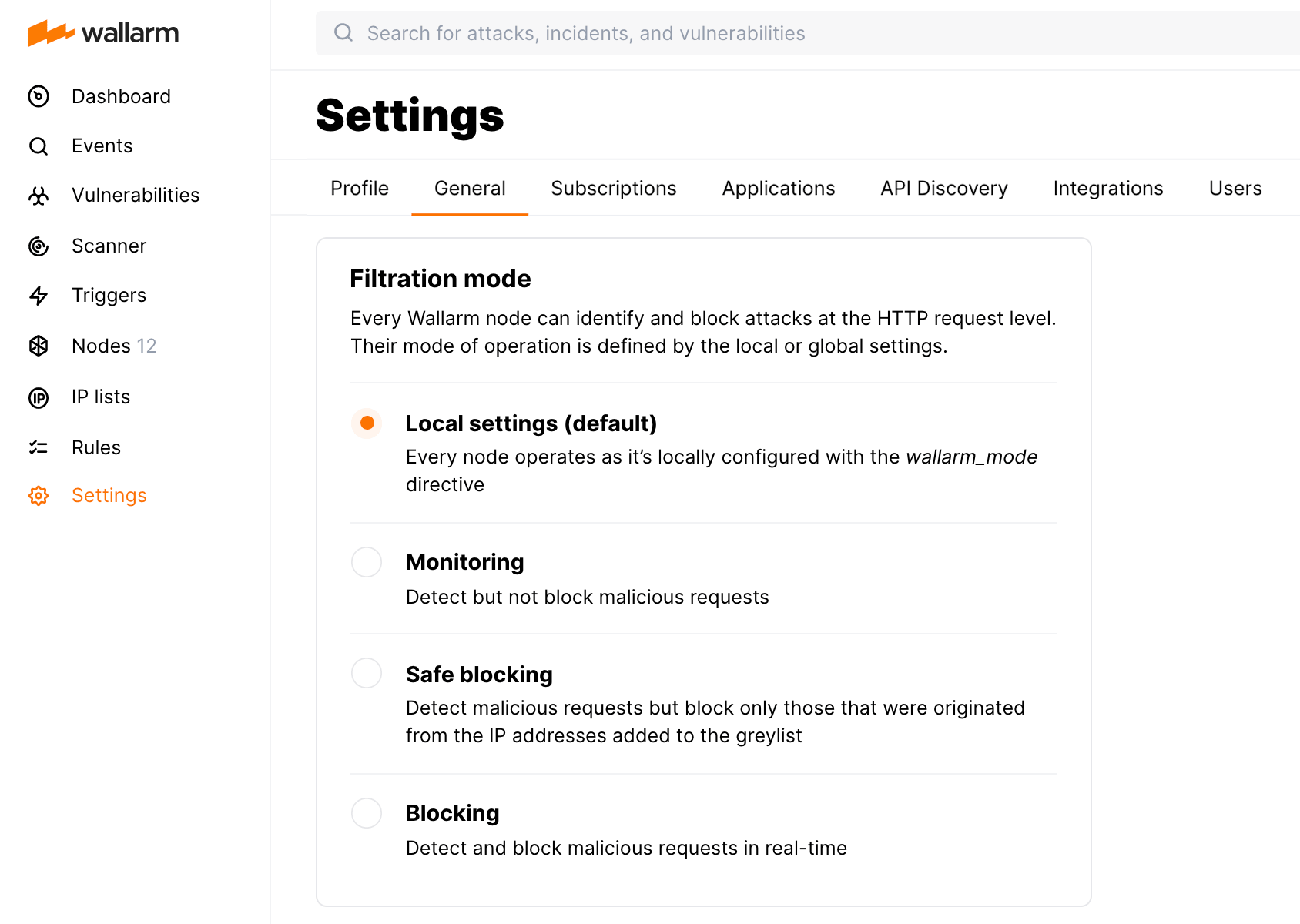
Filtration Mode¶
Filtration mode defines the filtering node behavior when processing incoming requests. These instructions describe available filtration modes and their configuration methods.
