Detecting Security Issues  ¶
¶
Once API Attack Surface Discovery finds the external hosts of your selected domains, Wallarm checks if these hosts have any security issues. Once found, the issues are listed and described in the Security Issues section. This article describes how to use the presented information.
Exploring security issues¶
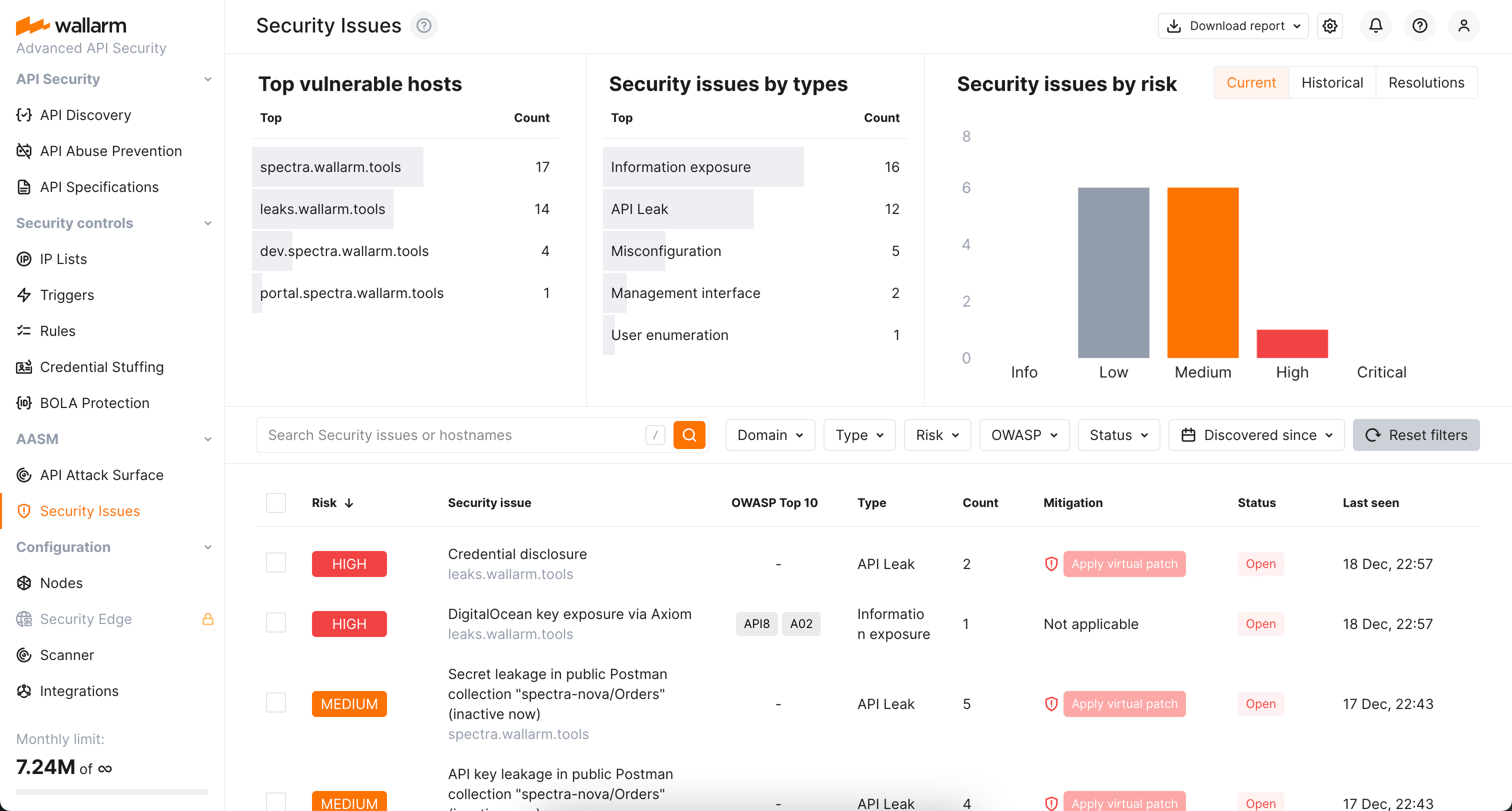
To explore the security issues found for your external hosts, in Wallarm Console go to the AASM's Security Issues section.
