لتخصيص العقدة Wallarm وفقا لمتطلباتك الخاصة.إنه القالب الذي يحتوي على التكوين الأساسي الذي يعمل عليها العقدة Wallarm في وضع المراقبة:
server { listen $PORT default_server; server_name _; wallarm_mode monitoring; location / { proxy_pass http://unix:/tmp/nginx.socket; include proxy_params; # Heroku apps are always behind a load balancer, which is why we trust all IPs set_real_ip_from 0.0.0.0/0; real_ip_header X-Forwarded-For; real_ip_recursive off; } error_page 403 /403.html; location = /403.html { root /usr/share/nginx/html; internal; } } server { listen 127.0.0.8:$PORT; server_name localhost; allow 127.0.0.0/8; deny all; wallarm_mode off; disable_acl "on"; access_log off; location ~/wallarm-status$ { wallarm_status on; } } -
أنشئ الملف التالي
entrypoint.shباستخدام التعليمات المرجعية لصورة Docker لـ Wallarm:#!/bin/bash set -e if [ ! -z "$WALLARM_API_TOKEN" ]; then echo "WALLARM_API_TOKEN is set, checking configuration" if [[ $DYNO == web.* ]]; then echo "Heroku dyno type [$DYNO] is 'web', running Wallarm configuration scripts" # Configure PORT in nginx config sed -i "s/\$PORT/$PORT/g" /etc/nginx/sites-available/default # Register Wallarm node in the Cloud /opt/wallarm/register-node --token "$WALLARM_API_TOKEN" -H "$WALLARM_API_HOST" --labels "$WALLARM_LABELS" # Read default Wallarm environment variables export $(sed -e 's/=\(.*\)/="\1"/g' /opt/wallarm/env.list | grep -v "#" | xargs) # Export $PORT as $NGINX_PORT (required for the `export-metrics` script) export NGINX_PORT="$PORT" # Read user-set Wallarm variables [ -s /etc/wallarm-override/env.list ] && export $(sed -e 's/=\(.*\)/="\1"/g' /etc/wallarm-override/env.list | grep -v "#" | xargs) # Launch all Wallarm services and NGINX under supervisord in the background /opt/wallarm/usr/bin/python3.8 /opt/wallarm/usr/bin/supervisord -c /opt/wallarm/etc/supervisord.conf else echo "Heroku dyno type [$DYNO] is not 'web', skipping Wallarm configuration" fi else echo "WALLARM_API_TOKEN is not set, just executing CMD" fi # Execute the CMD command exec "$@" -
اضبط أذونات الملف
entrypoint.shعلى-rwxr-xr-xعبر تنفيذ الأمر التالي: -
قم بتصميم ملف
403.htmlالذي يعرض صفحة مرتبة جيدًا للطلبات التي ستحجبها Wallarm. يمكنك نسخ الكود التالى:<!doctype html> <html> <head> <meta charset=utf-8> <meta content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1.0,minimum-scale=1.0,maximum-scale=1.0,user-scalable=no" name=viewport> <title>Forbidden</title> <link rel="shortcut icon" type="image/x-icon" href="https://www.herokucdn.com/favicon.ico"> <style>html, body { font-family: sans-serif; -ms-text-size-adjust: 100%; -webkit-text-size-adjust: 100%; background-color: #F7F8FB; height: 100%; -webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased; } body { margin: 0; padding: 0; display: flex; flex-direction: column; align-items: center; justify-content: center; } .message { text-align: center; align-self: center; display: flex; flex-direction: column; align-items: center; padding: 0px 20px; max-width: 450px; } .message__title { font-size: 22px; font-weight: 100; margin-top: 15px; color: #47494E; margin-bottom: 8px; } p { -webkit-margin-after: 0px; -webkit-margin-before: 0px; font-size: 15px; color: #7F828B; line-height: 21px; margin-bottom: 4px; } .btn { text-decoration: none; padding: 8px 15px; border-radius: 4px; margin-top: 10px; font-size: 14px; color: #7F828B; border: 1px solid #7F828B; } .hk-logo, .app-icon { fill: #DBE1EC; } .info { fill: #9FABBC; } body.friendly { background: -webkit-linear-gradient(-45deg, #8363a1 0%, #74a8c3 100%); background: linear-gradient(135deg, #8363a1 0%, #74a8c3 100%); } body.friendly .message__title { color: #fff; } body.friendly p { color: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.6); } body.friendly .hk-logo, body.friendly .app-icon { fill: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.9); } body.friendly .info { fill: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.9); } body.friendly .btn { color: #fff; border: 1px solid rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.9); } .info_area { position: fixed; right: 12px; bottom: 12px; } .logo { position: fixed; left: 12px; bottom: 12px; } </style> <base target=_parent /> </head> <body> <div class=spacer></div> <div class=message> <svg width=49 height=51 xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"><path d="M3.9468 10.0288L20.5548.995c2.4433-1.3267 5.45-1.3267 7.8936 0l16.6078 9.0338C47.4966 11.3585 49 13.8102 49 16.4666V34.534c0 2.6537-1.5034 5.1082-3.9438 6.438l-16.6078 9.0307c-2.4435 1.3297-5.4503 1.3297-7.8937 0L3.9467 40.972C1.5035 39.642 0 37.1876 0 34.534V16.4667c0-2.6564 1.5034-5.108 3.9468-6.4378z" class=app-icon fill-rule=evenodd /></svg> <div class=message__title> Your request has been blocked </div> <p> If you think this is a mistake, please get in touch with the app's support team. </p> </div> <div class=logo> <svg width=85 height=24 xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"><g class=info fill-rule=evenodd><path d="M27.8866 16.836h2.373v-3.504h2.919v3.504h2.373V8.164h-2.373v3.2227h-2.919V8.164h-2.373v8.672zm10.4888 0h6.4666V14.949h-4.0935v-1.6054h2.7764v-1.8282h-2.7765v-1.4062h3.8918V8.164h-6.265v8.672zm8.8396 0h2.3256V13.824h.6526L51.89 16.836h2.5154l-1.863-3.3165c1.151-.3867 1.7325-1.1718 1.7325-2.5312 0-2.086-1.3765-2.8242-3.631-2.8242h-3.429v8.672zm2.3256-4.793v-1.9805h1.0204c.973 0 1.4.2578 1.4.9844 0 .7264-.427.996-1.4.996h-1.0204zM60.8363 17c2.112 0 4.307-1.3242 4.307-4.5 0-3.1758-2.195-4.5-4.307-4.5-2.124 0-4.319 1.3242-4.319 4.5 0 3.1758 2.195 4.5 4.319 4.5zm0-1.875c-1.2458 0-1.946-1.0313-1.946-2.625 0-1.5938.7002-2.5664 1.946-2.5664 1.234 0 1.934.9726 1.934 2.5664 0 1.5938-.7 2.625-1.934 2.625zm6.7157 1.711h2.373v-2.6954l.6764-.7734 2.0764 3.4687h2.6816l-3.2155-5.25 2.9543-3.422h-2.7527l-2.4205 3.1407V8.164h-2.373v8.672zm13.4552.1288c2.563 0 3.6782-1.3125 3.6782-3.6093V8.164H82.36v5.1798c0 1.1953-.3798 1.7343-1.329 1.7343-.9493 0-1.3408-.539-1.3408-1.7342V8.164h-2.373v5.1915c0 2.2968 1.127 3.6093 3.69 3.6093zM2.4444 0C.9214 0 0 .8883 0 2.3226v19.3548C0 23.1068.9215 24 2.4444 24h17.1112C21.0736 24 22 23.1117 22 21.6774V2.3226C21.995.8883 21.0735 0 19.5556 0H2.4444zm16.8973 1.9c.4025.0045.7583.3483.7583.7214v18.7572c0 .3776-.3558.7214-.7583.7214H2.6583c-.4025 0-.7583-.3438-.7583-.7214V2.6214c0-.3777.3558-.7214.7583-.7214h16.6834z"/><path d="M16.43 20h-2.2527v-6.8048c0-.619-.1917-.838-.3786-.9666-1.131-.7667-4.3855-.0334-6.3458.7333l-1.553.6475L5.9048 4h2.2814v6.3333c.4314-.1333.973-.2714 1.524-.3857 2.4206-.5143 4.1987-.3762 5.3586.4048.6375.4286 1.3612 1.2714 1.3612 2.8428V20zM11.57 8h2.6675c1.4042-1.75 1.9732-3.35 2.1925-4h-2.6623c-.3967.95-1.1223 2.55-2.1977 4zM5.9 20v-5.6l2.43 2.8L5.9 20z"/></g></svg> </div> </body> </html> -
أنشئ ملف