Available filtration modes¶
The Wallarm filtering node can process incoming requests in the following modes (from the mildest to the strictest):
-
off -
monitoring -
safe_blocking- blocks only where it is safe to block (graylist). -
block
| Wallarm node behavior | off | monitoring | safe_blocking | block |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analyzes incoming requests for input validation, virtual patch, and regex-based malicious payloads | - | + | + | + |
| Uploads malicious requests to the Wallarm Cloud so that they are displayed in the event list | - | + | + | + |
| Blocks malicious requests | - | - | Only those originated from graylisted IPs | + |
| Blocks requests originated from denylisted IPssee exception (IPs added manually and automatically by multi-attack protection and behavioral protection: API abuse prevention, manual BOLA, brute force and forced browsing) | - | + | + | + |
| Blocks requests originated from graylisted IPs (IPs added manually and automatically by the same protection measures as for denylist) | - | - | Only those containing malicious payloads | - |
| Allows requests originated from allowlisted IPs | - | + | + | + |
Exception for denylist
If wallarm_acl_access_phase off, the Wallarm node does not block requests from denylisted IPs in the monitoring mode.
Configuration methods¶
The filtration mode can be configured in the following ways:
Priorities of the filtration mode configuration methods are determined in the wallarm_mode_allow_override directive. By default, the settings specified in Wallarm Console have a higher priority than the wallarm_mode directive regardless of its value severity.
Setting wallarm_mode directive¶
You can set the node filtration mode on the node side using the wallarm_mode directive. Peculiarities of how the wallarm_mode directive is set in different deployments are described below.
Note that described configuration is applicable only for in-line deployments - for out-of-band (OOB) solutions only the monitoring mode can be active.
For the NGINX-based nodes installed on Linux with all-in-one installer, you can set the wallarm_mode directive in the filtering node configuration file. You can define filtration modes for different contexts. These contexts are ordered from the most global to the most local in the following list:
http: the directives are applied to the requests sent to the HTTP server.server: the directives are applied to the requests sent to the virtual server.location: the directives are only applied to the requests containing that particular path.
If different wallarm_mode directive values are defined for the http, server, and location blocks, the most local configuration has the highest priority.
See configuration example below.
When deploying the NGINX-based Wallarm nodes via docker containers, pass the WALLARM_MODE environment variable:
docker run -d -e WALLARM_API_TOKEN='XXXXXXX' -e WALLARM_LABELS='group=<GROUP>' -e NGINX_BACKEND='example.com' -e WALLARM_API_HOST='us1.api.wallarm.com' -e WALLARM_MODE='monitoring' -p 80:80 wallarm/node:6.2.0
Alternatively, include the corresponding parameter in the configuration file and run the container mounting this file.
For NGINX Ingress controller, use the wallarm-mode annotation:
kubectl annotate ingress <YOUR_INGRESS_NAME> -n <YOUR_INGRESS_NAMESPACE> nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/wallarm-mode=monitoring
See example of how traffic analysis for your NGINX-based Ingress controller is enabled by setting the filtration mode to monitoring.
For the Wallarm Sidecar solution, in the Wallarm-specific part of the default values.yaml, set the mode parameter:
See details on specifying the filtration mode for Sidecar here.
For Security Edge connectors, you specify the wallarm_mode value in the Filtration mode selector during the connector deployment.
- For Native Node all-in-one installer and Docker image, use the
route_config.wallarm_modeparameter. - For Native Node Helm chart, use the
config.connector.route_config.wallarm_modeparameter.
General filtration mode¶
You can define the general filtration mode for all incoming requests using mitigation controls (Advanced API Security subscription) or rules (Cloud Native WAAP subscription)..
The general filtration mode for all incoming requests is defined by "all traffic" Real-time blocking mode mitigation control:
| Setting | Filtration mode |
|---|---|
| Inherited | Filtration mode is inherited from the all-traffic Real-time blocking mode and the configuration of the Wallarm node. |
| Excluding | off |
| Monitoring | monitoring |
| Safe blocking | safe_blocking |
| Blocking | block |
Inherited is default. You can change the global mode at any moment.
You can define the general filtration mode for all incoming requests in Settings → General in the US or EU Cloud.