Here, the detailed information on found issues is presented, including:
-
Full filterable list of issues with brief and detailed description of each
-
Top vulnerable hosts list
-
Distribution of security issues by type
-
Risk level evaluation and distribution of security issues by these levels
-
Monthly historical information on detected and resolved issues for the last 6 month
List of detected issues¶
Wallarm automatically detects the following security issues:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Management interface | The remote management interface or administrative panel is publicly accessible over the Internet, exposing the system to potential attacks. Malicious adversaries could exploit this by performing password-guessing attacks, credential stuffing, or leveraging known vulnerabilities in the service to gain unauthorized access. |
| Authentication bypass | An authentication bypass vulnerability allows an attacker to circumvent the authentication mechanism and gain unauthorized access to protected resources. This security flaw can lead to unauthorized access to sensitive data, privilege escalation, or complete system compromise. |
| BOLA | Attackers can exploit API endpoints vulnerable to broken object-level authorization by manipulating the ID of an object sent within the request. This may lead to unauthorized access to sensitive data. See details. |
| File read | The application has an arbitrary file read vulnerability, allowing an attacker to read files on the server without proper authorization. This security flaw can lead to unauthorized access to sensitive information, including configuration files, source code, or user data, compromising the entire system's security. |
| File upload | An arbitrary file upload vulnerability allows a malicious user to upload potentially harmful files to a server, bypassing intended restrictions. This security flaw can lead to remote command execution through web shells, overwriting of critical system files, malware distribution, or even complete server compromise. |
| Information exposure | This vulnerability involves the unauthorized disclosure of sensitive information by an application, potentially providing attackers with sensitive data for further malicious activities. See details. |
| LFI | A local file inclusion (LFI) vulnerability allows an attacker to manipulate file paths within an application due to inadequate input validation. This security flaw can result in unauthorized access to sensitive system files, code execution, and potentially complete system compromise, often as a stepping stone for more severe exploits. |
| Misconfiguration | Security misconfigurations include vulnerabilities caused by improperly configured systems, such as enabled debug mode, excessive information in error messages, TLS/SSL misconfiguration, and missing or wrongly set CORS policy. |
| Missing authentication | Sensitive application or API endpoint is accessible without proper authentication mechanisms in place. This vulnerability can lead to unauthorized access and manipulation of sensitive data, potentially resulting in data breaches, service disruptions, or compromise of the entire system's integrity. |
| RCE | Remote code execution - this vulnerability occurs due to incorrect validation and parsing of user input. An attacker can inject malicious code into an API request and this code will be executed. Also, the attacker can try to execute certain commands for the operating system that the vulnerable application runs on. See details. |
