Running Docker Envoy‑based Image¶
These instructions describe the steps to run the Wallarm Docker image based on Envoy 1.18.4. The image contains all systems required for correct Wallarm node operation:
-
Envoy proxy services with the embedded Wallarm module
-
Tarantool modules for postanalytics
-
Other services and scripts
The Wallarm module is designed as an Envoy HTTP filter for requests proxying.
Supported configuration parameters
Please note that the most directives for the NGINX‑based filtering node configuration are not supported for the Envoy‑based filtering node configuration. Consequently, rate limiting and credential stuffing detection is not available in this deployment method.
See the list of parameters available for the Envoy‑based filtering node configuration →
Use cases¶
Among all supported Wallarm deployment options, Envoy-based Docker image is recommended for Wallarm deployment in these use cases:
-
If your organization utilizes Docker-based infrastructure, Wallarm Docker image is the ideal choice. It integrates effortlessly into your existing setup, whether you are employing a microservice architecture running on AWS ECS, Alibaba ECS, or other similar services. This solution also applies to those using virtual machines seeking a more streamlined management through Docker containers.
-
If you require fine-grained control over each container, the Docker image excels. It affords a greater level of resource isolation than typically possible with traditional VM-based deployments.
Requirements¶
-
Docker installed on your host system
-
Access to
https://hub.docker.com/r/wallarm/envoyto download the Docker image. Please ensure the access is not blocked by a firewall -
Access to the account with the Administrator role in Wallarm Console in the US Cloud or EU Cloud
-
Access to
https://us1.api.wallarm.comif working with US Wallarm Cloud or tohttps://api.wallarm.comif working with EU Wallarm Cloud. Please ensure the access is not blocked by a firewall -
Access to the IP addresses of Google Cloud Storage listed within the link. When you allowlist, denylist, or graylist entire countries, regions, or data centers instead of individual IP addresses, the Wallarm node retrieves precise IP addresses related to the entries in the IP lists from the aggregated database hosted on Google Storage.
Options for running the container¶
The filtering node configuration parameters can be passed to the docker run command in the following ways:
-
In the environment variables. This option allows for configuration of only basic filtering node parameters, the most parameters cannot be changed through environment variables.
-
In the mounted configuration file. This option allows for configuration of all the filtering node parameters.
Run the container passing the environment variables¶
To run the container:
-
Get Wallarm token of the appropriate type:
-
Run the container with the node:
You can pass the following basic filtering node settings to the container via the option -e:
| Environment variable | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
WALLARM_API_TOKEN | Wallarm node or API token. | Yes |
ENVOY_BACKEND | Domain or IP address of the resource to protect with the Wallarm solution. | Yes |
WALLARM_API_HOST | Wallarm API server:
api.wallarm.com. | No |
WALLARM_MODE | Node mode:
monitoring.Detailed description of filtration modes → | No |
WALLARM_LABELS | Available starting from node 4.6. Works only if
...will place node instance into the | Yes (for API tokens) |
TARANTOOL_MEMORY_GB | Amount of memory allocated to Tarantool. The value can be an integer or a float (a dot . is a decimal separator). By default: 0.2 gygabytes. | No |
The command does the following:
-
Creates the file
envoy.yamlwith minimal Envoy configuration in the/etc/envoycontainer directory. -
Creates files with filtering node credentials to access the Wallarm Cloud in the
/etc/wallarmcontainer directory:node.yamlwith filtering node UUID and secret keyprivate.keywith Wallarm private key
-
Protects the resource
http://ENVOY_BACKEND:80.
Run the container mounting envoy.yaml¶
You can mount the prepared file envoy.yaml to the Docker container via the -v option. The file must contain the following settings:
-
Filtering node settings as described in the instructions
-
Envoy settings as described in the Envoy instructions
To run the container:
-
Get Wallarm token of the appropriate type:
-
Run the container with the node:
- The
-eoption passes the following required environment variables to the container:
Environment variable Description Required WALLARM_API_TOKENWallarm node token. Using one token for several installations
You can use one token in several installations regardless of the selected platform. It allows logical grouping of node instances in the Wallarm Console UI. Example: you deploy several Wallarm nodes to a development environment, each node is on its own machine owned by a certain developer.