Dockerfileلتوصف عملية بناء صورة Docker لـ Wallarm:FROM ubuntu:22.04 ARG VERSION="4.10.1" ENV PORT=3000 ENV WALLARM_LABELS="group=heroku" ENV WALLARM_API_TOKEN= ENV WALLARM_API_HOST="us1.api.wallarm.com" RUN apt-get -y update && apt-get -y install nginx curl && apt-get clean # Download and unpack the Wallarm all-in-one installer RUN curl -o /install.sh "https://meganode.wallarm.com/$(echo "$VERSION" | cut -d '.' -f 1-2)/wallarm-$VERSION.x86_64-glibc.sh" \ && chmod +x /install.sh \ && /install.sh --noexec --target /opt/wallarm \ && rm -f /install.sh # Set Tarantool's $PORT variable explicitly as it conflicts with Heroku's $PORT RUN sed -i '/^\[program:tarantool\]$/a environment=PORT=3313' /opt/wallarm/etc/supervisord.conf # Run supervisord in background. Our foreground process is the Heroku app itself RUN sed -i '/nodaemon=true/d' /opt/wallarm/etc/supervisord.conf # Add NGINX to supervisord RUN printf "\n\n[program:nginx]\ncommand=/usr/sbin/nginx\nautorestart=true\nstartretries=4294967295\n" | tee -a /opt/wallarm/etc/supervisord.conf # Heroku runs everything under an unprivileged user (dyno:dyno), so we need to grant it access to Wallarm directories RUN find /opt/wallarm -type d -exec chmod 777 {} \; # Copy NGINX configuration COPY nginx.conf /etc/nginx/nginx.conf COPY default.conf /etc/nginx/sites-available/default # Herokuesque 403 error page COPY 403.html /usr/share/nginx/html/403.html # Add entrypoint.sh COPY entrypoint.sh /entrypoint.sh # Let entrypoint modify the config under dyno:dyno and redirect NGINX logs to console RUN chmod 666 /etc/nginx/nginx.conf \ && chmod 777 /etc/nginx/ \ && ln -sf /dev/stdout /var/log/nginx/access.log \ && ln -sf /dev/stderr /var/log/nginx/error.log ENTRYPOINT ["/entrypoint.sh"]
الخطوة 2: بناء صورة Docker الخاصة بـ Wallarm لـ Heroku¶
نفذ الأوامر التالية ضمن الدليل الذي تم إنشاؤه مسبقًا:
docker build -t wallarm-heroku:4.10.1 .
docker login
docker tag wallarm-heroku:4.10.1 <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/wallarm-heroku:4.10.1
docker push <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/wallarm-heroku:4.10.1
الخطوة 3: تشغيل الصورة المُبنية Docker على Heroku¶
لنشر الصورة على Heroku:
-
انتقل إلى الجذر لدليل التطبيق الخاص بك لتنفيذ العمليات التالية.
-
بناء ملف
Dockerfileالذي سيشمل تثبيت الاعتماديات اللازمة خاصة لوقت التشغيل لتطبيقك. بالنسبة لتطبيق Node.js، استخدم القالب التالي:FROM <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/wallarm-heroku:4.10.1 ENV NODE_MAJOR=20 # Install NodeJS v20 from NodeSource RUN apt-get update \ && apt-get install -qqy ca-certificates curl gnupg \ && mkdir -p /etc/apt/keyrings \ && curl -fsSL https://deb.nodesource.com/gpgkey/nodesource-repo.gpg.key | gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/nodesource.gpg \ && echo "deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/nodesource.gpg] https://deb.nodesource.com/node_$NODE_MAJOR.x nodistro main" | tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nodesource.list \ && apt-get update \ && apt-get install nodejs -qqy \ && apt-get clean ADD . /opt/webapp WORKDIR /opt/webapp # Install dependencies and build the app RUN npm install --omit=dev ENV npm_config_prefix /opt/webapp # Note that in private spaces the `run` section of heroku.yml is ignored # See: https://devcenter.heroku.com/articles/build-docker-images-heroku-yml#known-issues-and-limitations CMD ["npm", "run", "start"] -
قم بإنشاء ملف تكوين
heroku.ymlبالمحتوى التالي: -
قم بتكيف تطبيقك للاستماع على
/tmp/nginx.socketبدلاً من$PORTلأن$PORTيتم استخدامها بواسطة NGINX. على سبيل المثال، قد يبدو التكوين على النحو التالي:// app.js const app = require('express')() let port = process.env.PORT || 3000 // Wallarm is not configured, listen on $PORT if(process.env.WALLARM_API_TOKEN) port = '/tmp/nginx.socket' // Wallarm is configured app.listen(port, (err) => { if (err) throw err console.log(`> App is listening on ${port}`) }) app.get('/', (req, res) => { res.send('This app is protected by Wallarm') }) -
أنشئ رمز العقدة التصفية من النوع المناسب لربط عينة العقدة Wallarm بالسحابة Wallarm:
- افتح وحدة التحكم Wallarm → الإعدادات → رموز API في السحابة الأمريكية أو السحابة الأوروبية.
