Adding Rules in the Application Profile¶
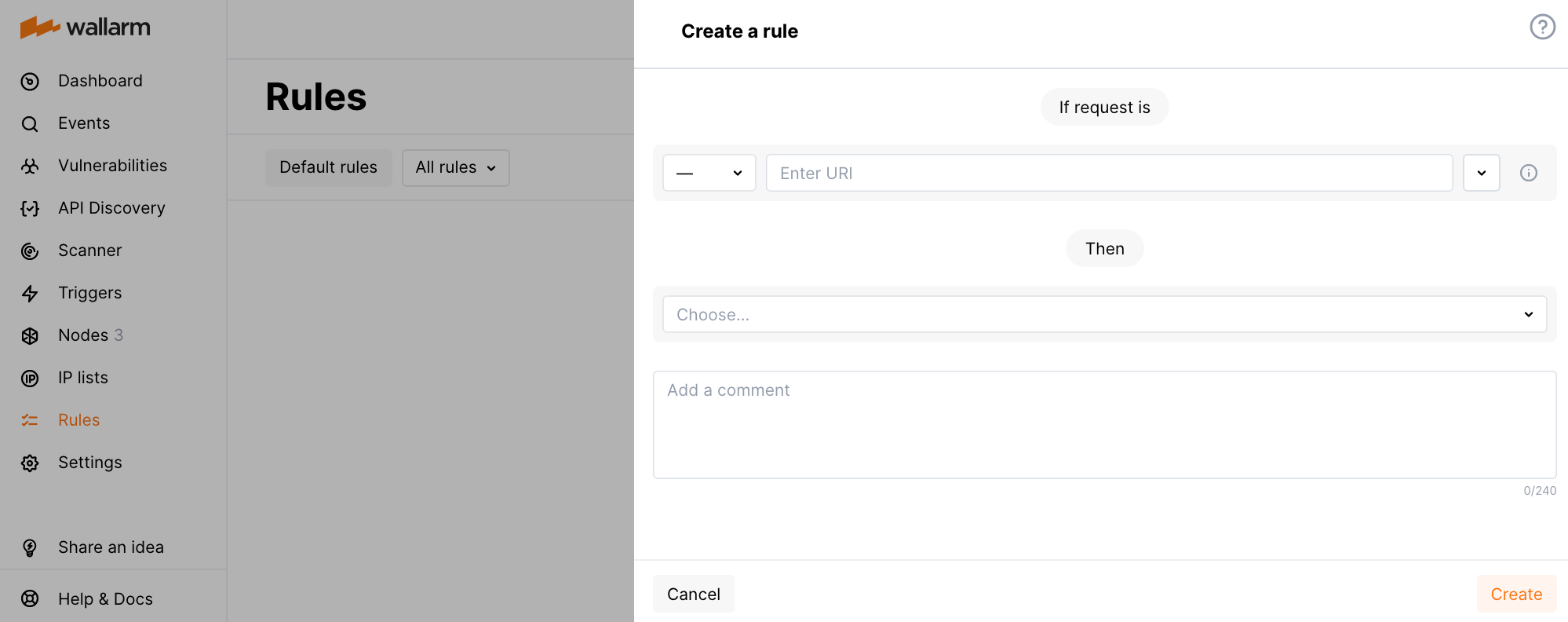
To add a new rule, go to the Rules tab.
Rules can be added to both existing and new branches. They can be created from scratch or based on one of the existing branches.
To add a rule to an existing branch, click Add rule (after hovering the mouse cursor over the branch description line, the button will appear in the pop-up menu on the right). You can also perform this operation on the rule page of this branch.
If necessary, it is possible to modify the branch to which a rule will be added. For this, click on the If request is clause in the rule-adding form and make changes to the branch description conditions. If a new branch is created, it will appear on the screen, and the application structure view will be updated.
Branch Description¶
A branch description consists of a set of conditions for various parameters that an HTTP request must fulfill; otherwise, the rules associated with this branch will not be applied. Each line in the If request is section of the rule-adding form refers to a separate condition comprised of three fields: point, type, and comparison argument. The rules described in the branch are only applied to the request if all the conditions are fulfilled.
Points¶
The point field indicates which parameter value should be extracted from the request for comparison. At present, not all of the points that can be analyzed by the filter node, are supported.
The following points are currently supported:
-
application: application ID.
-
proto: HTTP protocol version (1.0, 1.1, 2.0, ...).
-
scheme: http or https.
-
uri: part of the request URL without the domain (for example,
/blogs/123/index.php?q=aaafor the request sent tohttp://example.com/blogs/123/index.php?q=aaa). -
path, action_name, action_ext is hierarchical URI component sequence where:
- path: an array with URI parts separated by the
/symbol (the last URI part is not included in the array). If there is only one part in the URI, the array will be empty. - action_name: the last part of the URI after the
/symbol and before the first period (.). This part of the URI is always presented in the request, even if its value is an empty string. - action_ext: the part of the URI after the last period (
.). It may be missing in the request.
- path: an array with URI parts separated by the
-
query: query string parameters.
-
header: request headers. When you enter a header name, the most common values are displayed in a drop-down list. For example:
HOST,USER-AGENT,COOKIE,X-FORWARDED-FOR,AUTHORIZATION,REFERER,CONTENT-TYPE. -
method: request methods. If the value is not explicitly specified, the rule will be applied to requests with any method.