| Open redirect | An open redirect vulnerability allows user-controlled input to specify a link to an external site for redirection. Attackers can exploit this to redirect users to malicious websites, potentially leading to phishing attacks or other security risks. |
| Sensitive API exposure | Due to improper security measures or misconfiguration, an API endpoint, documentation, or functionality is unintentionally exposed or accessible to unauthorized users. This exposure can potentially lead to more targeted attacks, unauthorized access to sensitive data, or the exploitation of system vulnerabilities by providing attackers with valuable information about the system's structure. |
| SQLi | SQL injection - vulnerability to this attack occurs due to insufficient filtration of user input. An SQL injection attack is performed by injecting a specially crafted query to an SQL database. See details. |
| SSRF | Server‑side request forgery - a successful SSRF attack may allow an attacker to make requests on behalf of the attacked web server; this potentially leads to revealing the network ports in use, scanning the internal networks, and bypassing authorization. See details. |
| Subdomain takeover | A subdomain is vulnerable to potential takeover because it points to non-existent resources. This vulnerability allows attackers to claim and control these subdomains, potentially leading to phishing attacks, data theft, or reputation damage for the original domain owner. |
| User enumeration | A vulnerability allows the unauthorized enumeration of user accounts or sensitive data through system responses. This weakness can lead to unauthorized access, targeted attacks, or serve as a starting point for further system exploitation. |
| Vulnerable component | Using obsolete software components containing known vulnerabilities poses a risk as it allows potential attackers to exploit known vulnerabilities. Furthermore this indicates insufficient patch management processes within the organization. |
| XSS | Cross‑site scripting - a cross‑site scripting attack allows an attacker to execute a prepared arbitrary code in a user's browser. See details. |
| XXE | Attack on XML external entity - the vulnerability allows an attacker to inject an external entity in an XML document to be evaluated by an XML parser and then executed on the target web server. See details. |
| API leak | A leaked API key can allow attackers to impersonate authorized users, access confidential financial data, and even manipulate transaction flows. See details. |
| Vulnerable software | Vulnerable software versions pose a significant risk of unauthorized access to systems, stolen data, malware, or operation disruption. The vulnerability has a high risk of exploitation, as the attackers actively seek out known vulnerabilities in outdated software. |
Issue details and lifecycle¶
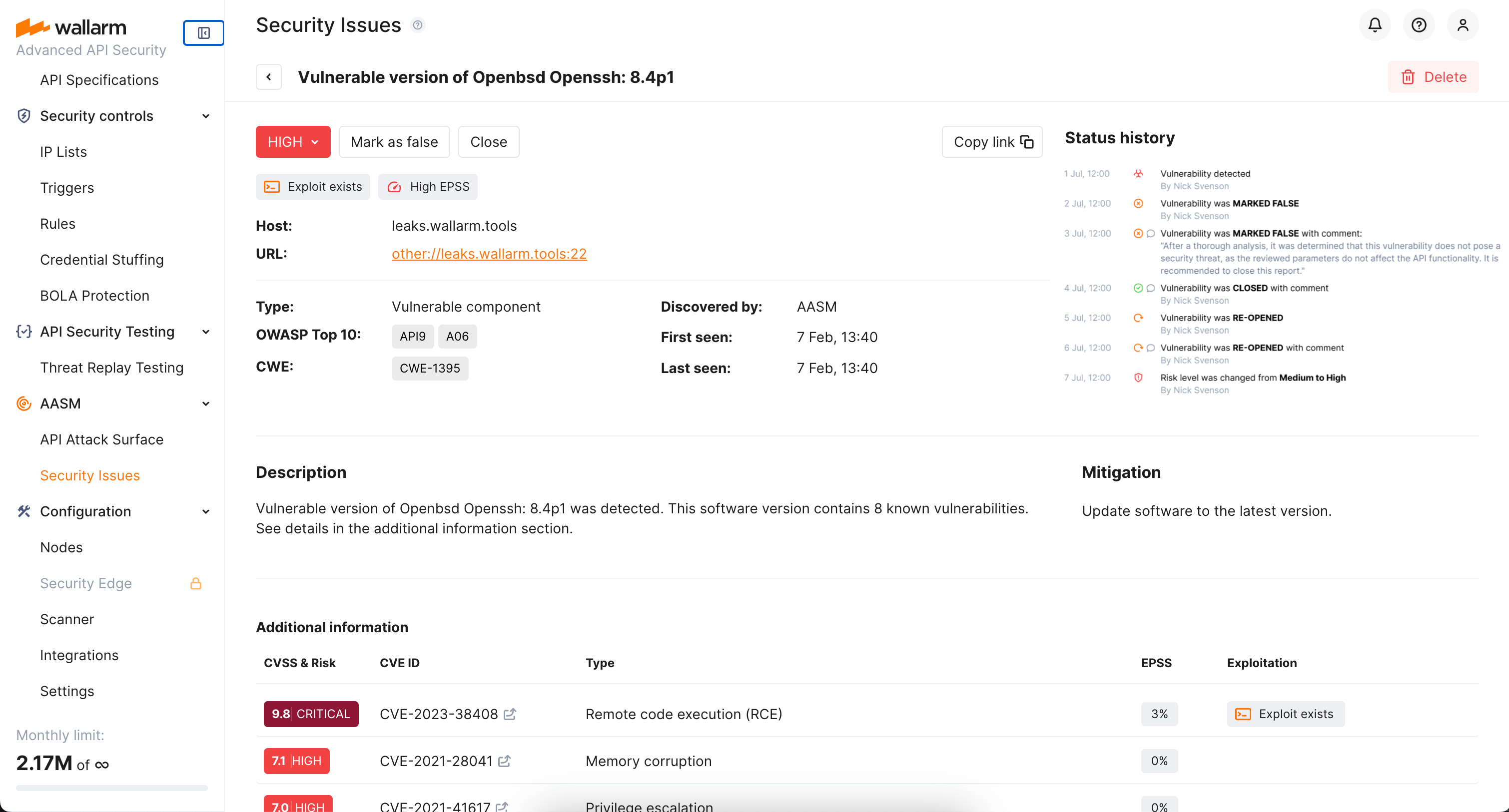
Wallarm provides detailed information on each detected security issues to allow clear understanding of what is happening and what can be done. Click the issue in the list to open its details, such as:
- Basic info (type, host and url, first and last seen time)
- Detailed Description
- Measures for Mitigation
- Information on linked CVEs ranked by risk as Additional information
Issue lifecycle
Once a security issue is detected, it obtains the Open status meaning some measures are required to mitigate it. In the issue details, you can close it (means it was resolved) or mark as false.
It is useful to provide comment on each status change, giving others the full view of what is the reason of change. Author and time of change are tracked automatically.
Issues can be re-opened. For your to be on track, the full history of status changes with comments is displayed in the Status history section.
You can also re-evaluate and adjust the risk level of the issue.
Issue risk level¶
Each discovered security issue is automatically assessed by how much risk it poses as described in the table.
| Risk | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Critical | The vulnerability's presence may lead to a system compromise, allowing an attacker to remotely execute code or cause a denial of service (DoS) or service degradation. Immediate reaction is required. |
|
| High | The presence of the vulnerability may lead to partial system compromise, such as database access or limited access to the filesystem. In specific circumstances (e.g., if special requirements are met or if chained with other vulnerabilities), the vulnerability may lead to system compromise (e.g., remote code execution). |
|
| Medium | The vulnerability may lead to bypassing security controls, limited exposure or access, but without full compromise. It can allow access to sensitive data or configurations and potentially be leveraged in a more complex attack chain. |
|
| Low | The vulnerability has minimal impact and does not directly lead to significant damage or exploitation as requirements/conditions are too complex. However, it can be combined with other vulnerabilities to escalate an attack. |
|
| Info | The issue does not pose an immediate security risk but should still be reviewed for potential manual validation. It often involves exposure of non-critical data or violation of best practices. |
|
* If the software version contains multiple CVEs, including critical ones, the overall risk level is assessed as high. The risk level is reduced by one level because the presence of a vulnerable version does not explicitly indicate the existence of the vulnerability. For example, the vulnerability may occur only in a specific, non-default configuration or require certain conditions to be met.
You can re-evaluate and manually adjust the risk level at any moment.
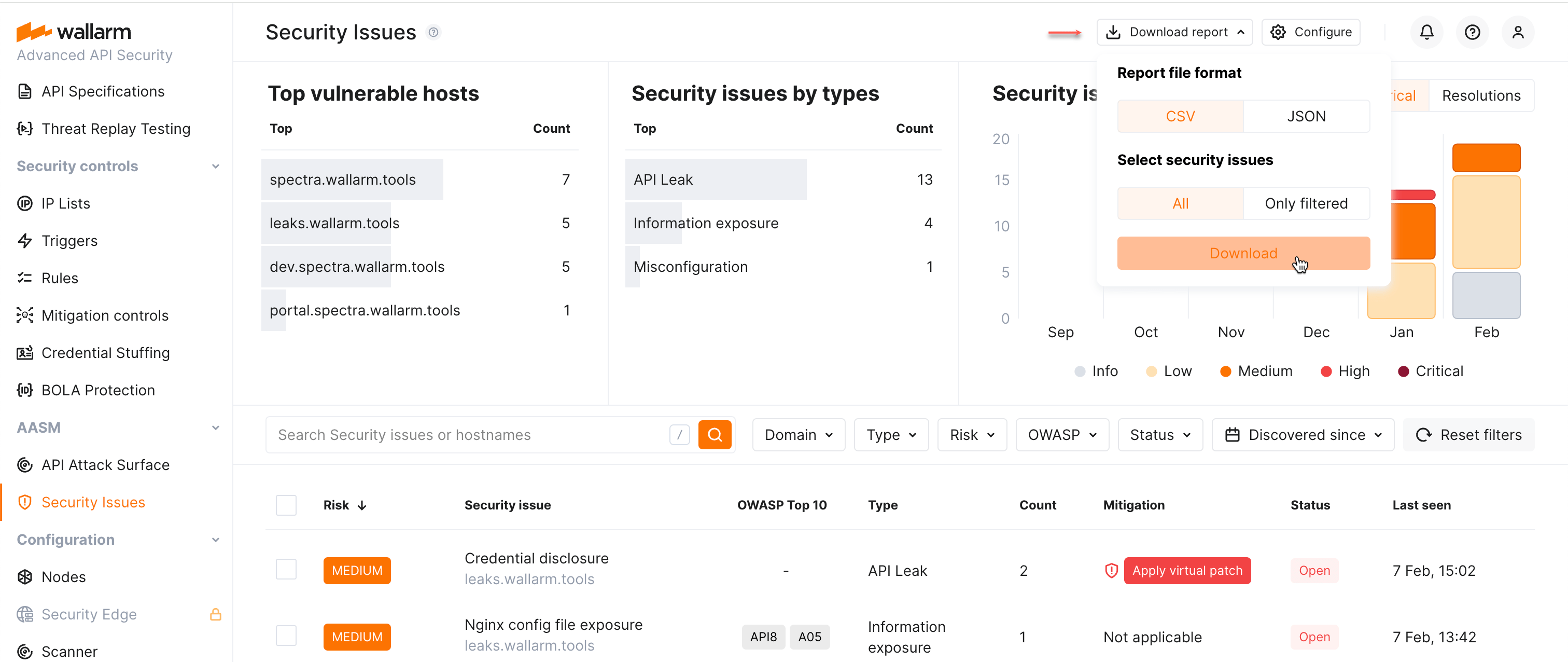
Security issue reports¶
You can get report on all or filtered security issues in CSV or JSON format using the Download report button.
Information of you choice about security issues is also included into the detailed DOCX report on your API attack surface.
Notifications¶
Email¶
You automatically receive notifications to your personal email (the one you use to log in) about discovered hosts and security issues, including:
-
Daily critical security issues (new only) - all critical security issues opened for the day, sent once a day with a detailed description of each issue and instructions on how to mitigate it.
-
Daily security issues (new only) - statistics for security issues opened for the day, sent once a day with information on how many issues of every risk level were found and general action items for mitigation.
-
Weekly AASM statistics - information about hosts, APIs, and statistics for security issues discovered for your configured domains within last week.
The notifications are enabled by default. You can unsubscribe at any moment and configure any additional emails to get all or some of these notifications in Wallarm Console → Configuration → Integrations → Email and messengers → Personal email (you email) or Email report (extra emails) as described here.
Instant notification¶
You can configure instant notification for the new and re-opened security issues. Select all or only some risk levels that should trigger notification. Separate message will be sent for each security issue.
Example:
[Wallarm System] New security issue detected
Notification type: security_issue
New security issue was detected in your system.
ID: 106279
Title: Vulnerable version of Nginx: 1.14.2
Host: <HOST_WITH_ISSUE>
Path:
Port: 443
URL: <URL_WITH_ISSUE>
Method:
Discovered by: AASM
Parameter:
Type: Vulnerable component
Risk: Medium
More details:
Client: <YOUR_COMPANY_NAME>
Cloud: US
You can configure instant notification for the security issues in Wallarm Console → Configuration → Integrations → YOUR_INTEGRATION as described in your integration documentation.
API leaks¶
Among other types of security issues, Wallarm detects cases of public exposure of API credentials (API leaks). The leaked API keys can allow attackers to impersonate authorized users, access confidential financial data, and even manipulate transaction flows.
Wallarm searches for the API leak security issues with the following two-step procedure:
-
Passive scan: checks public resources for published (leaked) data related to these domains.
-
Active scan: automatically searches the listed domains for subdomains. Then - as an unauthenticated user - sends requests to their endpoints and checks responses and the source code of pages for the presence of sensitive data. The following data is searched for: credentials, API keys, client secrets, authorization tokens, email addresses, public and private API schemas (API specifications).
You can manage the decisions on what to do with the found leaks:
-
If you have a deployed Wallarm node(s), apply a virtual patch to block all attempts to use the leaked API credentials.
A virtual patch rule will be created.
Note that creating virtual patch is only possible when the leaked secret value is 6 or more symbols or regular expression is no more than 4096 symbols -
Not applicableremediation status will be displayed if these conditions are not met. The limitations aim to prevent the legitimate traffic blocking. -
Mark the leak as false if you think it was added by mistake.