- ابحث أو أنشئ رمز API بدور المصدر
Deploy. - انسخ هذا الرمز.
- حدد اسم مجموعة العقدة لإضافة العقدة Wallarm إليها في متغير البيئة التالي:
-
حدد المعلمات لربط العقدة بالسحابة داخل المتغيرات ذات الصلة:
-
قم بدفع تطبيقك لتنشيط إعادة التشغيل، وبالتالي نشر عقدة Wallarm:
الخطوة 4: اختبار التنصيب¶
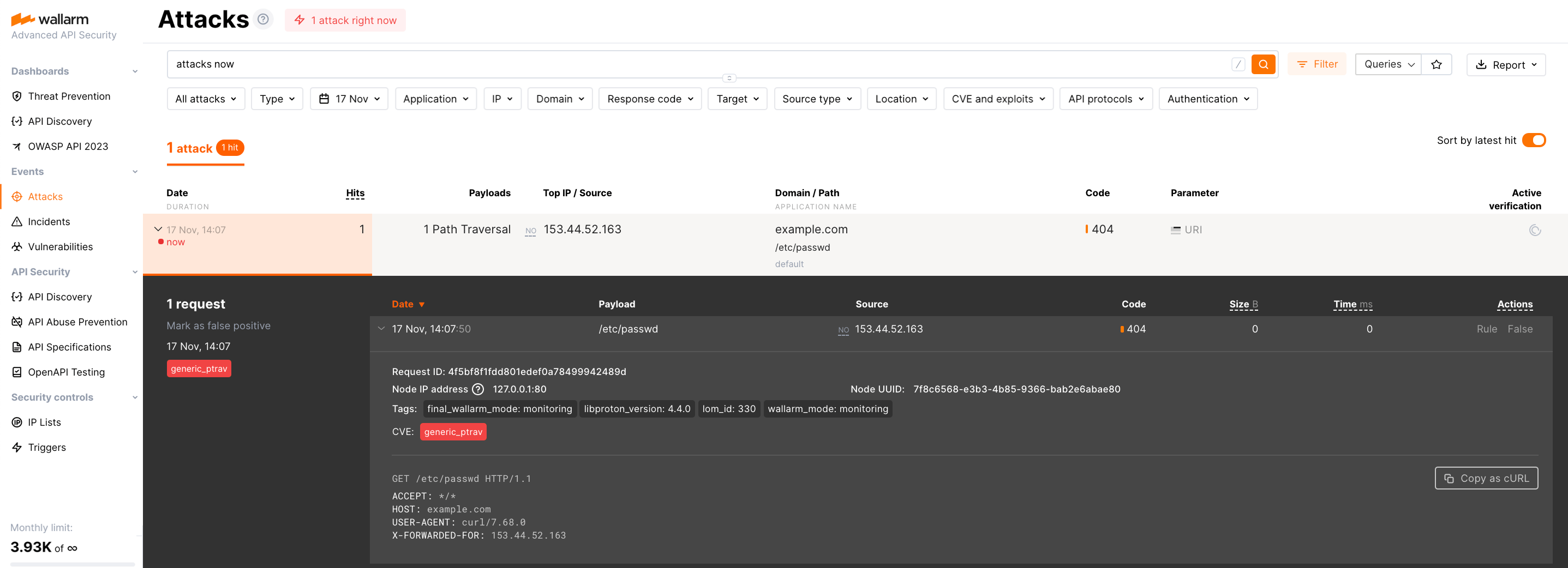
للتأكد من أن التنصيب مُشغل بنجاح، قم ببدء هجوم اختبار باستخدام استغلال التجاوز:
بما أن العقدة تعمل في أنماط التنقية في وضع المراقبة افتراضياً، فإن العقدة Wallarm لن تقوم بحظر الهجوم ولكن ستقوم بتسجيله. للتحقق من تسجيل الهجوم، انتقل إلى وحدة التحكم Wallarm → الهجمات:
تصحيح الأخطاء¶
إذا واجهت أي صعوبات مع صورة Docker الأساسية لـ Wallarm، قم بفحص سجلات Heroku للرسائل الخطأ المحتملة:
إذا كنت بحاجة إلى مساعدة خلال التنصيب، اتصل بفريق الدعم لـ Wallarm.