Protection Against Forced Browsing¶
A forced browsing attack is one of the attack types not detected by Wallarm out-of-the-box, its detection should be appropriately configured as this guide describes.
Forced browsing attacks are characterized by a large number of response codes 404 returned to requests to different URIs for a limited timeframe.
This attack aims to enumerate and access hidden resources (e.g. directories and files containing information on application components). The forced browsing attack type usually allows attackers to collect information about the application and perform other attack types by exploiting this information.
Configuration method¶
Depending on your subscription plan, one of the following configuration methods for brute force protection will be available:
-
Mitigation controls (Advanced API Security subscription)
-
Triggers (Cloud Native WAAP subscription)
Mitigation control-based protection  ¶
¶
Wallarm's Advanced API Security subscription provides advanced enumeration attack protection, including protection from forced browsing attacks.
Trigger-based protection¶
Configuring¶
Consider the example below to learn how to configure forced browsing protection.
Let us say you own the online book-sale application. You want to prevent malicious actors from trying names of hidden directories and files under its book-sale-example.com domain (forced browsing attack). To provide this protection, for your domain, you can limit number of 404 responses per time interval, and set to block IPs exceeding this limit:
To provide this protection:
-
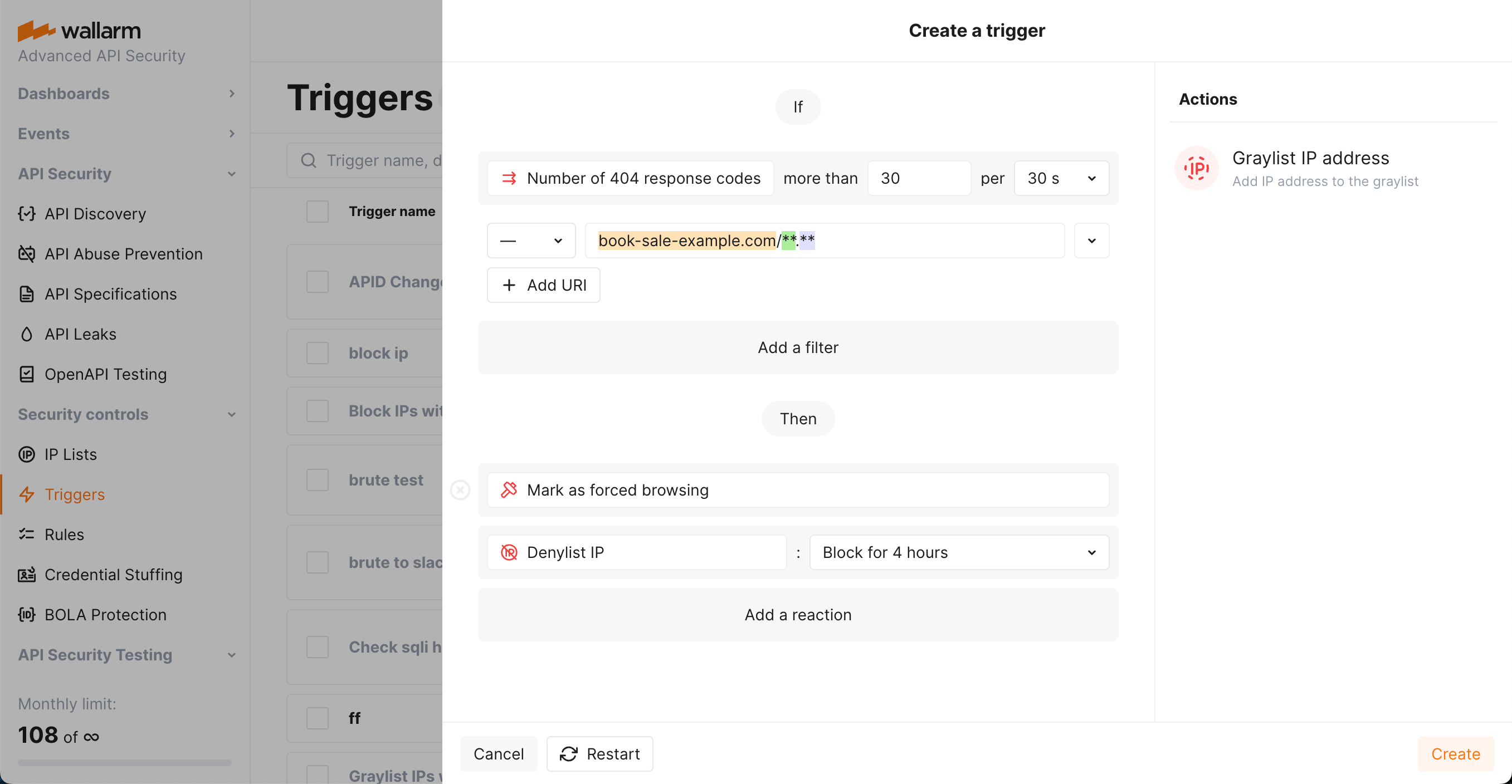
Open Wallarm Console → Triggers and open the window for trigger creation.
-
Select the Forced browsing condition.
-
Set the threshold for the number of 404 response codes returned to the requests having the same origin IP requests to 30 per 30 seconds.
Note that these are the example values - when configuring trigger for your own traffic, you should define a threshold considering your legitimate usage statistics.
Allowed threshold time periods
When adjusting the threshold time period, the value must be a multiple of 30 seconds or 10 minutes, depending on the selected unit.
-
Set the URI filter as displayed on the screenshot, including:
-
**wildcard in the path meaning "any number of components". They will cover all the addresses under thebook-sale-example.com. -
Besides configuring the pattern we need in this example, you can enter specific URIs (for example, URI of your resource file directory) or set trigger to work at any endpoint by not specifying any URI.
- If using nested URIs, consider trigger processing priorities.
-
-
Do not use in this case:
- The Application filter, but be aware that you can use it to set triggers only to react to the requests targeting domains or specific endpoints of selected applications.
- The IP filter, but be aware that you can use it to set triggers only to react to specific IPs originating requests.
-
Select the Denylist IP address -
Block for 4 hourtrigger reaction. Wallarm will put origin IP to the denylist after the threshold is exceeded and block all further requests from it.Note that even if the bot IP is placed into the denylist by forced browsing protection, by default, Wallarm collects and displays statistics regarding blocked requests originating from it.
-
Select the Mark as forced browsing trigger reaction. Requests received after exceeding the threshold will be marked as the forced browsing attack and displayed in the Attacks section of Wallarm Console. Sometimes, you can use this reaction alone to have information about the attack but not to block anything.
-
Save the trigger and wait for the Cloud and node synchronization completion (usually, it takes 2-4 minutes).
You can configure several triggers for forced browsing protection.
Testing¶
Testing in your environment
To test the Forced browsing trigger in your environment, in the trigger and the requests below, replace the domain with any public one (e.g. example.com).
To test the trigger described in the Configuring section:
-
Send the number of requests that exceeds the configured threshold to the protected URI. For example, 50 requests to
https://book-sale-example.com/config.json(matcheshttps://book-sale-example.com/**.**): -
If the trigger reaction is Denylist IP address, open Wallarm Console → IP lists → Denylist and check that source IP address is blocked.
If the trigger reaction is Graylist IP address, check the section IP lists → Graylist of Wallarm Console.
-
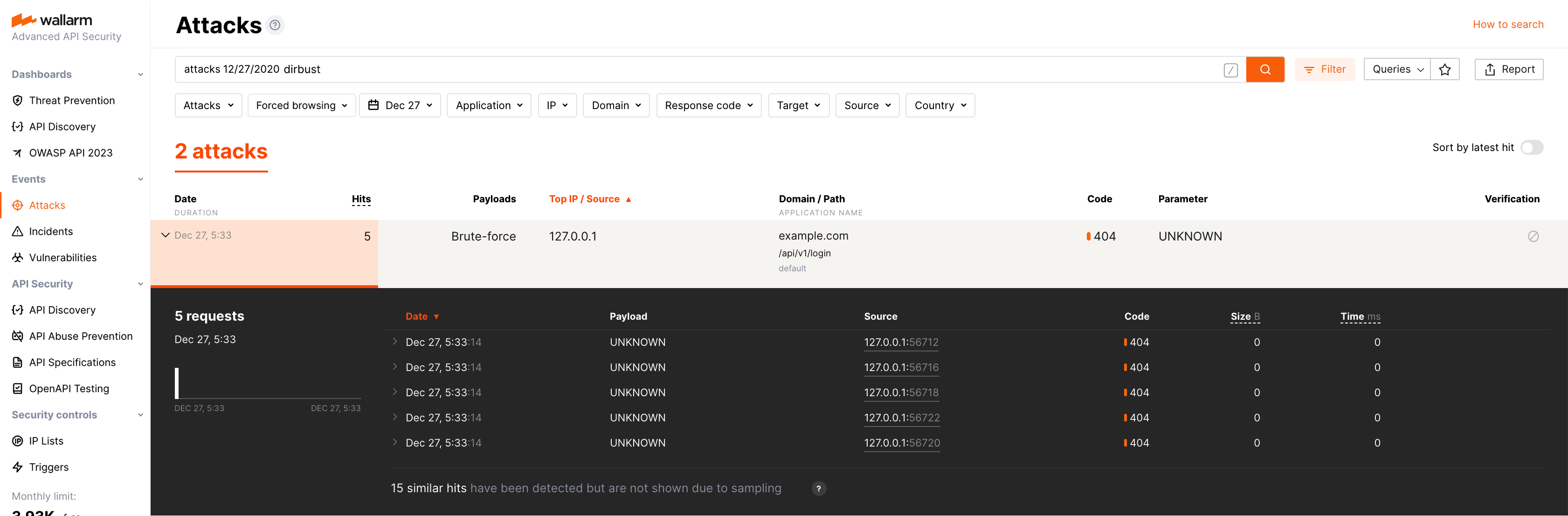
Open the section Attacks and check that requests are displayed in the list as a forced browsing attack.
The number of displayed requests corresponds to the number of requests sent after exceeding the trigger threshold (more details on detecting behavioral attacks). If this number is higher than 5, request sampling is applied and request details are displayed only for the first 5 hits (more details on requests sampling).
To search for forced browsing attacks, you can use the
dirbustfilter. All filters are described in the instructions on search use.
Requirements and restrictions¶
Requirements
To protect resources from forced browsing attacks, real clients' IP addresses are required. If the filtering node is deployed behind a proxy server or load balancer, configure displaying real clients' IP addresses.
Restrictions
When searching for forced browsing attack signs, Wallarm nodes analyze only HTTP requests that do not contain signs of other attack types.