-
Close the leaks to mark that the problem is solved.
-
Even if a leak is closed, it is not deleted. Reopen it to mark that problem is still actual.
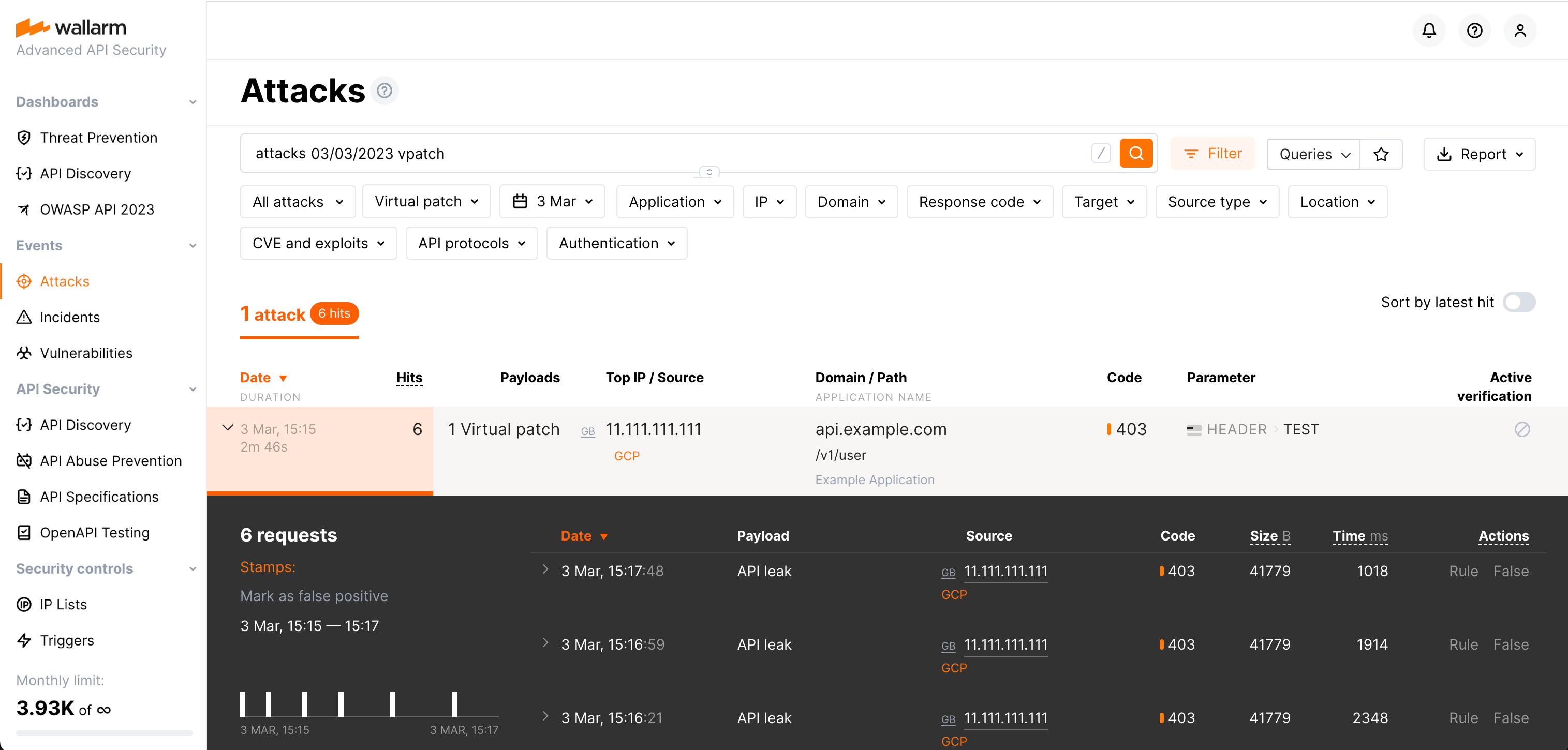
Viewing requests blocked by virtual patches
You can view requests blocked by virtual patches in Wallarm Console → Attacks by setting the Type filter to Virtual patch (vpatch).
Note that this filter will list not only the virtual patch events caused by the Security Issues functionality but also all the other virtual patches, created for different purposes.