Yes WALLARM_API_HOSTWallarm API server: us1.api.wallarm.comfor the US Cloudapi.wallarm.comfor the EU Cloud
api.wallarm.com.No - The
-voption mounts the directory with the configuration fileenvoy.yamlto the/etc/envoycontainer directory.
- The
The command does the following:
-
Mounts the file
envoy.yamlinto the/etc/envoycontainer directory. -
Creates files with filtering node credentials to access the Wallarm Cloud in the
/etc/wallarmcontainer directory:node.yamlwith filtering node UUID and secret keyprivate.keywith Wallarm private key
-
Protects the resource specified in the mounted configuration file.
Configuration of log rotation (optional)¶
The log file rotation is preconfigured and enabled by default. You can adjust the rotation settings if necessary. These settings are located in the /etc/logrotate.d directory of the container.
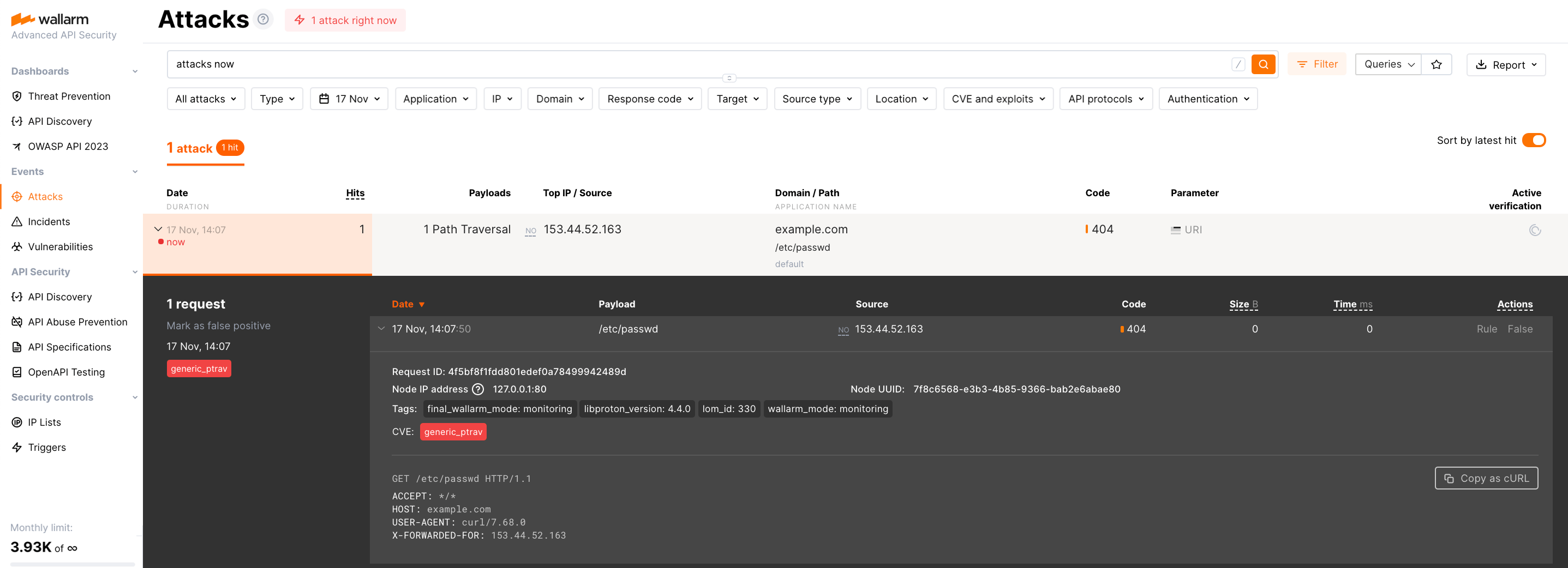
Testing Wallarm node operation¶
-
Send the request with test Path Traversal attack to a protected resource address:
-
Open Wallarm Console → Attacks section in the US Cloud or EU Cloud and make sure the attack is displayed in the list.