The general filtration mode setting is represented as Set filtration mode default rule in the Rules section. Note that endpoint-targeted filtration rules in this section have higher priority.
Conditioned filtration mode¶
You can set filtration mode for specific branches, endpoints and relying on other conditions using mitigation controls (Advanced API Security subscription) or rules (Cloud Native WAAP subscription).
You can set filtration mode for specific branches, endpoints and relying on other conditions. Wallarm provides the Real-time blocking mode mitigation control.
Before proceeding: use the Mitigation Controls article to get familiar with how Scope and Mitigation mode are set for any mitigation control.
To create a new filtration mode mitigation control:
- Proceed to Wallarm Console → Mitigation Controls.
- Use Add control → Real-time blocking mode.
- Describe the Scope to apply the mitigation control to.
-
In the Mitigation mode section, select filtration mode for the specified scope:
Setting Filtration mode Inherited Filtration mode is inherited from the all-traffic Real-time blocking mode and the configuration of the Wallarm node. Excluding offMonitoring monitoringSafe blocking safe_blockingBlocking block -
Save changes and wait for the mitigation control compilation to complete.
You can set filtration mode for specific branches, endpoints and relying on other conditions. Wallarm provides the Set filtration mode rule to do this. Such rules have higher priority than the general filtration rule set in Wallarm Console.
To create a new filtration mode rule:
-
Proceed to Wallarm Console:
- Rules → Add rule or your branch → Add rule.
- Attacks / Incidents → attack/incident → hit → Rule.
- API Discovery (if enabled) → your endpoint → Create rule.
-
Choose Fine-tuning attack detection → Override filtration mode.
- In If request is, describe the scope to apply the rule to. If you initiated the rule for specific branch, hit or endpoint, they will define the scope - if necessary, you can add more conditions.
-
Select filtration mode for the specified scope:
Setting Filtration mode Default Filtration mode is inherited from the global filtration mode setting and the configuration of the Wallarm node. Disabled offMonitoring monitoringSafe blocking safe_blockingBlocking block -
Save changes and wait for the rule compilation to complete.
Note that to create a filtration mode rule, you can also call the Wallarm API directly.
Prioritization of methods¶
Support of the wallarm_mode_allow_override directive on the Edge node
Please note that the wallarm_mode_allow_override directive cannot be customized on the Wallarm Edge inline and connector nodes.
The wallarm_mode_allow_override directive manages the ability to apply mode rules/mitigation controls that are defined on Wallarm Console instead of using the wallarm_mode directive values from the filtering node configuration file.
The following values are valid for the wallarm_mode_allow_override directive:
-
off: mode rules/mitigation controls specified in Wallarm Console are ignored. Rules specified by thewallarm_modedirective in the configuration file are applied. -
strict: only the mode rules/mitigation controls specified in the Wallarm Cloud that define stricter filtration modes than those defined by thewallarm_modedirective in the configuration file are applied.The available filtration modes ordered from the mildest to the strictest are listed above.
-
on(by default): mode rules/mitigation controls specified in Wallarm Console are applied. Rules specified by thewallarm_modedirective in the configuration file are ignored.
The contexts in which the wallarm_mode_allow_override directive value can be defined, in order from the most global to the most local, are presented in the following list:
-
http: the directives inside thehttpblock are applied to the requests sent to the HTTP server. -
server: the directives inside theserverblock are applied to the requests sent to the virtual server. -
location: the directives inside thelocationblock are only applied to the requests containing that particular path.
If different wallarm_mode_allow_override directive values are defined in the http, server, and location blocks, then the most local configuration has the highest priority.
The wallarm_mode_allow_override directive usage example:
http {
wallarm_mode monitoring;
server {
server_name SERVER_A;
wallarm_mode_allow_override off;
}
server {
server_name SERVER_B;
wallarm_mode_allow_override on;
location /main/login {
wallarm_mode_allow_override strict;
}
}
}
This configuration example results in the following applications of the filtration mode rules from Wallarm Console:
-
The filtration mode rules defined/mitigation controls in Wallarm Console are ignored for requests sent to the virtual server
SERVER_A. There is nowallarm_modedirective specified in theserverblock that corresponds to theSERVER_Aserver, which is why themonitoringfiltration mode specified in thehttpblock is applied for such requests. -
The filtration mode rules/mitigation controls defined in Wallarm Console are applied to the requests sent to the virtual server
SERVER_Bexcept for the requests that contain the/main/loginpath. -
For those requests that are sent to the virtual server
SERVER_Band contain the/main/loginpath, the filtration mode rules defined in Wallarm Console are only applied if they define a filtration mode that is stricter than themonitoringmode.