Condition types¶
EQUAL¶
The point value must match precisely with the comparison argument. For example, only example matches with the point value example.
EQUAL condition type for the HOST header value
To cover more requests with the rules, we have restricted the EQUAL condition type for the HOST header. Instead of the EQUAL type, we recommend using the type IEQUAL that allows parameter values in any register.
If you have previously used the EQUAL type, it will be automatically replaced with the IEQUAL type.
IEQUAL¶
The point value must match with the comparison argument in any case. For example: example, ExAmple, exampLe match with the point value example.
REGEX¶
The point value must match the regular expression.
Regular expression syntax
To match requests with regular expressions, the PIRE library is used. Mostly, the syntax of expressions is standard but has some specifics as described below and in the README file of PIRE repository.
Show regular expression syntax
Characters that can be used as‑is:
- Lowercase Latin letters:
a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z - Capital Latin letters:
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z - Digits:
0 1 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 - Special characters:
! " # % ' , - / : ; < = > @ ] _ ` } - Whitespaces
Characters that must be placed into square brackets [] instead of escaping with \:
. $ ^ { [ ( | ) * + ? \ & ~
Characters that must be converted to ASCII according to ISO‑8859:
- UTF‑8 characters (for example, the character
ʃconverted to ASCII isÊ)
Character groups:
.for any character except a newline()for grouping regular expressions, searching symbols present inside()or establishing a precedence order[]for a single character present inside[](case sensitive); the group can be used for the specific cases:- to ignore case (for example,
[cC]) [a-z]to match one of lowercase Latin letters[A-Z]to match one of capital Latin letters[0-9]to match one of digits[a-zA-Z0-9[.]]to match one of lowercase, or capital Latin letters, or digits, or dot
- to ignore case (for example,
Logic characters:
~is equal to NOT. The inverted expression and the character must be placed into(),
for example:(~(a))|is equal to OR&is equal to AND
Characters to specify string boundaries:
^for the start of the string$for the end of the string
Quantifiers:
*for 0 or more repetitions of the preceding regular expression+for 1 or more repetitions of the preceding regular expression?for 0 or 1 repetitions of the preceding regular expression{m}formrepetitions of the preceding regular expression{m,n}formtonrepetitions of the preceding regular expression; omittingnspecifies an infinite upper bound
Character combinations that work with specifics:
^.*$is equal to^.+$(empty values does not match with^.*$)^.?$,^.{0,}$,^.{0,n}$are equal to^.+$
Temporarily not supported:
- Character classes like
\Wfor non-alphabetics,\wfor alphabetics,\Dfor any non-digits,\dfor any decimals,\Sfor non-whitespaces,\sfor whitespaces
Not supported syntax:
- Three-digit octal codes
\NNN,\oNNN,\ONNN \cNpassing control characters via\c(for example,\cCfor CTRL+C)\Afor the start of the string\zfor the end of the string\bbefore or after the whitespace character in the end of the string??,*?,+?lazy quantifiers- Conditionals
Testing regular expressions
To test the regular expression, you can use the cpire utility on supported Debian or Ubuntu:
-
Add Wallarm repository:
sudo apt install dirmngr curl -fsSL https://repo.wallarm.com/wallarm.gpg | sudo apt-key add - sh -c "echo 'deb https://repo.wallarm.com/debian/wallarm-node stretch/2.18/' | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/wallarm.list" sh -c "echo 'deb https://repo.wallarm.com/debian/wallarm-node stretch-backports/2.18/' | sudo tee --append /etc/apt/sources.list.d/wallarm.list" # for correct Wallarm node operation, uncomment the following line in /etc/apt/sources.list`: # deb http://deb.debian.org/debian stretch-backports main contrib non-free sudo apt update -
Install the cpire utility:
-
Run the cpire utility:
-
Enter the value to check whether it matches with the regular expression. The utility will return the result:
0if the value matches with the regular expressionFAILif the value does not match with the regular expression- Error message if the regular expression is invalid
Specifics of handling the
\characterIf the expression includes
\, please escape it with[]and\(for example,[\\]).
Examples of regular expressions added via Wallarm Console
-
To match any string that includes
/.git -
To match any string that includes
.example.com -
To match any string ending with
/.example.*.com -
To match all IP addresses excluding 1.2.3.4 and 5.6.7.8
-
To match any string ending with
/.example.com.php -
To match any string that includes
sqlmapwith letters in lower and upper case:sqLmAp,SqLMap, etc -
To match any string that includes one or several values:
admin\.exe,admin\.bat,admin\.sh,cmd\.exe,cmd\.bat,cmd\.sh -
To match any string that includes one or several values:
onmousewith letters in lower and upper case,onloadwith letters in lower and upper case,win\.ini,prompt -
To match any string that starts with
Mozillabut does not contain the string1aa875F49III -
To match any string with one of the values:
python-requests/,PostmanRuntime/,okhttp/3.14.0,node-fetch/1.0
ABSENT¶
The request should not contain the designated point. In this case, the comparison argument is not used.
Rule¶
The added request processing rule is described in the Then section.
The following rules are supported: