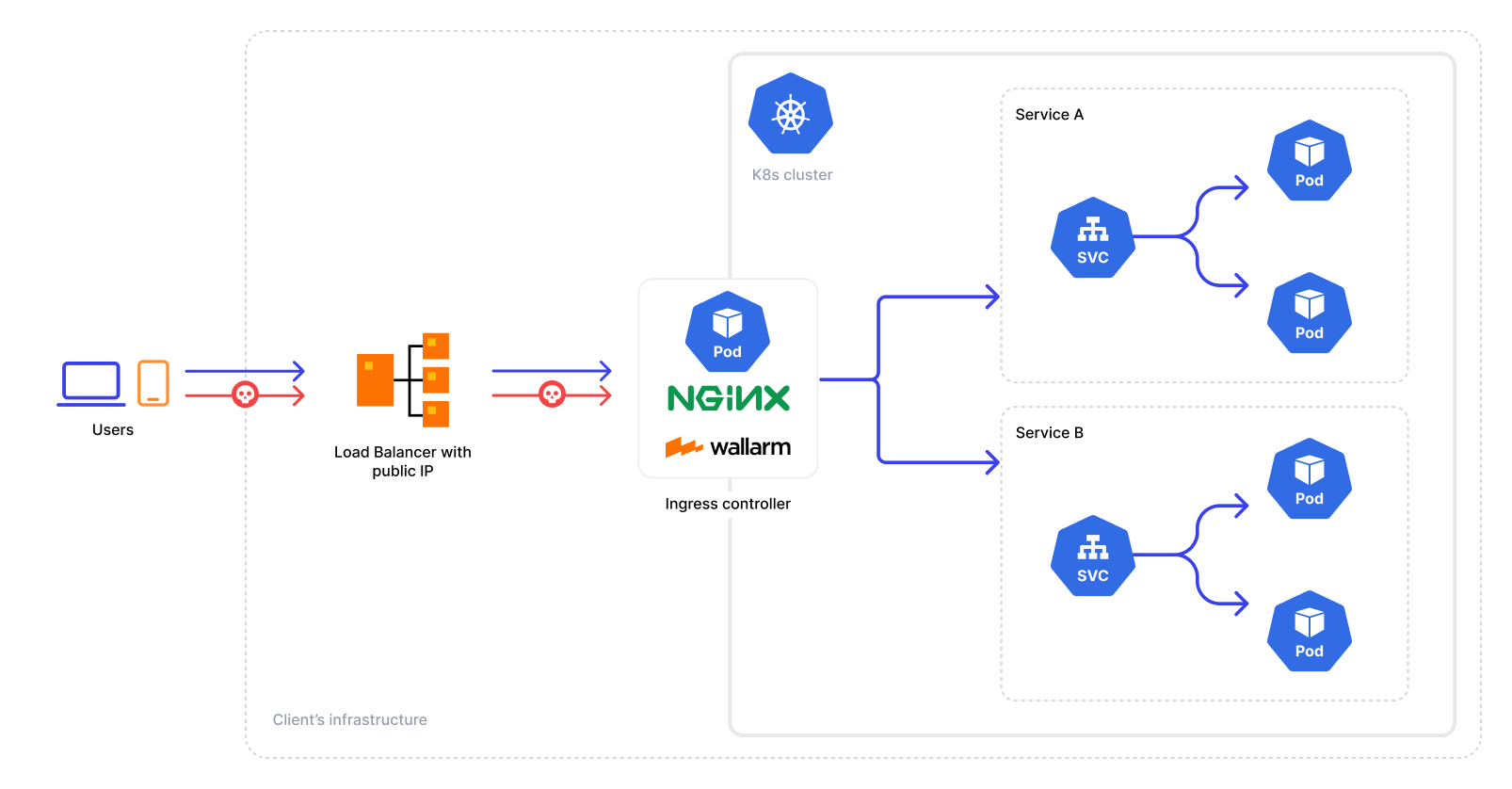
Deploying NGINX Ingress Controller with Integrated Wallarm Services¶
These instructions provide you with the steps to deploy the Wallarm NGINX-based Ingress controller to your K8s cluster. The solution is deployed from the Wallarm Helm chart.
The solution is built on the Community Ingress NGINX Controller with integrated Wallarm services. The latest version uses Community Ingress NGINX Controller 1.11.5 with NGINX stable 1.25.5.
It has the following architecture:
Use cases¶
Among all supported Wallarm deployment options, this solution is the recommended one for the following use cases:
-
There is no Ingress controller and security layer routing traffic to Ingress resources compatible with Community Ingress NGINX Controller.
-
You are currently using the Community Ingress NGINX Controller and are in search of a security solution that offers both the standard controller functionality and enhanced security features. In this case, you can effortlessly switch to the Wallarm-NGINX Ingress Controller detailed in these instructions. Simply migrate your existing configuration to a new deployment to complete the replacement.
For simultaneous use of both the existing Ingress controller and the Wallarm controller, refer to the Ingress Controller chaining guide for configuration details.
Requirements¶
-
Kubernetes platform version 1.26-1.30
-
Helm package manager
-
Compatibility of your services with the Community Ingress NGINX Controller version 1.11.5
-
Access to the account with the Administrator role in Wallarm Console for the US Cloud or EU Cloud
-
Access to
https://us1.api.wallarm.comfor working with US Wallarm Cloud or tohttps://api.wallarm.comfor working with EU Wallarm Cloud -
Access to
https://charts.wallarm.comto add the Wallarm Helm charts. Ensure the access is not blocked by a firewall -
Access to the Wallarm repositories on Docker Hub
https://hub.docker.com/r/wallarm. Make sure the access is not blocked by a firewall -
Access to the IP addresses below for downloading updates to attack detection rules and API specifications, as well as retrieving precise IPs for your allowlisted, denylisted, or graylisted countries, regions, or data centers
See also
Known restrictions¶
-
Operation without the postanalytics module is not supported.
-
Scaling down postanalytics module may result in a partial loss of attack data.
Installation¶
-
Install the Wallarm Ingress controller.
-
Enable traffic analysis for your Ingress.
-
Check the Wallarm Ingress controller operation.
Step 1: Installing the Wallarm Ingress Controller¶
To install the Wallarm Ingress Controller:
-
Generate a filtering node token of the appropriate type:
-
Create a Kubernetes namespace to deploy the Helm chart with the Wallarm Ingress controller:
-
Add the Wallarm chart repository:
-
Create the
values.yamlfile with the Wallarm configuration. Example of the file with the minimum configuration is below.When using an API token, specify a node group name in the
nodeGroupparameter. Your node will be assigned to this group, shown in the Wallarm Console's Nodes section. The default group name isdefaultIngressGroup.You can also store the Wallarm node token in Kubernetes secrets and pull it to the Helm chart. Read more
Deployment from your own registries
You can overwrite elements of the
values.yamlfile to install the Wallarm Ingress controller from the images stored in your own registries. -
Install the Wallarm packages:
helm install --version 6.2.0 <RELEASE_NAME> wallarm/wallarm-ingress -n <KUBERNETES_NAMESPACE> -f <PATH_TO_VALUES><RELEASE_NAME>is the name for the Helm release of the Ingress controller chart<KUBERNETES_NAMESPACE>is the Kubernetes namespace you have created for the Helm chart with the Wallarm Ingress controller<PATH_TO_VALUES>is the path to thevalues.yamlfile
Step 2: Enabling traffic analysis for your Ingress¶
kubectl annotate ingress <YOUR_INGRESS_NAME> -n <YOUR_INGRESS_NAMESPACE> nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/wallarm-mode=monitoring
kubectl annotate ingress <YOUR_INGRESS_NAME> -n <YOUR_INGRESS_NAMESPACE> nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/wallarm-application="<APPLICATION_ID>"
-
<YOUR_INGRESS_NAME>is the name of your Ingress -
<YOUR_INGRESS_NAMESPACE>is the namespace of your Ingress -
<APPLICATION_ID>is a positive number that is unique to each of your applications or application groups. This will allow you to obtain separate statistics and to distinguish between attacks aimed at the corresponding applications
Step 3: Checking the Wallarm Ingress Controller operation¶
-
Get the list of pods:
The Wallarm pod status should be STATUS: Running and READY: N/N:
-
Send the request with the test Path Traversal attack to the Ingress Controller Service:
If the filtering node is working in the
blockmode, the code403 Forbiddenwill be returned in the response to the request and the attack will be displayed in Wallarm Console → Attacks.
ARM64 deployment¶
With the NGINX Ingress controller's Helm chart version 4.8.2, ARM64 processor compatibility is introduced. Initially set for x86 architectures, deploying on ARM64 nodes involves modifying the Helm chart parameters.
In ARM64 settings, Kubernetes nodes often carry an arm64 label. To assist the Kubernetes scheduler in allocating the Wallarm workload to the appropriate node type, reference this label using nodeSelector, tolerations, or affinity rules in the Wallarm Helm chart configuration.
Below is the Wallarm Helm chart example for Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), which uses the kubernetes.io/arch: arm64 label for relevant nodes. This template is modifiable for compatibility with other cloud setups, respecting their ARM64 labeling conventions.
controller:
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/arch: arm64
admissionWebhooks:
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/arch: arm64
patch:
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/arch: arm64
wallarm:
postanalytics:
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/arch: arm64
enabled: true
token: "<NODE_TOKEN>"
apiHost: "us1.api.wallarm.com" # if using EU Cloud, comment out this line
# If using an API token, uncomment the following line and specify your node group name
# nodeGroup: defaultIngressGroup
controller:
tolerations:
- key: kubernetes.io/arch
operator: Equal
value: arm64
effect: NoSchedule
admissionWebhooks:
patch:
tolerations:
- key: kubernetes.io/arch
operator: Equal
value: arm64
effect: NoSchedule
wallarm:
postanalytics:
tolerations:
- key: kubernetes.io/arch
operator: Equal
value: arm64
effect: NoSchedule
enabled: true
token: "<NODE_TOKEN>"
apiHost: "us1.api.wallarm.com" # if using EU Cloud, comment out this line
# If using an API token, uncomment the following line and specify your node group name
# nodeGroup: defaultIngressGroup
Deployment from your own registries¶
If you cannot pull the Docker images from the Wallarm public repository due to some reasons, for example because you company security policy restricts usage of any external resources, instead you can:
-
Clone these images to your private registry.
-
Install Wallarm NGINX-based Ingress controller using them.
The following Docker images are used by the Helm chart for NGINX-based Ingress Controller deployment:
To install Wallarm NGINX-based Ingress controller using images stored in your registry, overwrite the values.yaml file of Wallarm Ingress controller Helm chart:
controller:
image:
## The image and tag for wallarm nginx ingress controller
##
registry: <YOUR_REGISTRY>
image: wallarm/ingress-controller
tag: <IMAGE_TAG>
wallarm:
helpers:
## The image and tag for the helper image
##
image: <YOUR_REGISTRY>/wallarm/node-helpers
tag: <IMAGE_TAG>
Then run installation using your modified values.yaml.
Configuration¶
After the Wallarm Ingress controller is successfully installed and checked, you can make advanced configurations to the solution such as:
To find parameters used for advanced configuration and appropriate instructions, please follow the link.