Configuration example¶
Let us consider the example of a filtration mode configuration that uses all of the methods mentioned above.
Node configuration file¶
http {
wallarm_mode block;
server {
server_name SERVER_A;
wallarm_mode monitoring;
wallarm_mode_allow_override off;
location /main/login {
wallarm_mode block;
wallarm_mode_allow_override strict;
}
location /main/signup {
wallarm_mode_allow_override strict;
}
location /main/apply {
wallarm_mode block;
wallarm_mode_allow_override on;
}
location /main/feedback {
wallarm_mode safe_blocking;
wallarm_mode_allow_override off;
}
}
}
Settings in Wallarm Console¶
-
General filtration mode: Monitoring.
-
Conditioned filtration mode settings:
-
If the request meets the following conditions:
- Method:
POST - First part of the path:
main - Second part of the path:
apply,
then apply the Default filtration mode.
- Method:
-
If the request meets the following condition:
- First part of the path:
main,
then apply the Blocking filtration mode.
- First part of the path:
-
If the request meets the following conditions:
- First part of the path:
main - Second part of the path:
login,
then apply the Monitoring filtration mode.
- First part of the path:
-
Request examples¶
Examples of the requests sent to the configured server SERVER_A and the actions that the Wallarm filtering node applies to them are the following:
-
The malicious request with the
/newspath is processed but not blocked due to thewallarm_mode monitoring;setting for the serverSERVER_A. -
The malicious request with the
/mainpath is processed but not blocked due to thewallarm_mode monitoring;setting for the serverSERVER_A.The Blocking rule defined in Wallarm Console is not applied to it due to the
wallarm_mode_allow_override off;setting for the serverSERVER_A. -
The malicious request with the
/main/loginpath is blocked due to thewallarm_mode block;setting for the requests with the/main/loginpath.The Monitoring rule defined in Wallarm Console is not applied to it due to the
wallarm_mode_allow_override strict;setting in the filtering node configuration file. -
The malicious request with the
/main/signuppath is blocked due to thewallarm_mode_allow_override strict;setting for the requests with the/main/signuppath and the Blocking rule defined in Wallarm Console for the requests with the/mainpath. -
The malicious request with the
/main/applypath and theGETmethod is blocked due to thewallarm_mode_allow_override on;setting for the requests with the/main/applypath and the Blocking rule defined in Wallarm Console for the requests with the/mainpath. -
The malicious request with the
/main/applypath and thePOSTmethod is blocked due to thewallarm_mode_allow_override on;setting for those requests with the/main/applypath, the Default rule defined in Wallarm Console, and thewallarm_mode block;setting for the requests with the/main/applypath in the filtering node configuration file. -
The malicious request with the
/main/feedbackpath is blocked only if it originates from a graylisted IP due to thewallarm_mode safe_blocking;setting for the requests with the/main/feedbackpath in the filtering node configuration fileThe Monitoring rule defined in Wallarm Console is not applied to it due to the
wallarm_mode_allow_override off;setting in the filtering node configuration file.
Best practices on gradual filtration mode application¶
For a successful onboarding of a new Wallarm node, follow these step-by-step recommendations to switch filtration modes:
-
Deploy Wallarm filtering nodes in your non-production environments with the operation mode set to
monitoring. -
Deploy Wallarm filtering nodes in your production environment with the operation mode set to
monitoring. -
Keep the traffic flowing via the filtering nodes in all your environments (including testing and production) for 7‑14 days to give the Wallarm cloud-based backend some time to learn about your application.
-
Enable Wallarm
blockmode in all your non-production environments and use automated or manual tests to confirm that the protected application is working as expected. -
Enable Wallarm
blockmode in the production environment and use available methods to confirm that the application is working as expected.